Navigating the Complexities of Maritime Sanctions: An Overview from 2020 to 2025
As global sanctions frameworks evolve, maritime stakeholders must adapt to the changing regulatory environment. This update outlines key developments in sanctions from January 2025, providing insights into emerging risks and compliance strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- The US has intensified sanctions against Russia and Cuba, revoking General License 93 and issuing eight new Russia-related General Licenses (GLs), including GL 8L and GL 115A.
- A total of 183 vessels linked to Russian and Iranian oil shipments have been designated, focusing on AIS manipulation and ship-to-ship (STS) transfers.
- Russian maritime insurers Ingosstrakh and Alfastrakhovanie have been sanctioned, along with nearly 80 entities in Russia’s LNG sector and over 30 oilfield service providers.
- The Cuba Restricted List has been reinstated, targeting entities associated with Cuba’s military and intelligence sectors.
- These measures indicate increased scrutiny on maritime compliance, insurance, and shipping practices.
Market Analysis
In January 2025, US sanctions policy underwent a significant shift, impacting maritime operations and global energy markets. The revocation of General License 93, which allowed transactions involving Sovcomflot vessels, highlights a strategic move to limit Russia’s maritime influence. Concurrently, OFAC issued eight new Russia-related General Licenses to adjust compliance pathways.

Source: Kpler
The designation of 183 vessels, primarily oil tankers linked to Russian and Iranian shipments, reflects a regulatory focus on “shadow fleet” operations that circumvent sanctions. The blacklisting of Russian maritime insurers has increased risks for shipping companies dependent on these providers.
Source: Kpler
The US State Department has broadened its sanctions, targeting nearly 80 entities in Russia’s LNG sector and over 30 oilfield service companies, which directly affects crude production and LNG exports. The reinstatement of the Cuba Restricted List complicates maritime logistics for entities involved with Cuba’s military-linked enterprises.
Implications for the Shipping Industry
These sanctions present immediate challenges for maritime stakeholders. The designation of 183 vessels necessitates enhanced due diligence and real-time tracking to avoid inadvertent sanctions breaches. Compliance teams must quickly update screening tools and risk assessments for affected entities.
Shipping companies are under increased scrutiny regarding chartering, insurance, and supply chain operations, especially on routes involving Russia, Iran, and Cuba. The focus on deceptive shipping practices requires investment in advanced monitoring technologies and robust compliance frameworks. Insurers must also reassess coverage policies due to sanctions against key Russian providers, potentially leading to higher premiums and limited options.
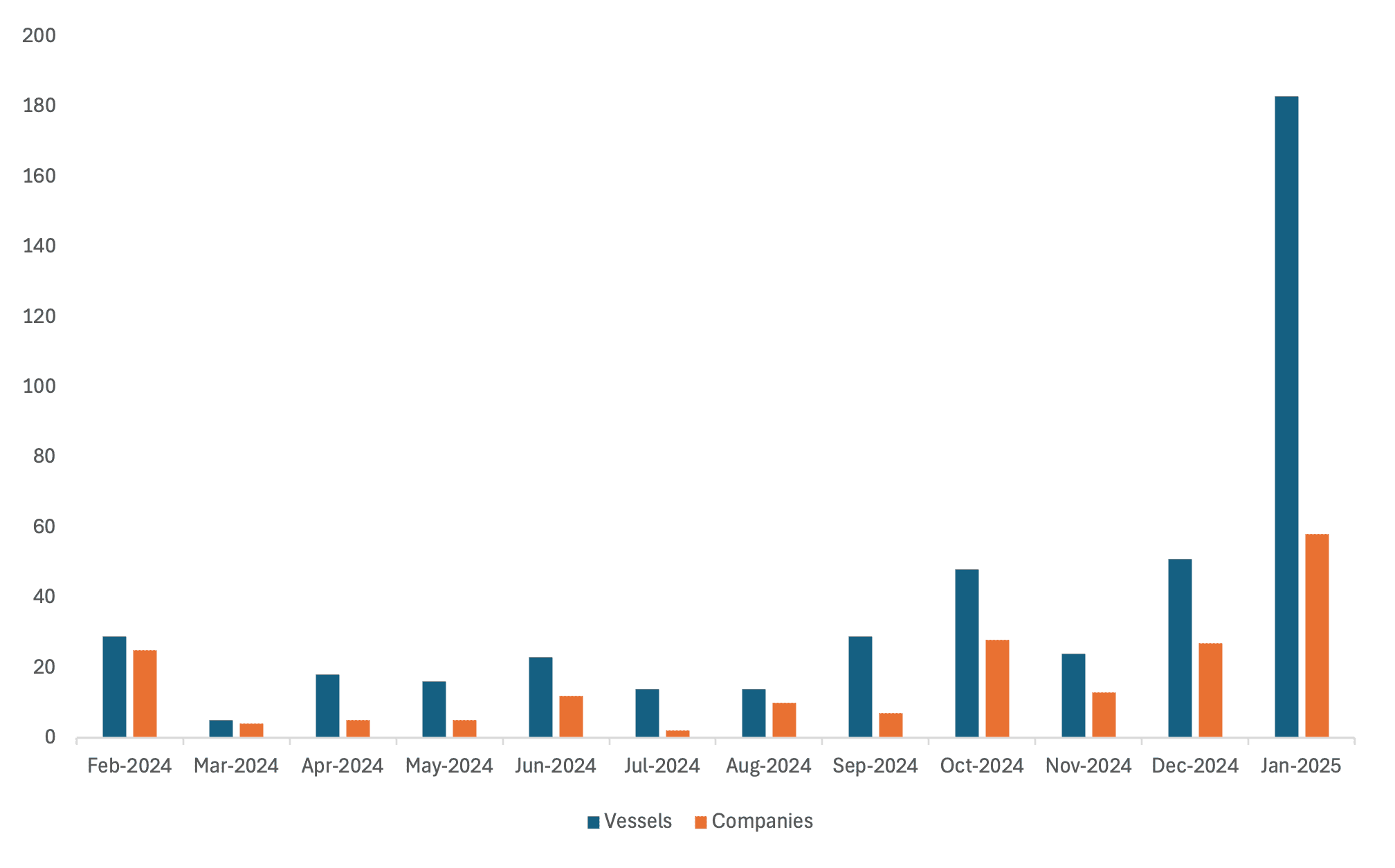
Source: Kpler
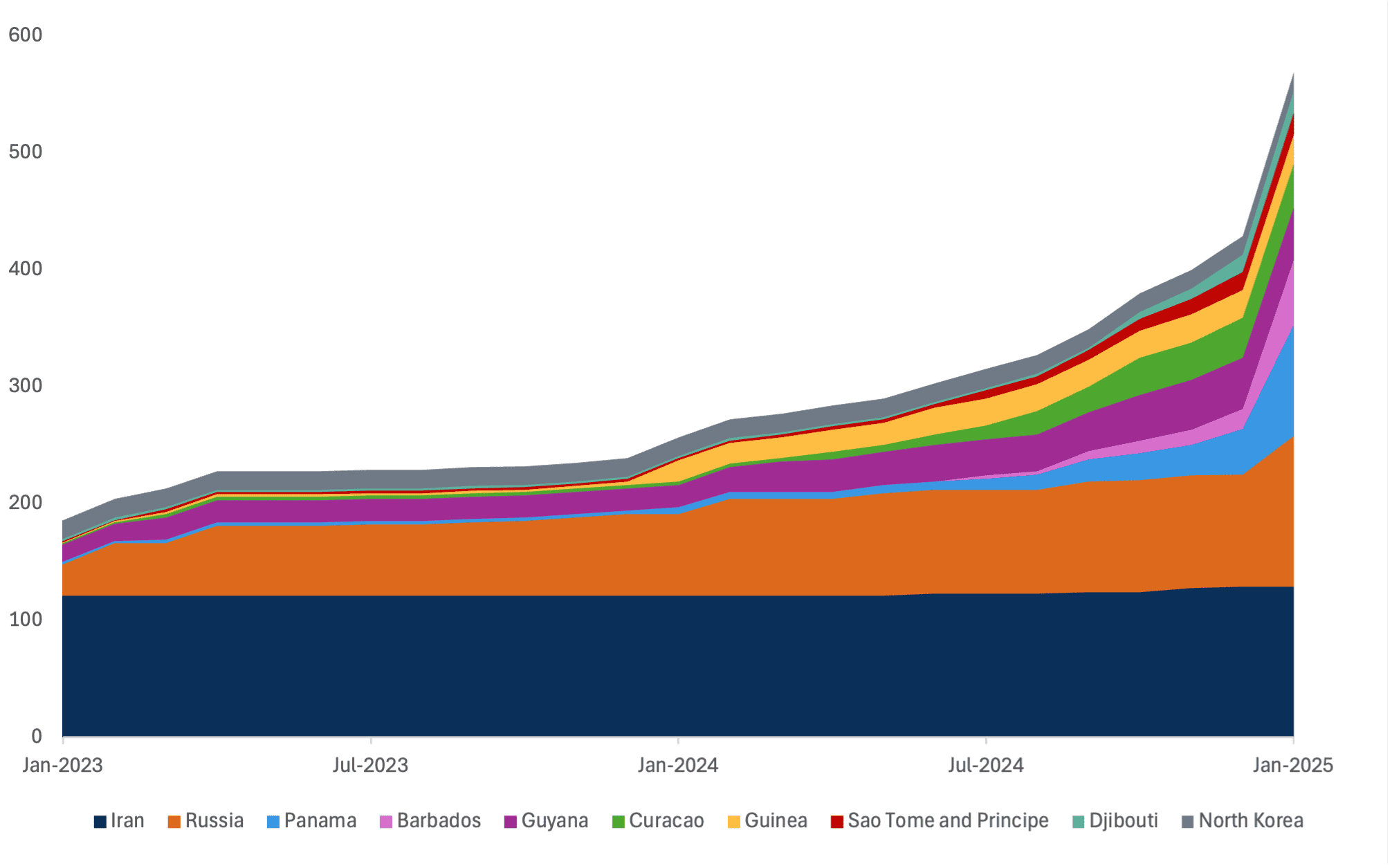
The enforcement of sanctions has intensified, with the number of sanctioned vessels rising from approximately 380 in January 2020 to nearly 1,200 by January 2025, marking a 215 % increase. The number of sanctioned companies has also grown significantly, reflecting the expanding scope of enforcement actions.
Conclusion
Proactive compliance is crucial in navigating the evolving sanctions landscape, characterized by a dramatic increase in enforcement actions. Industry professionals must remain vigilant, continuously monitoring regulatory updates and adapting compliance frameworks to detect emerging risks. In this dynamic environment, informed and agile compliance strategies are essential for safeguarding operations and ensuring business continuity.

