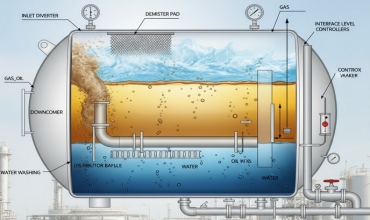
LNG & LPG
LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) are two types of gases which are go through a process of liquefaction for transportation and storage purposes. Although similar in their liquid state, they differ significantly in composition, usage, and production methods.
LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas)
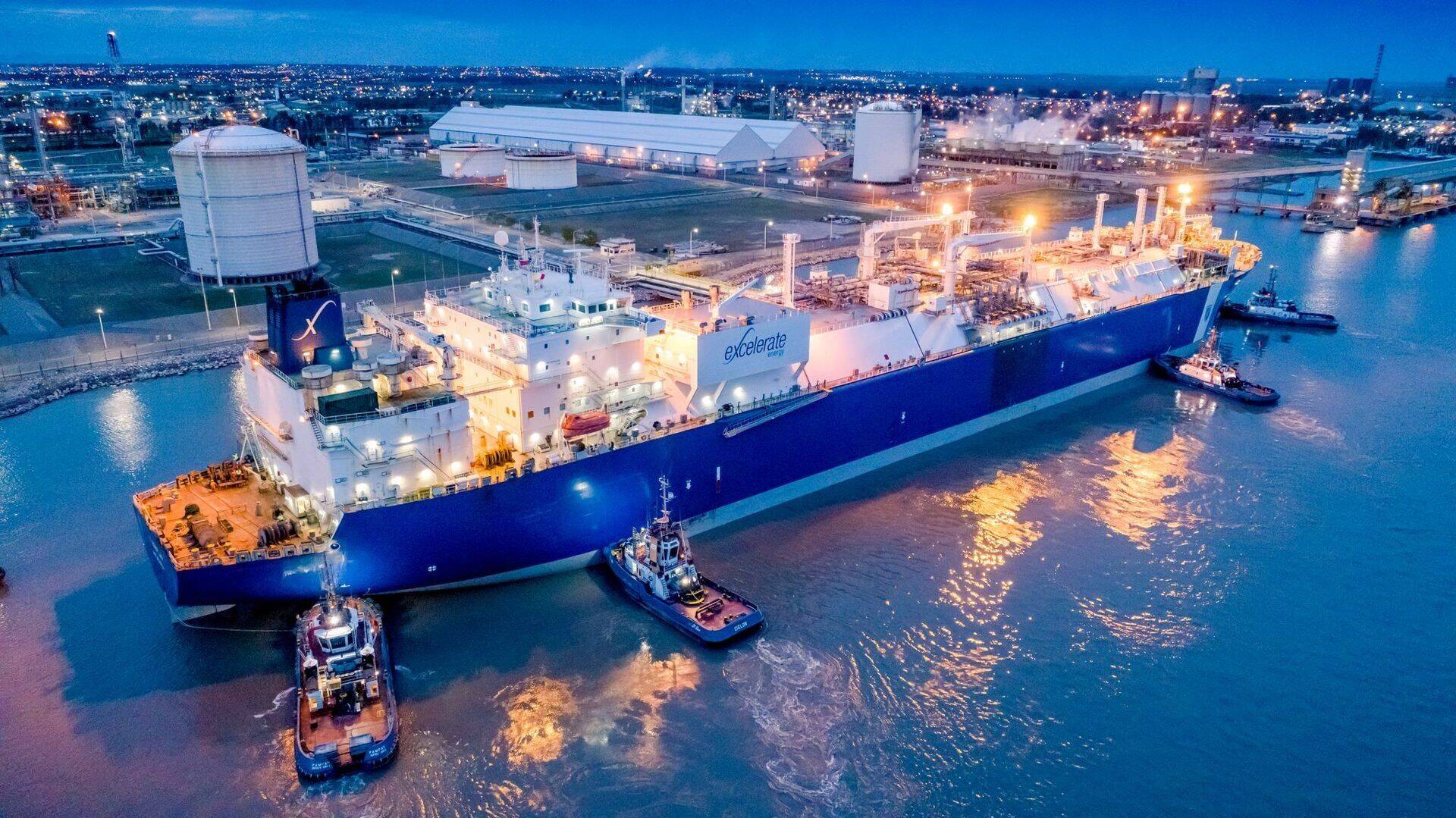
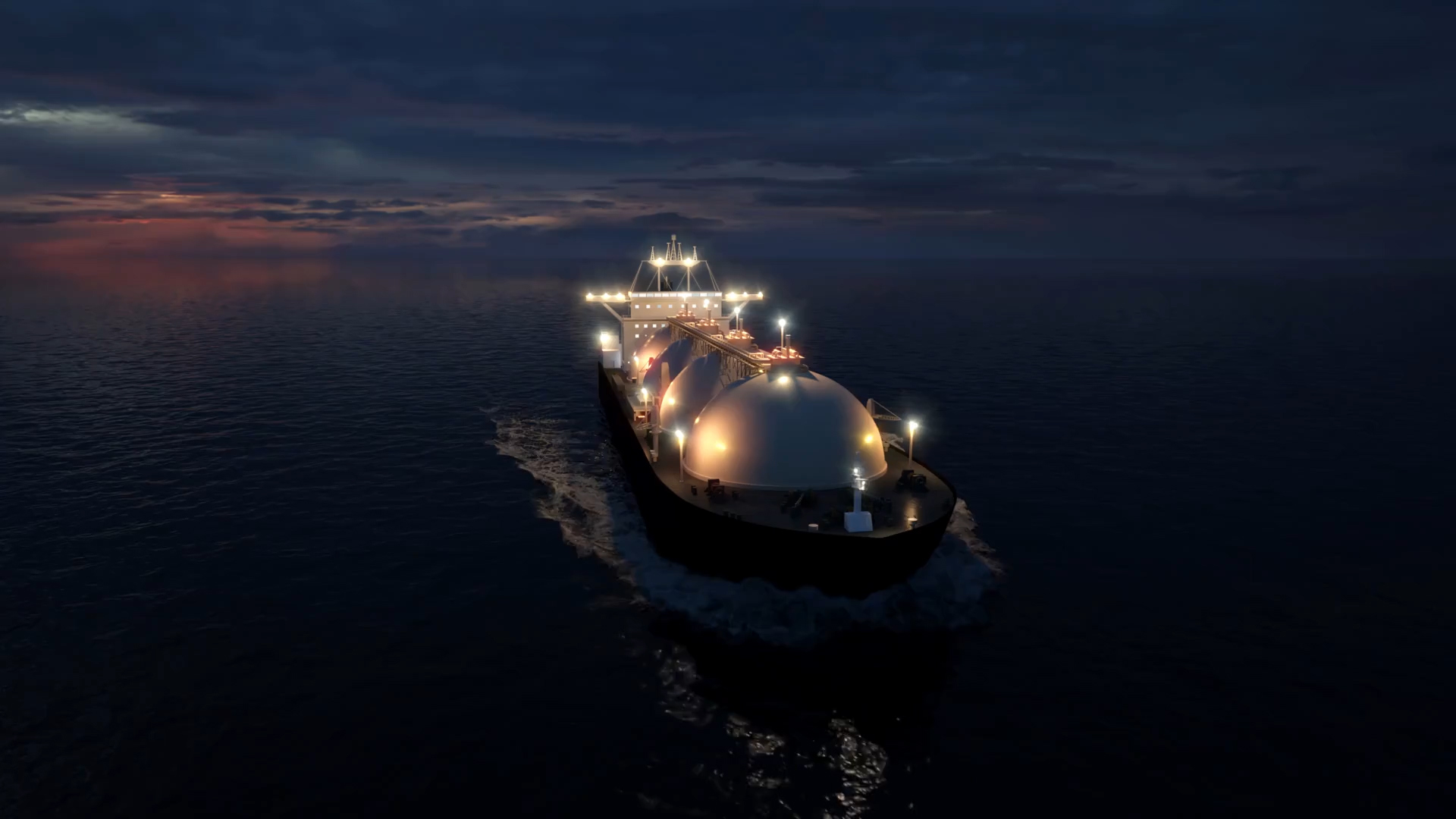
LNG is primarily methane (CH4) gas that has been cooled to a temperature of approximately -162 degrees Celsius (-260 degrees Fahrenheit). At this temperature, methane condenses into a liquid form, which takes up about 1/600 th of the volume it occupies as a gas at standard atmospheric temperature and pressure. This significant reduction in volume makes LNG economical to transport over long distances where pipelines are not feasible, such as across oceans. LNG is used mainly for heating and as a fuel for electricity generation and is increasingly used in the transportation sector, especially for ships and heavy-duty vehicles.
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
LPG is a mixture of propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10), gases that are found naturally in crude oil and natural gas. LPG is produced during natural gas processing and oil refining. It is stored and transported in liquid form under moderate pressure, which makes it easier to store and handle compared to LNG. LPG is widely used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and in vehicles. It is also used in industrial applications and is a popular choice for portable cooking and heating equipment in areas not connected to a natural gas network.
Both LNG and LPG play crucial roles in the global energy supply, offering cleaner alternatives to traditional fossil fuels like coal and oil. They contribute significantly to reducing emissions and air pollution in various applications.