GMDSS: Ensuring the Safety of the Vessel and Effective Emergency Response
The Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is a comprehensive international framework designed to enhance security and crisis response capabilities in the marine industry. It is a set of protocols, resources and connection methods that assure rapid and efficient contact between boats, shore-based facilities and deliver coordination centers. The Global Marine Distress and Safety System plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk of accidents, saving lives and protecting property at sea.
Components and Functionality of GMDSS
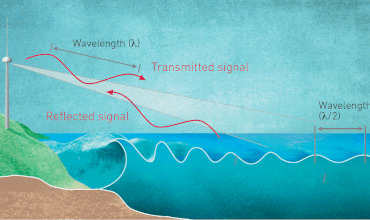
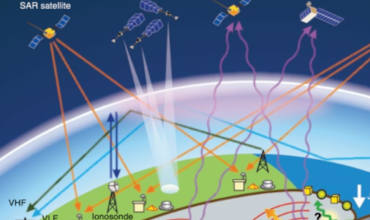
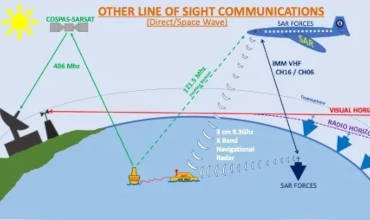
The Global Maritime Distress and Safety System consists of various components, including satellite and terrestrial connection processes, affliction worrying devices and search and safeguard supplies. These elements work together to provide a reliable and automated means of transmitting and receiving concern alarms, security information and seafaring protection broadcasts. The structure also enables the coordination of search and reclaim operations, allowing to a swift and effective response to difficulties at sea.
Importance of GMDSS for Deck Officers
Mates play a vital role in ensuring the proper functioning and utilization of the GMDSS on board ships. They are responsible for maintaining and testing the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System equipment, as well as being proficient in its operation. In the event of an emergency, assistants to the master must be able to quickly and accurately transmit care alarms and communicate with relevant authorities to coordinate rescue efforts. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the GMDSS and its procedures is essential to naval officers to fulfill their duties and contribute to the overall protection of the craft and its crew.