Free Mintra tests for marine specialists
Questions and answers to Mintra tests online for preparing sailors for exams and certification.
Mintra Tests
On our website, you can prepare online for Mintra exams. We offer tests and answers to facilitate effective learning, ensuring you have what it takes to succeed in your tests. Our curated materials and practical assessments will help you confidently approach the evaluation of your skills and knowledge.
To ensure efficient and consistent assessment of individuals prior to crewing decisions, operators rely on Mintra’s Crew Evaluation Test (CET). With a global seafarer workforce exceeding 1.6 million, this tool is specifically crafted to aid organizations in the training, recruitment, and promotion of maritime personnel.
The online assessment tool assesses individual skillsets and identifies additional training needs based on the Standards of Training, Certification, and Watchkeeping (STCW). This enables organizations to enhance overall performance and competence.If you find any mistake in tests – please let us know posting it in comments section.

Introduction to Abrasive Wheels

Accident and Incident Investigation

Accommodation Safety

Behaviour Based Safety

Chemical Tankers – Basic

Cultural Awareness

Dangerous Edges

Diesel Engine Analysis

Electrical Safety Rules

Enclosed Space Entry

Engine Room Safety

Engine Room Watchkeeping

Examining Lifting Appliances and Loose Gear

Fatigue Management

Fluid Hammer Effect

Garbage Record Book

Good Business Writer

Hand-Arm Vibration Safety

Handling and Storage of Hazardous Substances

Harassment and Bullying

Hazard Identification

Helicopter Operations at Sea

Hydrogen Sulphide Awareness

Personal Hygiene

Interventions

Introduction to Inert Gas Systems

Introduction to Oily Water Separators

Introduction to ISO 14001 and Environmental Management

ISO 45001 Occupational Health and Safety

Ladder Safety

Liquefied Gas Fire Hazard Management

Lubrication Systems

Marine Fuel Management and Switching Operations

Maritime Health and Lifestyle

Maritime Leadership

Mental Health

Oil Record Book

On-board Assessor

Personal Protective Equipment

Prevention of Marine Spills (SOPEP)

Prevention of Vessel Air Pollution

Risk Assessment

Safe Cargo Handling

Safe Use of Rigging Equipment

Safe Welding Operations

Safety Officer

Sewage and Wastewater Treatment

Slips, Trips and Falls

Tank Cleaning and Wall Wash

Tanker Operations – Bunkering

Tanker Operations – Ship to Ship (STS)

Use and Storage of Pressurised Cylinders

Vapour Emission Control

Working at Height

Working with High Voltage

Cyber Security

COLREGS General

Piracy and Armed Robbery
Drug and Alcohol Awareness and Policy

Safe use of Maritime Cranes Training

Life Rafts

Respiratory Protection

Rescue and Fast Rescue Boat – Launch and Operations

CO2 Firefighting Systems

Anchoring – Operational Safety

Best Navigational Practices

Command and Control of an Incident

ECDIS – Practises and Port State Control Inspections

Energy Efficiency

Managing a Safety Committee
Medicals and Medication

Launches and Personnel Transfers

Mooring System Maintenance

Pilot Transfer Arrangements

Port State Control

Recovery Person From the Water

Resource Management

Ship Safety Officer

Enclosed Places Are Dangerous Places

SIRE 2.0 What to Expect

SOLAS Safety Radio

Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) as Fuel Bunkering Operations

Social Media Awareness (Maritime) MGM-061

Introduction to Safe Cargo Operations MGM-113

International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargo (IMSBC) Code (Maritime) MGM-084
Mentoring

Waste Management

Mooring Deck Safety (DNV Sertified)
1/ Help
:
* Some questions may have more than 1 correct answer.

“Mintra test” finished! Your result:
Correct answers:
Introduction to Abrasive Wheels
There are several steps that must be undertaken before beginning grinding operations:
Step 1: “Sound” the wheel (if appropriate); Step 2: Ensure the wheel is properly clamped to the machine; Step 3: “Dress” and “True” the wheel.
Step 1: “Dress” and “True” the wheel; Step 2: Ensure the wheel is properly clamped to the machine; Step 3: “Sound” the wheel (if appropriate).
Step 1: Ensure the wheel is properly clamped to the machine; Step 2: “Dress” and “True” the wheel; Step 3: “Sound” the wheel (if appropriate).
Which of the following are precautions that must be taken when using portable grinding equipment?
Wheel Flaking.
Slow Grinding Speed.
Fast Grinding Speed.
Wheel “Perspiring”.
Excessive Run-out or “Wobble”.
Rapid Disc Wear/Short Blade Life.
Which of the following are precautions that must be taken when using portable grinding equipment?
Always ensure that an appropriate guard is in place before you start your work.
Always consider the electrical dangers that may be presented from equipment cables or plugs.
Always carry out a visual check of the equipment to look for signs of damage.
Always ensure there are two points of exit from the grinding location in case of emergency.
Always wear breathing apparatus.
Select the statements which identify safe working practices for the use of abrasive wheels.
To minimise the risk of bursting, abrasive wheels should always be run within the specified maximum rotation speed.
If a wheel is large enough the maximum rotation speed will be marked on the wheel.
Guards must be provided (on all types of wheel) to contain fragments that may fly off if the wheel bursts.
Relevant information and training should be provided to all personnel involved in the use of grinding operations.
For smaller wheels there should be a notice highlighting the maximum speed for each size of wheel.
Guards must be provided (on pedestal grinders only) to contain fragments that may fly off if the wheel burst.
Wheel rotation speeds (for all size of wheel) must be displayed on a notice.
Select the statements which identify safe working practices for the use of abrasive wheels.
To minimise the risk of bursting, abrasive wheels should always be run within the specified maximum rotation speed.
What are the main hazards associated with grinding operations?
Loss of eyesight from flying shards.
Trapped or crushed fingers.
Serious friction burns from coming into contact with the wheel.
Repetitive Strain Injury.
Chemical burns.
Which of the following types of abrasive wheel has a long, wide surface with no centre mounting support or hollow?
Cylinder wheel.
Tapered wheel.
Saucer wheel.
Straight wheel.
Carrying out grinding operations: “Guarding”:
The wheel should be guarded so that only the area of the wheel needed for the work is exposed.
There should be no guarding; the whole wheel should be exposed.
Only the area of the wheel needed for the work should be guarded; the non-work area of the wheel should be exposed.
Abrasive wheels are bonded together using ____ or inorganic substances, such as ____ to form a solid circular shape. However, unlike a saw, which has teeth only on its edge, the grinding wheel has abrasive grains distributed ____ the wheel. Thousands of these hard, tough ____ move against the work-piece to cut away tiny chips of material.
… organic … resin … saw … throughout … grains.
… inorganic … oil … saw … grains … throughout.
A grinding machine guard has two main functions: the first is to ____ the wheel parts if the wheel ____ and the second is to prevent anyone from coming into ____ with the wheel. Guards must be securely anchored to the machine frame or, if using a portable grinder, an ____ face guard must be worn.
… contain … breaks … contact … adjustable.
… breaks … contain … contact … adjustable.
… contact … breaks … contain … adjustable.
Select the relevant pieces of PPE to identify the minimum PPE required for grinding operations.
Earmuffs.
Goggles.
Dust mask.
Face shield.
Select if the following is true:
Wheel Storage – store wheels in a cool, dry area where there is no risk of them rolling or falling over.
Wheel Operation – only one person should use a wheel at any one time and it should always be switched off after use.
Wheel Selection – the wheel selected must be suitable for its purpose.
Wheel Mounting – wheels should only be mounted on a machine that they are designed for and by someone trained and competent to do so.
Wheel Inspection – inspect the wheel for damage before each use (and ensure a “sounding” test has been carried out on pedestal grinders).
Wheel Guarding – the wheel should be guarded so that only the area of the wheel needed for the work is exposed.
Grinding Machines – all machines must be stable. Machines on benches should be bolted to the bench or securely fastened in some other way.
Accident and Incident Investigation
What is the correct order to prioritise control measures?
1. Eliminate risk; 2. Combat risk at source; 3. Minimise reliance on human behaviour.
1. Combat risk at source; 2. Eliminate risk; 3. Minimise reliance on human behaviour.
1. Minimise reliance on human behaviour; 2. Eliminate risk; 3. Combat risk at source.
What is the key question to ask when performing a root cause analysis (RCA)?
Why?
Who?
How?
What is the objective of an accident and incident investigation?
To establish the root cause.
To establish the worst possible outcome.
To establish who is to blame.
Why should an investigation team include personnel from various levels of an organisation?
To ensure a necessary range of practical knowledge and experience in the team.
To ensure that management don’t try to hide problems in the organisation.
This is a requirement in OMI legislation.
Ship owners and operators are not obligated to keep records of accidents or incidents.
False.
True.
A benefit of performing an investigation following an accident or incident is that you get an understanding of the ways people can be exposed to conditions or circumstances that may affect their health.
True.
False.
The severity of an accident or incident determines what level of investigation is required.
True.
False.
What do you determine by using a risk matrix in an accident and incident investigation?
The severity of an accident or incident.
The urgency of which preventive measures must be put in place.
The severity of the injuries resulting from an accident.
What is the purpose of an action plan?
To establish what needs to be done, when and by whom.
To establish who was responsible for the accident or incident.
To establish if current operations must be suspended or not.
An essential part of an investigation report is the basics of where and when the event occurred, who was involved and how it happened.
True.
False.
There are three types of human factors that can lead to accidents and incidents: skill-based errors, mistakes and violations.
True.
False.
What are the correct main steps in an accident and incident investigation?
1. Gather information; 2. Analyse information; 3. Identify control measurers; 4. Create and implement action plan.
1. Gather information; 2. Assess severity; 3. Implement control measures; 4. Assess control measures.
1. Question involved personnel; 2. Implement control measures; 3. Assess control measures; 4. Distribute penalties.
Each immediate cause identified can be resolved directly, as there rarely are underlying or root causes.
False.
True.
Who is responsible for reporting accidents and incidents?
Everyone.
Health and safety officers.
Vessel officers.
An accident is an event that results in injury or ill health.
True.
False.
Accommodation Safety
Every crew member is responsible for ensuring that the accommodation area is kept clean, tidy and safe and provides a pleasant living environment for everyone onboard.
True.
False.
Which of the following steps can be taken to prevent and reduce the risk of fires occurring?
Report flickering lights.
Unplug all chargers and other electrical items when not in use.
Avoid using extension cables where possible.
Only smoke in designated areas and ensure all cigarettes are extinguished before disposing of them.
Cover electrical items in your cabin.
Ignore faulty or dangerous equipment.
Which of the following precautions can be taken to reduce the risk of slips, trips and falls?
Using handrails whenever possible.
Wearing the correct footwear for the location you are in.
Never running or rushing around the vessel.
Leaving hatches and covers open and unattended.
Which of the following emergency equipment must be provided in your cabin?
Life jacket.
Immersion suit.
Personal escape breathing apparatus.
Life raft.
Inertia reel.
Which of the following can help to reduce the spread of diseases?
Regularly washing your hands with soap and water.
Always holding on to the handrail when using stairs.
Segregating waste and placing it in the correct receptacles.
Behaviour Based Safety
Crew members should comply with the incident reporting requirements in place onboard their vessel.
True.
False.
When implementing a BBS program, which of the following people should be included in the BBS design team?
Both management and front-line employees.
The board of the company.
Front-line employees only.
Only management.
What does the ABC model stand for?
Antecedent, Behaviour, Consequence.
Action, Behaviour, Consequence.
Antecedent, Behaviour, Creativity.
What is the main goal of a behaviour based safety approach?
The goal is to ensure that unsafe behaviours are corrected, not punished.
The goal is to find culprits and learn from their mistakes.
The goal is to punish unwanted behaviour.
A person with a strong sense of personal responsibility should have which of the following qualities?
Strong communication skills.
Organisation.
Courage.
Persistence.
Persuasion skills.
Level of attractiveness.
Why is feedback given in a BBS program?
To encourage a change of behaviour.
To be in compliance with RIDDOR.
To document routines in case of an audit.
To check whether or not the person receiving the feedback has understood what to do.
Incident reports overall show that as many as 80-90 % of serious injuries and accidents have been attributed to human errors.
True.
False.
Research suggests that the more experienced you are in doing your job, the more likely you are prone to accidents.
True.
False.
What is the Bradley DuPont Curve?
A graphical representation of how we can transition from an unsafe, to a safe organisation.
A graphical representation of the number of unsafe behaviours that are recorded within one organisation.
A graphical representation of the inherent risks in the organisation.
A graphical representation of how safe your organisation is to work in.
In the academic field of applied behavioural analysis, behaviour is understood as the result of:
A stimulus – response mechanism.
Subconscious urges.
Genetic predispositions.
Rational and logical thinking.
Chemical Tankers – Basic
Which type of cargo can be heated using high-pressure saturated steam?
Cargoes that react violently with water.
Molasses.
Coal Tar.
Edible oils.
Where possible, interconnecting pipelines should have pipe spool pieces removed and blind flanges fitted.
True.
False.
Thermal oil heating systems are suitable for which type of cargo?
Cargoes that react violently with water.
Food grade cargoes.
High temperature cargoes.
Main deck ____ can be achieved by using redundant fire hoses that have multiple holes made along their length. These are then spread on the main deck and connected to the fire main. This method has proved to ____ the main deck heat and the vapour space temperature by ____ or more.
… cooling … reduce … 15 °C.
… heating … reduce … 10 °C.
… cooling … increase … 15 °C.
If the cargo is supplied using a trade name, how can the correct shipping name be found?
In chapter 19 of the IBC Code.
By using one of the software packages.
Asking the operator or charterer.
Checking with the haulage company.
This is not required, it can be shipped under the trade name.
What temperature should molasses be discharged at?
21 °C.
41 °C.
100 °C.
Why should incompatible chemicals be stored apart?
Because this will slow down the discharge rate.
Because the load may be rejected by the buyer.
Because some chemicals will react if they come into contact with each other.
If a chemical is not listed in the IBC Code’s index of chemicals, then the transport of that chemical is not allowed without permission from the vessel’s Flag State.
True.
False.
What can affect the vessel radar ullaging system when loading molasses?
Foaming caused by the molasses.
Hot molasses sticking to the radar system.
The viscosity of the molasses.
Which of the following are involved in the Tripartite Agreement?
The producing state.
The International Maritime Organization.
The user state.
The transport provider state.
The Occupational Health and Safety Authority.
Cultural Awareness
To become more self-aware you should practise which of the following?
Research your background and culture.
Allow capacity for self-reflection and intervention.
Recognise your personal biases, cultural incompetence or exclusive behaviour.
Research other cultures.
People of the same ethnicity might share which of the following?
Language or dialect.
Environmental characteristics.
Physical characteristics.
Religion or customs.
Profession.
Skills.
What is the international language of the sea?
English.
Spanish.
Hindi.
Chinese.
Which of the following are Cultural Universals?
Language.
Geography.
Beliefs, Values and Rituals.
Skin colour.
Every one of us has our own cultural identity and racial heritage no matter where we are from in the world.
True.
False.
Dangerous Edges
When planning any work task, crew members should consider which of the following?
Any improvements that can be made to shipboard procedures to reduce the likelihood of accidents occurring in the future.
The safety measures that can be put in place to prevent accidents from occurring.
Areas on board where crew members are more likely to be exposed to dangerous edges or unguarded openings.
If any processes can be bypassed to complete the job faster.
When working aloft, outboard or in any location where there is a risk of falling, which of the following additional items of PPE will be required?
A safety harness or a safety belt with shock absorber.
A safety helmet and appropriate gloves.
A welding mask or apron.
Which of the following should be encouraged to help create a strong safety culture on board?
Participating fully during toolbox talks and safety briefings.
Contributing ideas for improvements.
Not reporting near misses.
Any opening, hatch or edge from where a crew member could fall (apart from a permanent access way) should be fitted with a secure guard, barrier or fencing.
True.
False.
Which of the following can help crew stay safe while working closely to unguarded openings and dangerous edges?
Carrying out a thorough risk assessment.
Maintaining good situational awareness.
Wearing the correct PPE.
Complying with relevant regulations.
Removing safety measures.
Ignoring procedures.
Diesel Engine Analysis
Why are dual pickups used on slow speed engines?
To reduce the effects of speed variations and increase the accuracy of the power figures.
Slower engines are usually larger in size.
To reduce the risk of one pickup failing during a reading.
Most ____ indicator devices can be used to produce both power and ____ cards and will have a small ____ which shows the data being ____.
… electronic … draw … display screen … captured.
… display screen … draw … electronic … captured.
… mechanical … crankshaft … display screen … draw.
The ____ of working with ____ need to be considered in a structured manner by ____ personnel. In every case the aim of a ____ is to reduce the risks to ____ as Is Reasonably Practicable (ALARP).
… risks … electricity … competent … risk assessment … As Low.
… hazards … electricity … not competent … captured.
Which of the following are the most commonly used types of indicator cards?
Power cards.
Draw cards.
Light spring cards.
Fuel cards.
The mean effective pressure is the average net pressure that acts on the piston area during one full power stroke.
True.
False.
Which of the following is required before manual switching operations can be carried out?
A risk assessment must be carried out.
The personnel carrying out the manual switching operation must be wearing the correct specialist PPE.
There must be an announcement made over the PA system.
All systems must be “live”.
Why is it important to regularly monitor the engine’s performance?
To ensure that the engine is operating at optimal condition.
To diagnose any potential faults as early as possible.
To ensure the structural stability of the hull.
To identify any contamination in the potable water supply.
Electrical Safety Rules
Which of the following statements apply to working on extra low voltage equipment?
Extra low voltage equipment must always be proved dead before work can commence.
Personal isolations are never allowed on extra low voltage equipment.
A risk assessment must always be carried out when working on live control and telecommunications plant and equipment.
In electrical terminology, what is the correct definition of extra low voltage?
A voltage which does not exceed 150 Volts AC between conductors or between any conductor and earth.
A voltage which does not exceed 50 Volts AC between conductors or between any conductor and earth.
The disconnection and separation of electrical equipment from every source of electrical energy.
A voltage that is not greater than 1 000 Volts.
The Electrical Safety Rules are designed to work in conjunction with a ship’s Risk Assessment Process and Permit to Work System.
True.
False.
Which of the following is the correct definition of a Hazardous Area?
An area in which explosive gas or air mixture are not present.
An area where all stored electrical energy has been discharged.
An area where all pieces of electrical equipment has been disconnected and separated from all sources of electrical energy.
An area in which explosive gas or air mixtures are present or may be expected to be present in quantities which require special precautions for the construction and use of electrical apparatus.
Which of the following statements are true in relation to the safe use of electrical equipment?
All equipment should be suitable for purpose.
All equipment should be properly maintained.
All equipment should be extra low voltage.
All equipment should have a permit attached to it.
All equipment should be used in line with the manufacturer’s guidelines.
All equipment should only be used by the Master.
Which of the following is used as guidance for electrical safety onboard seagoing vessels?
SOLAS Chapter II-1 Construction – Structure, subdivision and stability, machinery and electrical installations, Part D Electrical Installations.
SOLAS Chapter II-2 Construction – Fire protection, fire detection and fire extinction, Part A General.
SOLAS Chapter II-3 Life Saving Appliances and Arrangements, Part C General Alternative Arrangements.
The Master is responsible for ensuring the seaworthiness, navigation, cargo and maintenance of their vessel, in accordance with all mandatory regulations.
True.
False.
Which of the following members of personnel is responsible for the safe and efficient operation and maintenance all electrical plant and equipment onboard?
Master.
Captain.
Electro-Technical Officer.
Chief Engineer.
Which of the following are typical duties of the Electro-Technical Officer?
Overseeing all electrical work planning.
Compiling the Electrical Safety Rules for an organisation.
Ensuring that all records, manuals and technical drawings are updated and maintained in a correct and useable form.
Carrying out regular inspections of all electrical power management systems to ensure that they conform with standards of operation and maintenance.
Which of the following are the main roles that are directly involved in Electrical Safety?
Electro-Technical Officer.
Maintenance Technician.
Chief Engineer.
Master.
Staff Technician.
Which of the following statements concerning the Chief Engineer are true?
The Chief Engineer reports to the Master.
The Chief Engineer is responsible for the technical management of the vessel.
Any person onboard can be classed as the Chief Engineer.
Which of the following are specialised items of electrical safety equipment?
BA sets.
Insulated mats.
Double lanyards.
Insulated shepherd’s crooks.
It is extremely important for all personnel to wear the correct Personal Protective Equipment as it could provide protection from serious injury.
False.
True.
Which of the following statements are true in relation to the safe use of electrical equipment?
Electrical personnel must work within the Permit to Work System.
The requirements for PPE and adherence to the risk assessment process and Permit to Work System and ONLY to personnel working with electricity.
Electrical personnel must wear appropriate PPE.
There are specific precautions that must be taken for electrical work.
Which of the following is required before testing can be completed on high voltage electrical equipment?
Authorisation by a Technical Authority.
A Sanction for Test document.
Plant shutdown.
Which of the following precautions must be taken when working on low voltage systems?
All equipment must be proved dead by testing.
Barriers must be erected to stop unauthorised persons entering the area.
A face mask should be worn.
Danger notices must be attached to equipment or systems.
All equipment must be switched on.
Which of the following statements apply to electrical isolation?
All electrical equipment must be regarded as live until proven dead.
An electrical isolation must be secured with a suitable locking device.
Electrical testing and proving dead can be carried out by one person.
Gas tests are never required when proving dead electrical equipment.
What is the purpose of a lock out system?
To ensure that personnel cannot enter a switch room.
To ensure that it is not possible to de-isolate electrical equipment or systems with the proper authority and the correct procedure being followed.
To ensure that no unauthorised personnel can pass through an area where electrical work is taking place.
How is low voltage electrical equipment earthed?
By applying portable earthing leads.
By circuit testing.
By isolation.
The term “high voltage” equates to which of the following?
A voltage greater than 1 000 Volts AC or 1 500 Volts DC between conductors.
A voltage not exceeding 1 000 Volts.
A voltage greater than 600 Volts AC or 900 Volts DC between conductors and earth.
A voltage between 400 and 500 Volts AC.
What is the meant by Electrical Isolation?
Ensuring that personnel wear insulated PPE in order to mitigate the consequences of coming into contact with live electricity.
Maintaining a system of locking and tagging of electrical sources.
Ensuring a piece of electrical equipment is certified as dead.
The disconnection and separation of electrical equipment from every source of electrical energy in such a way that this disconnection and separation is secure.
All electrical equipment should undergo regular inspection and maintenance, and gas testing must always be carried out before and during any electrical work taking place in a hazardous area.
True.
False.
Which of the following hazards are related to battery bank systems?
Vibration.
Production of explosive gases during changing.
Corrosive materials.
High noise.
Static electricity is a particular hazard with which of the following types of equipment?
Telecommunications equipment.
Grit blasting equipment.
Rotating equipment.
Lighting.
What is PAT testing?
Testing high voltage equipment.
Testing portable equipment.
Testing to ensure that portable equipment is dead before work on it can commence.
Which are the most common hazards associated with electrical work?
Electrical fires.
Suspension trauma.
Electrocution.
Shock.
Asphyxiation.
Risk of fire or explosion from ignition of flammable gas, liquid or vapour.
Hydrogen sulphide.
Which of the following precautions must be taken when working on telecommunications equipment?
Magnetic tools should always be used when testing or fault finding in the proximity of high magnetic fields.
Non-magnetic tools should always be used when testing or fault finding in the proximity of high magnetic tools.
Any work carried out on antenna or aerial tuning units should be isolated to the same standard as electrical equipment so that they cannot be energised.
Any work carried out on antenna or aerial tuning units should be de-isolated to the same standard as electrical equipment so that they can be energised.
Enclosed Space Entry
Which of the following elements are essential when working in an enclosed space?
A non-IS torch.
Safety Data Sheet.
Isolation.
Competent and trained personnel.
Which of the following hazards is associated with working in enclosed spaces?
Suspension trauma.
Sim-ops.
Dropped objects.
Lack of oxygen.
Personnel that are entering an enclosed space must be made aware of which of the following?
The precautions to be taken prior to, and during, the enclosed space work.
Emergency procedures and the rescue plan.
Safety Data Sheets.
In an emergency situation, what should the Standby Person do?
Carry out atmospheric testing.
Contact the Bridge.
Instruct all personnel within the enclosed space to evacuate immediately.
Enter the enclosed space.
Which of the following are responsibilities of the Standby Person?
Ensuring that communication is maintained with the personnel within the enclosed space at all times.
Ensuring that atmospheric testing is carried out.
Ensuring that all personnel are fully trained and competent.
Establishing the location of the nearest telephone and manual alarm call point, in the event of an alarm or emergency.
Enclosed Space Entry can be defined as: “Any entry (including a ‘head and shoulders’ entry) by any person into any space that may contain toxic or asphyxiant gases or abnormal concentrations of oxygen in air”.
True.
False.
A space that has less than 20,0 % oxygen by volume is usually considered “oxygen enriched” and a space that has more than 22,0 % oxygen by volume is usually considered “oxygen deficient”.
False.
True.
Which of the following are relevant to working in enclosed spaces?
STCW.
SOLAS.
LOLER.
If it is necessary for the Authorised Gas Tester to enter an enclosed space to carry out a test, which of the following pieces of equipment should be worn?
Rope access system.
Safety harness.
Lifeline.
Work positioning system.
Approved breathing apparatus.
Which of the following pieces of safety equipment should always be available for enclosed space entry work?
Radio communication.
Breathing apparatus.
Rubber boots.
Rescue harness and safety line.
Chemical suit.
Engine Room Safety
Which of the following precautions can be taken to reduce the risk of slips, trips and falls?
Segregating waste materials and disposing of them in the correct waste streams.
Replacing all covers, floor plates and lids when work is complete.
Erecting barriers around any open spaces to prevent falls.
Permitting cables and wires to trail across the floor.
Leaving spills for others to clean up.
Which of the following surfaces will be hot to touch?
The turbo housing.
Exhausts.
Lagged pipes.
Fixed ladders.
Emergency exits.
Which of the following items of PPE are typically required when working in the engine room?
Safety gloves.
Safety glasses or goggles.
Hard hat.
Coveralls.
Ear defenders.
Immersion suit.
Life jacket.
When working in the engine room, crew should ensure they are familiar with the emergency escape routes and take care to keep them clear.
True.
False.
Which of the following will help to reduce the risk of fires?
Cleaning up spills immediately.
Keeping the bilges free of oil and water (so far as is reasonably practical).
Never leaving combustible materials near to a source of ignition.
Ignoring warning signs and barriers.
Storing oily rags on hot surfaces.
Engine Room Watchkeeping
Which of the following statements are correct?
If there is maintenance work being carried out in the engine room by another engineer the location of the maintenance work should be passed on to the relieving officer.
If it seems like the relieving officer is not in a condition to carry out the watch duties efficiency, do not hand over the watch and inform the Chief Engineer.
There is no need to use a checklist as a part of the vessel safety management system.
Where will be the alarm sound if the UMS is in control but there is an issue with engine room machinery?
The duty engineer’s cabin.
The duty officer’s cabin.
The captain’s cabin.
Engine room watchkeeping is integral to the marine engineer’s duties on board a ship. It should be carried out efficiently to ensure the safety of the crew and the vessel.
True.
False.
The number of engineers appointed to a ship will depend on which of the following factors?
The type of ship.
The area of operation.
The Safe Manning Certificate issued by the Flag State.
The length of the voyage.
Which of the following pieces of information should be passed on to the relieving officer when handling over the watch?
The levels of important tanks, such as ballast, bilges, sewage, reserve, slop, fuel or any tank, that may require attention.
Any special orders related to the operation of the ship, the control system or maintenance work.
All checks that have been made when entering or leaving a port.
Standing orders from the Chief Engineer or the company.
Which machinery checks can be skipped to save time.
There may be more than one engine room on some ships, for example, at the forward and the aft, or only one, at the port or starboard side.
True.
False.
All members of the engine room watch should have knowledge of which of the following?
The survival procedures to follow in case of emergency.
Their duties to a high level.
The location of safety equipment, such as fire-fighting equipment, and how it is used in the machinery space.
What is happening on the bridge at all times.
Which of the following hazards might be found in the engine room?
Heavy moving machinery.
Enclosed spaces.
Spaces that can be difficult to reach.
Power operated watertight doors.
Galley equipment.
Which of the following additional actions can an engineer do to ensure a safe watch?
Avoid fatigue.
Never neglect an alarm.
Obey orders.
Communicate clearly.
Call for help when in need.
Skip some machinery checks to save time.
Examining Lifting Appliances and Loose Gear
??? If the examiner finds any defects, the equipment does not meet the requirements or insufficient preparation has been carried out – what sanctions can they impose?
!!The lifting appliances may be condemned and removed from service.
!!The examination can be halted.
Detain the vessel.
Recommend the withdrawal of class.
??? Which of the following should be inspected during an examination of the engine room crane?
Bridge drive.
Hoist.
Deck fittings.
Pedestal.
Crab (or trolley).
Rail and wheels.
Which of the following hazards might the examiner be exposed to?
Bloodborne pathogens.
Working over water.
Working at height.
Simultaneous operations.
According to ILO 152, how often should ship mounted lifting appliances be retested?
Every 5 years.
Every 10 years.
Every 2 years.
If lifting appliances are removed from service or there is a delay in completing the examination, this can have a significant impact on operations and profit.
True.
False.
What type of survey and examination services are used for lifting appliances?
Certification.
Classification.
Coronation.
Correction.
Most maritime countries have introduced requirements similar to which of the following conventions in relation to lifting appliances and loose gear?
ILO 152.
IMO 155.
ISO 111.
The examiner is not required to wear personal protective equipment while on board.
True.
False.
To ensure that the appliance and its associated equipment is in the correct place, the examiner should review which of the following?
ECDIS charts.
The ship’s general arrangement diagram.
Block lists.
Reeving diagrams.
The ship’s logbook.
Manufacturer’s manuals.
A risk assessment should be carried out before every examination.
True.
False.
When should the examiner inspect the register of the ship’s lifting appliances and cargo handling gear (form one)?
After the examination is complete.
Before the examination takes place.
During the examination.
What are the three common types of slewing bearings found on ship’s cranes?
Three roller bearing.
Rotor bearing.
Twin ball bearing.
Triplet bearing.
Single ball bearing.
The sheave and block unit on a ram-luffed crane can be easily dismantled for inspection.
True.
False.
Which of the following are examples of protective devices?
Rope terminations.
Luffing-in limiters.
A slack rope switch.
The examiner may be required to inspect which of the following types of crane?
Ram-luffed cranes.
Cable-luffed cranes.
Engine room cranes.
Rope-luffed cranes.
Control room cranes.
Deck fittings must be examined to ensure which of the following?
The paintwork has no chips or cracks.
They show no signs of excessive wear, deformation or corrosion.
The welds attaching the eye plates and cleats to the deck are sound.
Masts that are permanently attached to the deck, do not need to comply with the regulations.
True.
False.
When examining derrick systems, which of the following should be inspected?
Pedestal.
Bridge.
Derrick boom.
Mast.
Gooseneck and derrick heel assembly.
Derricks must be fitted with protective devices.
True.
False.
Which of the following are examples of deck fittings?
Wire rope stoppers.
Blocks.
Cleats.
Hooks.
Eye plates.
All loose gear must be clearly and permanently marked with which of the following?
It’s manufacturer’s or surveyor’s stamp.
It’s safe working load.
It’s date of purchase.
It’s steel grade.
The name of the vessel.
What type of shackle is being shown?

Dee shackle.
Bow shackle.
What type of hook is being shown?
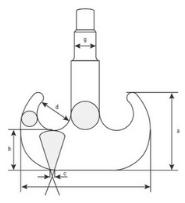
Ramshorn.
C shaped.
In general, the ____ is considered as the breaking load of a component, divided by a safety factor, to provide a safe load that can be lifted or carried in a given condition.
Safe working load.
Working load limit.
In general, the ____ is the maximum load (as specified by the manufacturer) that the gear can safely lift.
Working load limit.
Safe working load.
Loose gear is any equipment that is used to attack a load to the lifting appliance, but which does not form an integral part of the appliance.
True.
False.
What tools can the examiner use when examining ropes?
A steel spike.
A pair of clamps.
Callipers.
A grinder.
For normal lifting appliances, terminations must be proof tested to which of the following?
Twice the SWL of the rope.
Five times SWL of the rope.
Ten times SWL of the rope.
A rope failure will almost never result in an accident.
True.
False.
What are valley breaks evidence of?
The rope is too thick for the block.
That the centre of the rope is no longer supporting the strands.
The rope is rubbing against the sheave.
To assess the levels of deterioration in wire ropes, the examiner will do which of the following?
Count the number of visibly broken wires.
Dip the rope in water.
Measure the decrease in the rope’s diameter from external wear or abrasion.
Run the rope through their hands and guess the diameter.
Visually assess signs of damage.
What should the proof load be for appliances with an SWL of up to twenty tonnes?
1,1 times the SWL.
1,5 times the SWL.
1,25 times the SWL.
Loose gear does not have to be retested while it satisfies which of the following conditions?
It is clearly identifiable.
It has an appropriate colour code.
It cannot be clearly identified.
It has an appropriate test certificate.
It is in good condition.
Proof testing is designed to evidence that the appliance, gear and attachments are structurally sound and capable of withstanding the operational loads required of them.
True.
False.
Once testing is complete, all lifting equipment must be re-examined to ensure that nothing was damaged during the test.
True.
False.
When must proof testing be carried out?
Before new equipment is introduced into service.
After modifications or repair.
Monthly.
At set periods as required by national regulations.
Six months after equipment has been introduced into service.
Fatigue Management
Which of the following are common behavioural effects of fatigue?
Increased reaction times.
Lack of motivation and energy.
Slowed response times.
Poor mobility.
Irritability, impatience and mood changes.
Lack of lethargy and indifference.
If fatigue is not carefully managed, it can have disastrous consequences.
True.
False.
Which of the following are common causes of fatigue?
Annual leave.
Sufficient rest periods.
Overwork.
Anxiety.
Poor health.
Which of the following methods can be used to help identify personnel who may be suffering from fatigue?
Direct observation of a person’s behaviour.
Investigation findings following a workplace accident or incident.
Completion of a fatigue risk assessment.
Monitoring conformance with the vessel’s Maintenance Management System.
Which of the following are common symptoms of fatigue?
Fidgeting.
Head nodding.
Poor hand-eye co-ordination.
Yawning.
Coughing.
Nosebleeds.
____ is commonly accepted to be a state of mental or physical ____ that can significantly ____ on your ability to work ____, communicate clearly and react effectively in an emergency situation.
Fatigue … exhaustion … impact … safely.
Vitality … exhaustion … impact … quickly.
Seafarers ____ work for more than ____ hours without taking any ____.
… cannot … 14 … rest.
… can … 14 … rest.
Fatigue was found to be a significant contributing factor to which of the following major incidents?
Exxon Valdez.
Deepwater Horizon.
Piper Alpha.
Provide information and training about how non-work related factors can increase the risks of fatigue.
Non-work factors.
Stress.
Hours of work.
Repetitive monotonous work.
Ensure opportunities to clarify stress-related issues since they can impact on sleep and recovery.
Stress.
Non-work factors.
Hours of work.
Repetitive monotonous work.
Ensure that any extended watch hours do not result in excessive hours worked. Limit the use of on-call work, and provide additional rest time following a call-out.
Hours of work.
Non-work factors.
Stress.
Repetitive monotonous work.
Redesign jobs to eliminate boring and repetitive tasks.
Repetitive monotonous work.
Non-work factors.
Stress.
Hours of work.
What is a “safe and suitable” risk assessment designed to do?
Identify suitable control methods.
Identify the specific aspects of an operation that pose a particular fatigue risk.
Quantify the severity of the risk.
Identify which member of personnel should supervise the task.
Identify the number of personnel required to carry out the task.
Fluid Hammer Effect
What are common causes of fluid hammer?
Rapid manual valve opening or closing.
Too high-speed settings on remotely operated valves.
Overuse of swing valves.
Closed discharge valves.
Which type of fluid hammer is typically encountered within ballast water, cargo and engine cooling systems?
Hydraulic shock.
Differential shock.
Thermal shock.
Piston shock.
How can you prevent the risk of a slug forming in compressed air systems?
Open the inlet valve slowly.
Open the inlet valve quickly.
What is the fluid hammer effect?
The sudden increase in pressure inside a pipe.
The sudden decrease in pressure inside a pipe.
The use of high-pressured water to clean inside a pipe.
The use of high-pressure steam to clean inside a pipe.
What are some of the possible effects of fluid hammer?
Damage to pumps, valves and filters.
Chemical and oil cargo contamination.
Fractured pipework.
Damage to ballast water tanks.
Garbage Record Book
What methods are being considered to improve the garbage reception facilities?
Improving the effectiveness of port reception facilities and treatment in reducing marine plastic litter.
Providing separate garbage collection for plastic waste from vessels, including fishing gear to reuse or recycle.
Providing training on basic marine environment awareness for those practising fishing from vessels.
Ensuring port reception facilities are open 24/7 for garbage disposal.
Enhancing public awareness and education and seafarer training.
What are the special areas established under Annex V?
The North Sea.
The Caspian Sea.
The Black Sea.
The Adriatic Sea.
The Antarctic Sea.
The Mediterranean Sea.
Where does a large amount of the garbage that pollutes the oceans and washes up on beaches come from?
Holidaymakers.
Seafarers.
Oil spills.
Cities.
What are the system specifications required of the electronic record book?
Security.
Inexpensive.
System updates.
Accountability.
Ability to meet MARPOL regulations.
Data storage.
When did Annex V enter into force?
24 November 1987.
31 November 1988.
24 December 1987.
31 December 1988.
What procedures are part of the garbage management plan?
Having a garbage management specialist aboard each vessel.
Recording disposals in the Garbage Record Book.
Using the port reception facilities to dispose of garbage.
Issuing placards around vessels.
What are the exceptions regarding the disposal of garbage at sea?
Disposal from a vessel necessary for the purpose of securing the safety of a vessel and those onboard.
Disposal from a vessel necessary for the purpose of saving life at sea.
The escape of garbage resulting from damage to a vessel or it’s equipment, provided all reasonable precautions have been taken before and after the occurrence of the damage for the purpose of preventing or minimising the escape.
Disposal of broken synthetic fishing nets.
Marine pollution can cause mutations and diseases that can be harmful to the entire marine food web, as well as human beings.
True.
False.
Every vessel of more than 10 metres in length overall must display placards notifying the crew and passengers of the disposal requirements.
True.
False.
What are the different ways in which garbage is disposed of?
Incineration.
Plastic waste discharge into the sea.
Discharged to reception facilities ashore or to another vessel.
Accidental or other exceptional discharges of garbage.
Discharged into the sea.
Good Business Writer
“The project was completed by the engineers” is an example of active voice.
False.
True.
Avoid ____, acronyms, and the latest “business speak”.
Industry jargon.
Simple sentence.
Clear and crisp.
Use simple, direct words and short, concise sentences.
True.
False.
Hand-Arm Vibration Safety
!! Which of the following ways can help employees minimise their risk to health from vibration?
Changes to working practices to reduce vibration exposure.
Correct selection, use and maintenance of equipment.
Maintaining good blood circulation at work by keeping warm and massaging fingers.
Correct techniques for using equipment; for example, how to tighten grip force.
Manufacturers must provide which of the following safety information in the form of accompanying instruction books or manuals, for each piece of equipment?
Information on its safe use and, where necessary, training requirements.
Warnings about any vibration-related risk from using the equipment.
Information on how to maintain the equipment.
The price of the each piece of equipment.
Which of the following are the responsibilities of employers?
Assessing the vibration risk to employees.
Keeping health records for employees under health surveillance.
Providing information and training to employees on the health risks and the actions being taken to control risks.
Preventing job rotation.
Increasing the length of time employees handle vibrating equipment in order to get the job done quickly.
Why is it important to monitor exposure to vibration?
To identify any vibration-related disease at an early stage.
To check the effectiveness of existing vibration control measures.
To identify anyone that is exposed to hand-arm vibration who may be at particular risk.
To ensure all equipment is functioning correctly.
To reduce the need for risk assessment.
Which of the following control measures can be taken to reduce exposure to vibration?
Rotate jobs and switch tasks frequently.
Use suspension systems to reduce the need to grip heavy tools.
Limit the use of high vibration tools wherever possible.
Maintain equipment at regular intervals.
Avoid using gloves.
Use equipment that requires rotary and hammer actions.
Hand-arm vibration is ____ that is transmitted from work ____ into worker’s hands and ____.
… vibration … processes … arms.
… shock … owners … arms.
What type of jobs require the use of vibrating equipment?
Ship maintenance.
Shipbuilding.
Heavy engineering.
Construction.
Sea rescue.
Which of the following are symptoms of Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS)?
Tips of fingers turning white and then red.
Tingling and numbness in the fingers.
Inability to feel things with the fingers.
Bruising of the wrists.
Pooling of the blood in the fingers.
Which of the following pieces of information must manufacturers provide when supplying vibrating equipment?
Warnings about any vibration-related risk from using the equipment.
A statement of the equipment’s vibration emission together with information on the method that was used for vibration testing.
Health surveillance records.
Workplace risk assessments.
Which of the following effects can HAVS symptoms have on someone?
Reduced ability to work in cold or damp conditions.
Pain, distress and sleep disturbance.
Reduced grip strength.
A high fever.
Which of the following tools and equipment may present hand-arm vibration risks?
Polishers.
Hand-held grinders.
Impact wrenches.
Wrench.
Hammers.
Select the actions that employees can take to reduce the risk of HAVS:
Always use the right tool for each job.
Encourage good blood circulation by keeping warm and dry by wearing gloves, a hat and waterproofs.
Always use the right tool for each job.
Avoid wearing PPE when using vibrating equipment.
Increase the length of time spent using a tool.
Exposure Action Value (EAV) it is:
A daily amount of vibration exposure above which employers are required to take action to control exposure.
The maximum amount of vibration an employee may be exposed to on any single day.
Exposure Limit Value (ELV) it is:
A daily amount of vibration exposure above which employers are required to take action to control exposure.
The maximum amount of vibration an employee may be exposed to on any single day.
Employees should be provided with information and training in which of the following areas?
How to recognise and report symptoms.
Health effects of hand-arm vibration.
Marking equipment with the correct vibration-risk warnings.
Calculating vibration emission levels from individual pieces of equipment.
The Supply of Machinery (Safety) Regulations state that tool and machinery manufacturers are required to design equipment that will reduce vibration risks to as low a level as possible, making use of the latest technology.
True.
False.
Handling and Storage of Hazardous Substances
Which of the following are precautions that should be implemented to help to control any risks from working with hazardous substances?
Storing chemicals according to the SDS.
Keeping only the minimum quantity of substance necessary.
Ensuring employees are properly trained in the storage and handling of hazardous substances.
Storing compatible substances separately.
Safety Data Sheets, often referred to as SDS, provide detailed information on substances that have the potential to cause harm to people or the environment.
True.
False.
In which ways hazardous substances can enter the body?
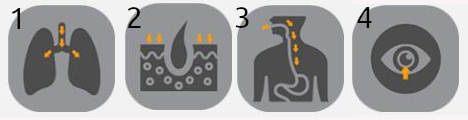
1. Inhalation; 2. Absorption; 3. Ingestion; 4. Contact with eyes.
1. Absorption; 2. Inhalation; 3. Ingestion; 4. Contact with eyes.
1. Absorption; 2. Inhalation; 3. Contact with eyes; 4. Inhalation.
Select the answer which is correct:
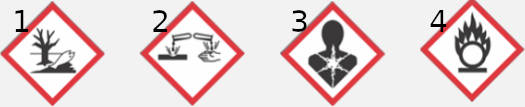
1. Dangerous to the Environment; 2. Corrosive; 3. Long term health hazards; 4. Oxidising.
1. Dangerous to the Environment; 2. Oxidising; 3. Long term health hazards; 4. Corrosive.
1. Dangerous to the Environment; 2. Long term health hazards; 3. Oxidising; 4. Corrosive.
Choose the correct order in the control hierarchy, starting with the most preferred option through to the least preferred option.
1. Eliminate; 2. Substitute; 3. Enclose; 4. Engineering controls; 5. Procedural controls; 6. Personal Protective Equipment.
1. Substitute; 2. Substitute; 3. Enclose; 4. Engineering controls; 5. Procedural controls; 6. Personal Protective Equipment.
1. Personal Protective Equipment; 2. Substitute; 3. Enclose; 4. Engineering controls; 5. Procedural controls; 6. Substitute.
Harassment and Bullying
What type of behavioural changes can highlight that someone might be experiencing harassment or bullying?
A lack of motivation resulting in unsatisfactory work performance.
Abusing drugs and alcohol.
A change in mood, becoming agitated, alert or aggressive.
A boost in job performance.
A ship is often seen as a seafarer’s home for many months at a time.
True.
False.
The perpetrator should have the right to a ____ where they have the opportunity to give their version of events and respond to the complaint. The victim and perpetrator must be treated ____ and should both have the option to call ____ if required.
… hearing … fairly … witnesses.
… debate … friends … differently.
… hearing … differently … witnesses.
How can Shipping Companies and Seafarer Organisations raise awareness on harassment and bullying?
By arranging for seafarers to participate in awareness, educational and social skills training programmes.
By introducing management and seafarers guidelines.
By displaying posters and notices in staff areas and articles in staff magazines.
By displaying photographs of perpetrators in staff areas.
What are the three most common types of harassment?
Physical.
Sexual.
Verbal or written.
Medical.
Criminal.
What are the responsibilities of seafarers in assisting in the elimination of harassment and bullying?
Report if harassment or bullying is observed or experienced.
Avoid harassing or bullying others and actively get involved if witnessing another seafarer being targeted.
Support the right of everyone to be treated with dignity.
Bullying those that you have witnessed bullying others.
What should be included in a Shipping Company’s harassment and bullying policy?
Examples of actions that would be deemed harassment or bullying, including cyberbullying.
A statement that sets out the company’s commitment to eliminate harassment and bullying aboard ships.
A clear overview of what the process of the complaint will be and how the outcome will look.
A list of crew members who are most likely to commit harassment and bullying acts.
Which of the following are protected characteristics?
Age.
Disability.
Gender.
Race.
Education.
Eye colour.
Which of the following are examples of sexual harassment?
Flirting, over-familiar behaviour, gesturing or making sexual remarks about a person’s appearance.
Inappropriate touching against a person’s will.
Displaying or sharing pornographic or sexual images, or other sexual content.
Asking a person to go on a date with you.
According to recent studies, bullying or harassment is a response to stress or internal suffering.
True.
False.
Hazard Identification
Which of the following are examples of “occupational hazards”?
Falls from height.
Slips, trips and falls.
Dropped objects.
Fire or explosion.
Hazard identification, often referred to as ____ is “the process of ____” hazards and ____ possible hazardous scenarios.
… HAZID … identifying … evaluating.
… HAZOP … identifying … evaluating.
… HAZID … eliminating … adding.
Pressure is the “amount of force applied over a surface area”.
True.
False.
When assessing ____ potential, the key aim is to bring the risk down to ____. The ____ posed from each identified hazard should ideally be reduced to ALARP.
… hazard … As Low as Reasonably Practicable (ALARP) … risk.
… hazard … As Low as Reasonably Practicable (ALARP) … reduce.
Poor hazard identification is one of the leading causes of ____ in the workplace. Effectively identifying potential hazards and ____ clearly about how to manage these hazards significantly ____ the chance of incidents occurring in the workplace.
… incidents … communicating … reduces.
… stress … eliminating … aims.
Which of the following are examples of common hazard groups found in the Maritime Industry?
Mechanical.
Noise.
Hazardous Substances.
Height.
Which of the following are issues that have resulted from human error?
Complacency due to repeated routine tasks.
Cutting corners to try and get a job completed as quickly as possible.
Not following, or understanding, work procedures.
Not wearing the correct PPE.
Bad weather.
After identifying all of the potential hazards, the risk that they pose must be ranked. What is used to “rank risk”?
Risk matrix.
Hazard Checklist.
Competency Matrix.
COSHH Assessment.
Which of the following are examples of control measures used to mitigate the risk from potential hazards?
Risk Assessments.
Work Procedures.
Toolbox Talks.
Shift Rotas.
Which of the following are examples of “major accident hazards”?
Failure of life support systems.
Serious structural damage.
Fire or explosion.
Slips, trips and falls.
Helicopter Operations at Sea
Why are helicopters used?
Delivering food offshore.
MEDIVAC.
Crew transfer.
Pilot transfer.
Winching renewable equipment sites.
To transport drilling equipment to rigs.
Which of the following are physical characteristics of helidecks outlined by Cap 437?
Markings and colours that fit the colour code – the deck is always green and the lettering is white.
Helideck area or “D Value” which is the largest overall dimension of the helicopter when rotors are turning.
Markings and colours that fit the colour code – the deck is always red and the lettering is white.
Windsocks to show which way the wind is blowing.
Match the description to the correct images. Select the answers that apply.

1 is a Winching, 2 is a Hi-Line.
1 is a Hi-Line, 2 is a Winching.
To perform a helicopter landing on a ship without a designated area, which of the following should be ensured?
Flags and pennants should be flown to give an indication of wind direction.
If at night the area should be well lit with no glare.
No loose equipment or debris should be in the vicinity to avoid accidents from downdraft.
It should not be performed at night time.
Deck personnel should be wearing the correct PPE.
What type of emergencies do drills prepare the crew for?
Fire.
Abandon ship.
Collision.
Tsunami.
As per SOLAS and the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System procedures all ships should comply with which of the following?
Are fitted with communication equipment.
Are fitted with aeronautical radio equipment.
Have clear communication protocols to follow.
When on the helideck, which of the following pieces of PPE are required for the helideck crew?
Safety boots or shoes.
An immersion suit.
Eye protection.
Ear protection.
It is not possible to carry dangerous goods by air.
True.
False.
What is the object shown on screen?

Wheel chock.
Hi-line.
Vessel radio.
Flying object debris (FOD).
This training involves ____ from an ____ helicopter to a ____ or into the water, as well as the necessary sea survival required, including rescue and recovery.
… escaping … overturned … life raft.
… parachuting … inflight … ship.
… escaping … overturned … ship.
Hydrogen Sulphide Awareness
Select the answer that apply. The long-term exposure limit for hydrogen sulphide is ____, averaged over an ____ reference period.
5 ppm … 8-hour.
15 ppm … 11-hour.
50 ppm … 8-hour.
10 ppm … 11-hour.
Select the answer that apply. The short-term exposure limit for hydrogen sulphide is ____, averaged over an ____ reference period.
10 ppm … 15-minute.
15 ppm … 20-minute.
50 ppm … 15-minute.
10 ppm … 20-minute.
Which of the following items of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) are required when working in areas where personnel may be exposed to hydrogen sulphide?
Waterproof, chemical resistant coveralls.
Waterproof, chemical resistant gloves.
Waterproof, chemical resistant boots.
Protective goggles.
Welding mask.
Ear plugs.
In relation to controlling exposure to hydrogen sulphide, which of the following are the responsibilities of employers under the COSHH Regulations?
Providing means of detecting, monitoring and protecting personnel from exposure to H2S.
Establishing H2S contingency plans and ensuring emergency escape and evacuation arrangements are in place.
Ensuring that defined occupational exposure levels are not exceeded.
Ensuring that exposure levels are always above defined occupational exposure levels.
Ensuring that all personnel have access to hazardous substance logbooks.
You may be able to detect a “rotten egg” smell at this stage, but this may disappear after a time as your sense of smell is damaged. Select H2S concentration level:
0-10.
50-100.
320-530.
This may lead to eye damage. Select H2S concentration level:
50-100.
0-10.
320-530.
This may result in pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) with the possibility of fatal consequences. Select H2S concentration level:
320-530.
0-10.
50-100.
Which of the following checks should be carried out on Respiratory Protective Equipment (RPE)?
Before use, check the air lines for air-supplied Breathing Apparatus.
Examine and test RPE thoroughly at least every month.
Examine and test RPE thoroughly at least every 6 months.
Check the air lines for air-supplied Breathing Apparatus on an annual basis.
When should bunkering fuel tanks be checked for H2S?
During bunkering.
Prior to bunkering.
After bunkering.
After training.
When specified by the Master.
Which of the following are the responsibilities of employees under the COSHH Regulations?
Co-operating with the ship’s Master and follow company procedures at all times.
Using the protective equipment they have been provided with as instructed.
Ensuring that exposure levels are always above defined occupational exposure levels.
Establishing H2S contingency plans.
Fixed detector is:
Strategically placed around the installation, this type of detector initiates toxic gas alarms to the bridge.
This type of detector includes hand-held sampling detectors that can be used for background monitoring of hydrogen sulphide levels.
This type of detector is worn by personnel, and must be worn within the user’s breathing zone.
Portable detector is:
This type of detector includes hand-held sampling detectors that can be used for background monitoring of hydrogen sulphide levels.
Strategically placed around the installation, this type of detector initiates toxic gas alarms to the bridge.
This type of detector is worn by personnel, and must be worn within the user’s breathing zone.
Where there is a potential risk of ____ to significant levels of ____ on oil and chemical tankers, the ship operator or owners are required to ____ the risk and put a contingency plan in place to ____ the identified risks.
… exposure … H2S … assess … manage.
… exposure … H2O … assess … manage.
… increase … H2S … consuming … manage.
… equipment … H2O … assess … increase.
You may be able to detect a “rotten egg” smell at this stage, but this may disappear after a time as your sense of smell is damaged. Which H2S level?
0-10.
50-100.
320-530.
This may lead to eye damage. Which H2S level?
0-10.
50-100.
320-530.
This may result in pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) with the possibility of fatal consequences. Which H2S level?
0-10.
50-100.
320-530.
Personal detector is:
This type of detector is worn by personnel, and must be worn within the user’s breathing zone.
Strategically placed around the installation, this type of detector initiates toxic gas alarms to the bridge.
This type of detector includes hand-held sampling detectors that can be used for background monitoring of hydrogen sulphide levels.
Select the graphics that represent the characteristics of hydrogen sulphide:
Heavier than air.
Flammable.
Burns with a blue flame.
Lighter than air.
Burns with a green flame.
Personal Hygiene
Why is it important to clean and cover all wounds?
To reduce the risk of infection and transfer of bacteria.
To prolong the healing process.
To reduce the risk of scarring.
Treatment should be sought immediately for minor injuries, cuts, rashes and abrasions.
True.
False.
What should you do to keep your cabin clean and tidy?
Keep surfaces clear and clean.
Keep shoes and clothes stowed away.
Launder clothes and bed linens regularly.
Store food in your locker.
Leave dirty laundry on the floor.
There are over 500 different species of bacteria that live in and on the human body.
True.
False.
How long should you wash your hands for?
20 seconds.
10 seconds.
15 seconds.
If you need to ____, you should always cover your mouth and ____ with a ____ (or the crook of your arm).
… cough or sneeze … nose … tissue.
… dispose … hands … nose.
… chin … beware … tissue.
____ of used tissues immediately, and wash (or sanitise) your ____ right away.
… dispose … hands.
… nose … hands.
… chin … dispose.
How often should you brush your teeth?
At least twice a day.
At least once a day.
At least five times a day.
Personal ____ is the steps that we all take, every day, to keep ourselves clean and ____.
… hygiene … healthy.
… hands … dirt.
… hygiene … touch.
Poor standards of hygiene, like not washing your ____, can spread ____ and bacteria to everything that we ____ – including the food that we eat.
… hands … dirt … touch.
… hands … dirt … hygiene.
… hygiene … touch … dirt.
Which of the following are potentially harmful bacteria?
E. coli.
Staphylococcus aureus.
Salmonella.
Bifidobacterium.
Lactobacillus.
Which of the following actions will help to ensure the health and wellbeing of everyone on board?
Washing your hands regularly.
Showering and washing your hair regularly.
Disposing of waste correctly.
Wearing clean clothes and using the laundry servises.
Brushing your teeth once a week.
Allowing dirt to accumulate under your fingernails.
Interventions
There are many reasons why crew members may be reluctant to intervene, including differences in departments, rank, age or nationality.
True.
False.
This intervention steps order is correct? 1. Stop the job if there is a risk to safety; 2. Ensure that the team or individual is in a safe position to carry out a discussion; 3. Make sure that the conversation is positive throughout; 4. Highlight and discuss what could go wrong; 5. Agree the actions or behaviours that were unsafe; 6. Record observations using a “no name no blame” approach.
Yes.
No.
When receiving feedback, crew members should do which of the following?
Be receptive.
Listen carefully to what is being said.
Ask questions to clarify any queries.
Become argumentative and defensive.
Ignore it.
How can senior officers demonstrate their commitment to creating a respectful workplace?
By following up on suggestions for improvement.
By promoting a culture of trust.
By asking crew members for their opinions.
By encouraging a culture of competition not cooperation.
An intervention can take which of the following forms?
Stopping a colleague during a task.
Seeking assistance from a senior officer.
A discussion prior to starting a task.
Punishing a colleague for making a mistake.
Ignoring the problem and hoping it resolves itself.
Introduction to Inert Gas Systems
A typical inert gas system includes which of the following components?
A scrubber tower.
A pressure vacuum breaker.
A fuel injector.
A demister.
If the inert gas system fails, what should the crew do?
Open all hatches and vents.
Take action to prevent any air ingress to the tanks.
Purge the tanks.
Close the deck isolating valve.
Open the pressure regulating valve.
Stop any cargo or ballast operations from inerted tanks.
Even with no cargo onboard, flammable vapours may still be present within a vessel’s storage tanks.
True.
False.
The inert gas system will be used during which of the following operations?
Tank cleaning.
Cargo loading.
Cargo discharge.
Bottom painting.
The relationship between the composition and flammability of a specific hydrocarbon gas, air and inert gas in cargo tanks is often displayed in which of the following?
A flammability diagram.
A switching plan.
A power card.
Introduction to Oily Water Separators
As the mixture flows through this filter, any remaining oil droplets are collected on the filter’s surface, where they are able to increase their size by joining up with other droplets.
True.
False.
Under MARPOL Regulations, in which circumstances can oily mixture be discharged?
After passing through the separation system, the oil in water content of the mixture does not exceed 15 parts per million.
When the mixture has been processed via an oily water separator meeting the requirements of MARPOL.
When the boat is at anchor.
If the oily mixture is contaminated with very large particles, then the separator will not function correctly and the oil content meter may not provide accurate readings.
True.
False.
What are the three components of a static separator?
An oil content meter.
A catch plate separation chamber.
Coalescence filters.
Inlet pump.
What should be added to ensure there is no air in the separation chamber?
Fresh water.
Seawater.
Oil.
Why is it important to shut down the separator when operations are finished?
To ensure that the equipment remains fit for purpose.
To reduce the likelihood of an environmental incident occurring.
To ensure the equipment does not overheat.
What is the oily water separator used to treat?
Contaminated water from any compartment in the ship.
Contaminated water and oily mixtures from bilge spaces.
Any accumulated water from bilge tank tops.
Contaminated oil from any compartment in the ship.
Which of the following are components of a centrifugal separator?
A centrifuge separator.
A motor to spin the centrifuge.
An inlet and outlet piping systems.
A coalescence filter.
For what reason might an alarm sound?
When the oil content meter measures an oil in water reading of more than 15 parts per million.
If the flow of the oily mixture from the supply tank is reduced.
When the oil content is too low.
Introduction to ISO 14001 and Environmental Management
Which of the following statements accurately describes the term environmental “aspect”?
Any element of an organisation’s activities, products or services that can interact with the environment.
Any change to the environment, whether adverse or beneficial, wholly or partially resulting from an organisation’s operations.
Every individual has a role to play in protecting the environment. Which of the following are responsibilities of all personnel?
Follow company policies and procedures and the conditions of any permits.
Always route all spills to drains.
Avoid unnecessary use of resources.
Only report major environmental incidents.
Always report any environmental incidents or near miss.
Which of the following measures can be taken to prevent spills and accidental discharges?
Keep bilges clean.
Segregate waste into the correct containers.
Follow loading and bunkering procedures.
Conduct regular inspections of high risk spill points.
Switch off equipment when not required.
Which of the following are examples of environmental objectives?
To reduce overheads.
To increase the volume of atmospheric emissions.
To reduce waste volumes.
To reduce energy use.
To increase the number of spills.
To increase staffing levels.
Every action, no matter how small, can contribute to positive environmental performance and help protect the environment.
True.
False.
Incident reporting is a critical component of good environmental practice and regulatory compliance.
True.
False.
What does the acronym EMS stand for?
Environmental Management System.
Environmental Monitoring Statement.
Environmental Maintenance Study.
Environmental Measurement Statistics.
Which of the following are significant environmental aspects of the Maritime Industry?
Atmospheric emissions.
Underwater noise.
Ballast water.
Ballast rocks.
What is data gathered from environmental monitoring used for?
To identify personnel who do not segregate waste.
To name and shame organisations that fail to meet their targets.
To demonstrate environmental credibility and integrity.
To assess a company’s progress in environmental performance against set targets.
An EMS should provide an organisation with clear financial objectives and targets, procedures and practices, roles and responsibilities.
True.
False.
Which of the following is the main international convention covering the prevention of pollution of the marine environment by ships?
International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL).
International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS).
International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW).
The Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs).
Which of the following is the internationally recognised standard for Environmental Management Systems?
ISO 14001.
ISO 9001.
ISO 27001.
ISO 15001.
Atmospheric pollution can lead to which of the following?
Acid rains.
Climate change.
Ozone depletion.
Sewage leaks.
ISO 45001 Occupational Health and Safety
Certification to the ISO 45001 standard is voluntary.
True.
False.
As an employee, you are responsible for which of the following?
Considering safety when planning all jobs, no matter how small.
Complying with the requirements of work permits.
Stopping the job if you have any concerns over safety.
Following all company policies and procedures.
Creating your own safety rules and following them strictly.
How can you reduce the risk of being injured by a slip, trip or fall?
Use dedicated walkways.
Hold onto the handrail on the stairs.
Ensure the deck is clean and uncluttered.
Carry equipment in a specialist belt when climbing a ladder.
By avoiding high noise areas.
What safety procedures should you follow to reduce your risk of injury aboard a vessel?
Familiarising yourself with safety signs.
Understanding the common causes of workplace accidents.
Wearing the correct Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Performing a new risk assessment at the beginning of each day, even if there are no changes to the risk level.
What does the “C” stand for in the PDCA cycle?
Check.
Change.
Close.
A permit to work is required for which of the following tasks?
Working on deck during adverse weather.
Conducting hot work.
Working aloft or outboard.
Entering an enclosed space.
Working on deck.
Ladder Safety
____ – low cost, tend to age quickly, can become wobbly.
Wood.
Fibreglass.
Aluminium.
When erecting a long ladder, who should stand at the base?
Heaviest person.
Lightest person.
Which of the following statements are true?
Always face the ladder during ascent and descent.
Allow only one person at a time on a ladder.
Keep your body aligned with the centre of the steps and avoid over reaching.
Maintain a 2-point contact with the ladder at all times.
Allow only two people at a time on a ladder.
Ladder should ____ be checked prior to use and inspected on a regular basis. Guidelines stipulate that ladder inspections should take place at regular intervals based on the frequency of ____ and ____ carried.
… always … use … loads.
… frequently … damage … loads.
… always … damage … people.
If a ladder is supported at 12 feet off the ground, how far should its base be from the wall?
3 feet.
2 feet.
4 feet.
6 feet.
____ – light weight, can bend easily, cannot be used near electricity.
Aluminium.
Fibreglass.
Wood.
____ – expensive, resilient in harsh weather, can be used near electricity.
Fibreglass.
Aluminium.
Wood.
Extension ladders should be stored in a vertical position.
False.
True.
Which type of ladder is self-supporting?
Step ladder.
Single ladder.
Extension ladder.
How many points of contact with a ladder should be maintained whilst climbing?
3.
2.
4.
What types of safety features are associated with fixed ladders?
Ladder safety device.
Well.
Box.
Tube.
Cage.
Extension ladders are usually made up for a ____ which sits on the ground and a fly which is the extendable moveable piece. They are most often used to reach ____ places, particularly when a ____ ladder is not long enough.
… base … high … single.
… rope … hot … single.
… base … hot … fixed.
Liquefied Gaz Fire Hazard Management
What are the four elements of the fire pyramid?
Chain reaction.
Oxygen.
Heat.
Fuel.
Smoke.
Nitrogen.
Which of the following steps can crew take to reduce the risk of fires onboard?
Never smoking out with designated smoking areas.
Recording any near misses so that lessons can be learned.
Always following the Permit to Work system – especially in relation to hot work activities.
Using mobile phones outside of the accommodation area.
Ignoring fire hazards.
The majority of liquefied gas transported by gas carriers are hydrocarbons and therefore are extremely combustible and inherently hazardous.
True.
False.
A flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases such as propane and butane that exist in a liquefied form. What is it?
Liquefied Petroleum Gases.
Liquefied Natural Gases.
Gases that come from a natural source and consist predominantly of methane, ethane, propane and a small amount of butane.
Liquefied Petroleum Gases.
Liquefied Natural Gases.
What must the crew do when carrying out product transfer operations?
Ensure precautions are in place to control any potential sources of ignition.
Comply with product handling procedures.
Familiarise themselves with the products Safety Data Sheet.
Ignore communications with onshore personnel.
If crew members discover a fire, what should they do?
Notify the bridge.
Stop all work.
Evacuate all non-essential personnel.
Immediately attempt to fight the fire.
Ignore it.
Select the answer that apply. A flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases such as propane and butane that exist in a liquefied form:
Liquefied Petroleum Gases.
Liquefied Natural Gases.
Select the answer that apply. Gases that come from a natural source and consist predominantly of methane, ethane, propane and a small amount of butane:
Liquefied Natural Gases.
Liquefied Petroleum Gases.
Which of the following must be included in the fire wallet?
An up to date crew list.
Cargo plan.
Fire plan which identifies the type and location of fire-fighting equipment.
Ship to Shore Safety Checklist.
What does the acronym BLEVE stand for?
Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapour Explosion.
Blasting Level Exceeds Viscose Exhausts.
Burning Limit and Explosive Vapour Emissions.
Unignited gas can result in the formation of an explosive vapour cloud, making it more dangerous that the fire itself.
True.
False.
What is water spraying typically used for?
To create a barrier to prevent fire from spreading.
To disperse gas.
To protect pipes and valves.
To extinguish a fire.
Lubrication Systems
These lubricators are designed to simultaneously feed lubrication to several different points in the system.
Multi-point automatic lubricators.
Progressive lubrication systems.
Circulating oil lubrication systems.
Minimal quantity lubrication systems.
Which of the following are benefits of using a lubrication system?
Reduced environmental impact.
Savings in repairs and spare parts.
Increased machine reliability.
Increased production output.
Increased user competence.
A lubrication system is a mechanical system designed to lubricate internal mechanical systems. Lubrication systems provide the appropriate amounts of lubrication at set intervals in order to minimise friction and wear and optimise the service life of the machinery.
True.
False.
Which of the following are types of lubrication systems?
Circulating oil lubrication systems.
Dual-line lubrication systems.
Single-point automatic lubricators.
Rotating lubrication systems.
Which parts require lubrication in a typical compressor system?
The contact area between the piston rings and the cylinder walls.
The contact area between the piston rod and the surface of the packing.
The rotating vanes of the impeller.
The contact area between the inlet valve and connecting pipework.
Marine Fuel Management and Switching Operations
Which of the following issues can arise during switching operations?
Failure to adjust the quantity requirements of the burner or fuel injector could result in a loss of power, increased smoke emissions and ignition problems.
Poor temperature control can result in thermal shock.
Mixing incompatible fuels can create sludge resulting in clogged pipes, pumps and filters.
Improved lubrication within the engine resulting in decreasing wear and tear.
The Global Sulphur Cap reduced the permissible sulphur emission limit to which of the following?
0,5 % m/m.
0,1 % m/m.
3,5 % m/m.
During switching operations, at what rate should temperatures be changed at to reduce the risk of thermal shock?
Around 2 °C per minute.
Around 2 °C per second.
Around 5 °C per hour.
MARPOL requires all vessels that use more than one fuel type to carry detailed procedures that specify which of the following?
Emergency procedures in case of engine failure or loss of propulsion.
How fuel oils are segregated.
The changeover plan for each passage into and out of an ECA.
How many crew are onboard.
The qualifications of all engine room personnel.
All steps of the change-over procedure must be recorded in which of the following?
Marine Sulphur Record Book.
Engine Logbook.
Bridge Logbook.
Oil Record Book.
Maritime Health and Lifestyle
How can a seafarer limit the risk of unpaid wages?
Ensure all outstanding salary is paid before leaving the ship.
Do not accept the suggestion that the money will be safer with the shipowner.
Report suspicious activity to the captain.
Conduct thorough research before joining a ship or beginning work for a new owner.
What should seafarers practise to reduce the risk of injury or death?
Report anything suspicious to the senior officer.
Conduct a risk assessment before any work begins.
Never undertake work without training.
Never take shortcuts.
Use alcohol to help stay awake during watches.
What conditions are highlighted under Title 2 of the Maritime Labour Convention?
Each ship should have a sufficient manning level.
Promotion and the development of skills should be available for every seafarer.
Cooks should be given proper training.
What is the minimum age of employment for a seafarer working in hazardous conditions?
18.
15.
16.
20.
How many hours of rest should be allocated to a seafarer?
At least 10 hours in any 24-hour period.
At least 77 hours in any 7-day period.
At least 79 hours in any 7-day period.
At least 12 hours in any 24-hour period.
Why do seafarers have an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease?
Seafarers are more likely to have unhealthy diets.
Seafarers lack the space to perform proper exercise.
Seafarers work in a stressful environment for long periods of time.
Seafarers lack communication at sea.
The shipping industry provides work to 1,5 million seafarers, and of all of those in the occupation, around the world.
True.
False.
In what ways can a seafarer reduce the chances of physical or mental health issues from manifesting?
By exercising more frequently.
By stopping or moderating smoking and drinking.
By keeping in touch with family and friends.
By risk assessing each task before beginning the job.
What factors can have a negative effect on the mental health of a seafarer?
Loneliness.
Fatigue.
Lack of communication.
Smoking.
The majority of fatal accidents at sea are related to which type of incident?
Weather conditions.
Human error.
Piracy.
Maritime Leadership
Which of the following behaviours are examples of AGGRESSIVE communication?
Demonstrating that you can violate the rights of a crew member.
Talking in a calm and empathic manner.
Stating your needs clearly and respectfully.
Which of the following aspects apply more often to the maritime industry than other industries?
Unstable workload due to changing weather.
Lack of requirements for technical skills.
Widespread use of hand over from one team to the next team.
Constantly changing teams due to leave rotations.
Which of the following statements characterises an engaged crew member?
I avoid bringing up any problems I have at work.
If I see a colleague making a mistake, I keep it to myself.
I have the training and resources needed to thrive in my role.
My opinion is heard and valued by my colleagues.
I know what is expected of my work.
Which of the following features commonly characterise ASSERTIVE communicators?
Speaking while using hand gestures and a calm or happy face.
Speaking for what they want without violating the rights of others.
Being verbally abusive.
Clearly stating their opinions.
What are the valuable benefits of a leader who has been on board and experienced hardship at sea (being “One of the team”)?
Higher empathy for the crew.
Higher respect from the crew.
Higher media awareness.
Which of the following actions are recommended in order to lead your team through difficult times?
Try to shield crew members from bad news about what’s going on.
Remind your team that their work is valuable.
Describe how the team or company plans to move forward.
Which of the following factors commonly contribute to maritime accidents?
Lack of communication between the Master and crew.
Lack of procedure training.
Lack of sustainability reporting.
Lack of teamwork in the crew.
When is a situation a conflict, which you need to confront and solve?
When a crew member is denying there is a problem rather than pointing it out.
When a crew member lacks situation awareness.
When a behaviour in the crew is negatively impacting the performance of others.
When the crew practices teamwork naturally.
Which of the following terms is defined as “The ability to identify and motivate individual employees to form a team that stays together, works together and achieves together”?
Team building.
Teamwork.
Which of the following are descriptions of self-aware leaders?
Being open-minded about their weaknesses.
Demonstrating unwillingness to listen to a different idea.
Being mindful of their own thoughts, emotions and values.
Frequently asking a question out of curiosity.
Mental Health
What simple steps can you practice if a fellow seafarer comes to you with mental health issues?
Stay calm.
Listen.
Keep social contact.
Force them to talk.
Set the pace.
Seek help on behalf of the sufferer.
What can cause those suffering from PTSD to relive a traumatic event?
Smells.
Nightmares.
Sounds.
Flashbacks.
Exercise.
What are some of the noticeable changes in a seafarer that might indicate they are suffering from mental health issues?
Inability to focus.
Changes in mood or behaviour.
Changes in eating habits.
Spending more time in the gym.
What factors contribute to mental health stigma in the shipping industry?
The shipping industry is considered more “macho” than others.
Cultural differences in crews.
Men make up the majority of the workforce and are a group who are less likely to share their mental health issues.
Effective mental health training for seafarers.
How does healthy food at sea contribute to a positive experience for seafarer?
It can lift the mood of the crew.
It can help to maintain a healthy weight.
It can reduce the physical symptoms of depression.
In what areas can loneliness cause problems for seafarers?
When recalling memories.
When making decisions.
When processing information.
When sleeping for short periods of time.
Which factors of sea life can cause isolation between seafarers?
Cultural differences.
Language barriers.
Technology distractions.
Lack of organised events.
Exercising with crewmates.
The global shipping industry provides work to 3 million seafarers.
False.
True.
What percentage of seafarers reported feelings of depression, but had not approached anyone for help?
45 %.
35 %.
55 %.
50 %.
What are the symptoms of anxiety?
Heart palpitation.
Difficulty concentrating.
Hyperventilation.
Increase in social activities.
Oil Record Book
Every year, oil tankers transport how many tonnes of crude oil and oil products around the globe?
2 400 million.
5 500 million.
3 400 million.
1 500 million.
How does oil enter seas and oceans?
Releases from petroleum extraction.
Marine recreational vehicles.
Accidental and exceptional discharges.
Watersheds that drain heavily in polluted areas.
Runoff from land-based activities, such as construction and farming.
Operational discharges, such as cargo washings.
Jettisoned aircraft fuel.
Marine life activity.
What must the system specifications for the electronic record book address?
Data storage.
System updates.
Ability to meet MARPOL regulations.
Security.
Accountability.
Low cost.
90 % of oil discharges are down to low-level releases associated with the extraction and consumption of petroleum.
True.
False.
For how long should the oil record book be preserved after the last entry has been made?
3 years.
5 years.
2 years.
In what circumstances must the Oil Record Book Part 1 be completed?
When collecting and disposing of oil residues.
When discharging overboard or disposal.
When ballasting or cleaning of oil fuel tanks.
When discharging dirty ballast or cleaning water from oil fuel tanks.
When closing applicable valves or similar devices after slop tank discharge operations.
When bunkering fuel or bulk lubricating oil.
All entries into the Oil Record Book must be:
Recorded with accuracy.
Completed and signed without delay by the officer in charge who performed the operation.
Readily available for inspection at all times.
Checked and signed on each page by the master of the vessel.
Signed by the master of the vessel at the end of every week.
Preserved for 5 years.
What information should be included in every entry in the record book?
The code letter indicating the type of disposal.
The signature of the officer in charge of operations occurred.
The name of the ship.
The coordinates of where the disposal was made.
The IMO number.
The date of discharge.
Item number.
A description of the discharge.
What are the possible consequences of errors in the Oil Record Book’s entries?
Vessel detentions.
Expensive and lengthy court battles.
Damage to ship operator reputation.
Career damage to, and criminal prosecution of, seafarers.
Praise from managers for following orders.
Demotion.
What are the challenges of the paper Oil Record Book?
Time-consuming process.
Heavy paperwork and administrative burden.
Inefficiency.
Easy to misplace.
On-board Assessor
Which type of assessment will normally test the candidate’s practical ability, which is demonstrated through action?
Skills-based assessment.
Knowledge-based assessment.
In which step of the on-board assessment process should the assessor inform about the documents involved in the recording the outcome? (For example, the Training and Assessment Record Book).
Step 2 (Conduct a pre-assessment briefing with the candidate).
Step 1 (Prepare for the assessment).
Step 3 (Observe the candidate’s performance and record the results).
Step 4 (Conduct an assessment debrief).
During Step 5 of the assessment (Conduct an assessment debrief), the assessor should start with the areas where the candidate’s performance did not fulfil expectations.
True.
False.
Which STCW Regulation stipulates that the Company has responsibility for ensuring that seafarers meet minimum standards of competency?
Regulation I/14.
Regulation I/6.
Regulation I/2.
The purpose of competence-based assessment is to collect sufficient evidence of workplace performance to demonstrate that individuals can perform or behave to the specified standards for a specified occupational role.
True.
False.
Which of the following terms is described as “the ability to do a task adequately”?
Competence.
Knowledge.
Proficiency.
After Step 1 in the on-board assessment process (Prepare for the assessment), what is the next step?
Conduct a pre-assessment briefing with the candidate.
Evaluate the process and determine the assessment outcome.
Observe the candidate’s performance and record the results.
In which step of the on-board assessment process should the assessor gather materials, conduct necessary safety checks and inform affected personnel?
Step 1 (Prepare for the assessment).
Step 3 (Observe the candidate’s performance and record the results).
Step 4 (Conduct an assessment debrief).
Step 2 (Conduct a pre-assessment briefing with the candidate).
The performance improvement plan is a document clarifying to the candidate all areas where improvement can be made.
True.
False.
Which STCW Regulation is about training and assessment and requires that all assessors are appropriately qualified and competent?
Regulations I/6.
Regulation I/14.
Regulation I/2.
After Step 3 in the on-board assessment process (Observe the candidate’s performance and record the results), which is the next step?
Evaluate the process and determine the assessment outcome.
Conduct an assessment debrief.
Conduct a pre-assessment briefing with the candidate.
Which of the following terms is defined as “the combination of knowing the theoretical and the practical”, and can be described as KNOWLEGDE + SKILLS?
Competence.
Understanding.
Proficiency.
Personal Protective Equipment
Which of the following are the responsibilities of employees?
Testing PPE.
Use PPE in accordance with the employer’s and manufacturer’s instructions.
Return PPE after use to an appropriate storage location.
Report any loss of, or damage to, PPE.
Assess the suitability of PPE.
PPE users must receive training in which of the following?
How to correctly fit and wear PPE.
The validity periods of PPE.
Limitations of the equipment.
The proper use of PPE.
The costs of PPE.
If more than one item of PPE is being worn, the different items of PPE must be compatible with each other; in such cases, when selecting PPE, it should be ensured that all items, when used together, would adequately control the risks against which they are provided to protect.
True.
False.
Effective protection is only achieved by suitable PPE which is correctly fitted and maintained, and used properly.
True.
False.
Which of the following factors should be considered when assessing the suitability of PPE?
Length of time that PPE must be worn.
Hazards of the job.
Health of individual employees.
Shift changes.
Number of personnel.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) can be defined as “all ____ which is intended to be worn or held by a person at work and which ____ them against one or more ____ to their health or safety, and any additional or accessory designed to meet that objective”.
… equipment … protects … risks.
… places … presents … PPE.
… places … presents … PPE.
Which of the following are requirements of the Flag State regulations?
PPE must be purchased by each individual employee.
PPE must be maintained and stored correctly.
PPE must be properly assessed before use to ensure that it is suitable.
PPE must be used correctly.
“Core” PPE includes which of the following items?
Hard hat.
Fire-resistant coveralls.
Safety harness.
Eye protection.
Self-contained Breathing Apparatus.
Safety footwear.
Gloves.
Hearing protection.
Prevention of Marine Spills (SOPEP)
Which of the following navigational actions should be considered in the event of a spill?
Possible ship-to-ship cargo transfers.
The weather, tide and swell forecast.
Altering the vessel’s course, position and/or speed.
Assessing damage and stress stability.
Sealing any leaks.
Initiating towage.
MARPOL requires all oil tankers of 150 gross tonnage and above, and all ships of 400 gross tonnage and above, to carry which of the following?
Shipboard Oil Pollution Emergency Plan (SOPEP).
Oil Pollution Emergency Plan (OPEP).
Shipboard Pollution Prevention Plan (SPPP).
Oily Discharge Prevention Plan (ODPP).
Which of the following incidents could pose an injury risk to personnel on-board?
Fire or explosion.
Ship collision.
Hazardous vapour release.
Excessive listing.
Loss of cabin pressure.
Turbulence.
Which of the following factors influence the environmental impact of an oil spill?
Weather conditions.
Quantity and properties of the oil spilled.
Number of crew on-board.
Size of the vessel.
What should all crew members do to help minimise the risk of spills?
Carry out a spill assessment as part of every pre-job risk assessment.
Check tank, vessel or container capacity before beginning any bunkering operations.
Know where the nearest spill kit is.
Undertake regular inspections of high risk spill points.
Bypass bunkering and offloading procedures to save time.
Which of the following details should be included in the initial SOPEP notification report?
Number of crew on-board.
Ship’s name, call sign and flag.
Date and time of event.
Ship size and type.
Course.
In the event of a spill, which of the following actions should be taken FIRST?
Alert all crew members.
Ensure suitable PPE is used.
Assess the external resources required.
Monitor on-board clean-up activities.
If a leak occurs from a pipeline, which of the following actions should be taken?
Use of the connection should be stopped immediately.
Any defective pipe sections should be isolated.
Affected sections should be drained down to an available slack tank.
Regular checks of topped up bunker tanks.
Which of the following personnel has overall responsibility for all steps required in the SOPEP process?
Vessel Master.
Chief Engineer.
Deck Duty Officer.
Duty Engineer.
The ship’s crew will be in the strongest position to take prompt action to mitigate and control any discharges during a spill incident. In the event of a spill, which of the following actions should be considered by the crew?
Ballasting or de-ballasting.
Internal cargo transfer operations.
Carrying out an initial risk assessment.
Implementing priority spill countermeasures.
Assessing nearby safe haven options.
Anchoring or setting aground.
In the event of an actual discharge of oil, the Master should begin mitigation measures prior to contacting the nearest coastal state.
True.
False.
Only actual spills must be reported.
False.
True.
Accidental discharges of oil or chemicals can arise from which of the following?
Equipment failure.
Overfilling of tanks.
Human error.
Failure to wear the correct PPE.
If an oil spill occurs during the ship’s stay in port, why is it important to report the spill without delay?
Prompt liaison with local agencies will help to mitigate any potential damage.
Prompt liaison with local agencies will ensure the ship’s operator does not receive a fine.
Prompt liaison with local agencies will help to expedite the ship’s departure.
Which of the following information must be detailed in the notification report?
Any relevant cargo, ballast or bunker dispositions.
The characteristics of the spilled oil.
Any noticeable slick movement.
Any contravention of local regulations.
The competence of personnel in attendance.
Any noticeable floating garbage.
The IMO maintains an up-to-date Focal Points List which details individual countries agencies or administrative bodies responsible for receiving and processing SOPEP reports.
True.
False.
What is the primary purpose of a SOPEP?
To allow robust, effective and tested spill response procedures to be implemented quickly should the need arise.
To promote safety of life and property at sea and the protection of the marine environment by establishing common international standards of training, certification and watch-keeping for seafarers.
To manage the risks to health that are generated by hazardous substances.
In the event of a spill incident, priority must be given to the safety of the personnel on board.
True.
False.
What is the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships commonly known as?
MARPOL.
STCW.
SOLAS.
COLREG.
Which of the following incidents resulted in an estimated 5 million barrels of crude oil leaking into the Gulf of Mexico?
Deepwater Horizon/Macondo.
Amoco Cadiz.
Little Buffalo.
Exxon Valdez.
Prevention of Vessel Air Pollution
The International Ship Management (ISM) code requires that a company establishes safety and pollution prevention objectives. Which of the following are covered by the ISM code?
Engine maintenance.
Fire-fighting systems.
Operating standards.
Incineration.
Fuel oil usage.
Refrigeration.
MARPOL Annex VI applies to which of the following?
Floating craft.
Emergency vessels.
Air-cushion vehicles.
All ship types operating with the flag of a convention state member.
Hydrofoil boats.
Floating platforms.
CO2 is a major greenhouse gas contributing to climate change by trapping the sun’s heat.
True.
False.
Overall, ships release less carbon dioxide (CO2) than other types of transport.
True.
False.
Which of the following practical measures can be implemented to reduce air pollution?
Deck modifications.
Engine modifications.
Exhaust cleaning.
Bulbous bow modification.
Slow steaming.
Which of the following ship-caused pollutants are closely linked to impacting public health?
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs).
Argon (Ar).
Sulphur oxides (SOx).
Particulate matter.
All ships of 400 GT and above must be surveyed to ensure compliance with MARPOL Annex VI and hold an Engine International Air Pollution Prevention Certificate (EIAPPC) or equivalent if engaged in international voyages.
True.
False.
To control NOx emissions, the IMO has adopted four tiers of emission limits based upon engine speed.
False.
True.
The sulphur content in fuel oil used within an ECA must not exceed which of the following?
0,50 % m/m.
0,30 % m/m.
0,10 % m/m.
ECAs provide environmental protection from pollution close to the land and sea areas, where it causes most damage.
False.
True.
Which of the following atmospheric pollutants emitted by ships are covered by the regulations?
Nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Sulphur oxide (SOx).
Helium (He).
Nitrogen (N).
Carbon dioxide (CO2).
What impact does particulate matter have on the environment?
It is a component of smog.
It forms black carbon.
It is a component of clouds.
It contributes to climate change.
Shipboard incinerators must possess an IMO type approval certificate.
True.
False.
Any vessel over 400 gross tonnes and it’s responsible officers can be detained if the regulations from MARPOL Annex VI are not complied with.
True.
False.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) contribute to which of the following?
Lung inflammation.
Algal blooms in inland lakes.
Increased crop nutrients.
Acid rain.
Risk Assessment
Which of the following are some of the requirements that personnel in the risk assessment team must meet?
Be experienced in the type of activity that is to be carried out.
Have knowledge of the equipment and systems that are to be worked upon.
Be aware of any relevant procedures and industry standards.
Be experienced in auditing and monitoring requirements.
Be qualified as a lead auditor.
Which colour in the risk matrix represents levels of risks in the As Low As Reasonably Practicable (ALARP) region?
Yellow.
Green.
Red.
According to the ISM Code, what should be the safety management objectives of a shipping company?
To assess all identified risks to its ships, personnel and the environment and establish appropriate safeguards.
To record and keep track of unintentional eventis.
To review the levels of competency of all personnel on-board.
The International Maritime Organisation (IMO) defines risk as the combination of which two elements?
The frequency/likelihood of occurence.
The hazard.
The severity of the conPage.
The residual risk.
During the task, if you are uncertain or unsure about ANYTHING then you must stop the job and ask for advice.
True.
False.
What is the remaining risk called when prioritised risks have been controlled and lowered to a tolerable and acceptable level?
Residual risk.
Acceptable risk.
Tolerable risk.
Initial risk.
Assessed risk.
What are the five steps of risk management?
Identify.
Analyse.
Assess.
Control.
Monitor.
Investigate.
Eliminate.
Document.
The success of the Risk Assessment depends a great deal upon how effectively it is communicated. Which three statements are correct?
A full discussion of the relevant risk assessment should take place during the Toolbox Talk or the Pre-job Safety Meeting.
Communication is critical to maintaining on-going hazard identification.
The personnel carrying out the task must thoroughly understand the hazards that may be present and the control measures that have been put in place.
Communication of the risk assessment only takes place in the last step of the risk management process.
The task may start even though not everyone is satisfied that the hazards have been correctly identified and the relevant control measures have been put in place.
Dynamic risk assessment is important in constantly changing external and internal environments. What are the purposes of continually monitoring and reviewing the risk assessment while the work task is ongoing?
To detect any changes to the risks and risk criteria which may require revision of the risk control measures and priorities.
To ensure that controls are effective and efficient in both design and operation.
To identify the personnel responsible for any “near misses”.
To identify emerging risks.
Which three elements does a Bow-tie diagram give a visual summary of?
What can cause an unintentional event or accident.
What the resulting events of such an accident could be.
What can cause an unintentional event or accident.
The frequency of an unintentional event or accident.
The areas in which personnel might be at risk of harm.
There are no requirements to maintain risk assessment records.
False.
True.
In which step of the risk management process is the risk level compared against established risk criteria?
Assess.
Analyse.
Identify.
Control.
Monitor.
Safe Cargo Handling
Which of the following checks and actions should be taken during a lifting operation?
A lift plan must be written.
A CSE Certificate must be completed.
The Person in Charge (PIC) must ensure that all required controls are in place.
Equipment must be checked to ensure that it is fit for its intended purpose and operating conditions.
A scafftag system must be put into operation.
The transfer of hazardous waste to shore should be accompanied by which of the following?
Control Note.
Waste Certificate.
Waste Tag.
Consignment Note.
At all stages of cargo handling, ____ should be completed and ____ and goods should be correctly packed, marked, ____ and documented by a ____ person.
… understood … labelled … risk assessments … competent.
… risk assessments … understood … labelled … competent.
When working with containers, which of the following should be considered?
Structural failure during loading or unloading due to overloading or lack of maintenance.
Temperature of each package.
Colour of each package.
Being struck by, knocked or blown off stacks.
Getting crushed or struck by the falling end of a flat rack.
In relation to waste management, the Master is required to provide which of the following?
Garbage Diary.
Waste Timeline.
Colour-coded waste chart.
Garbage Management Plan.
A dropped object is any loose item that is within cargo and has the potential to drop during transit by road or sea transport.
True.
False.
Which of the following situations should be reported to the Master if they occur during loading operations?
Shift or crew change.
The onset of adverse weather affecting loading or back-loading operations.
Accidental discharge of oil, chemicals or fluids affecting loading or back-loading operations.
Any incident such as an impact or fouling of anchors.
An increase in the number of personnel involved in the operation.
The carriage of dangerous goods by sea is governed by the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code established by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO).
True.
False.
In relation to cargo handling, which of the following are examples of bad practice?
Bunded storage.
Blocked drains.
Snagging cargo.
Segregated waste.
Match the substance to their IMDG Class. Corrosive Substance:
Class 8.
Class 3.
Class 1.
Match the substance to their IMDG Class. Flammable Liquids:
Class 3.
Class 8.
Class 1.
Match the substance to their IMDG Class. Explosives:
Class 1.
Class 3.
Class 8.
Safe Use of Rigging Equipment
Which of the following are the main hazards associated with rigging equipment involved in heavy lifts?
Overloading the rigging equipment.
Rigging equipment failure.
Unsecure connections.
Heat generation.
Gas leakage.
Moving loads should never be touched by hand.
True.
False.
____ are commonly found in the engine room to move heavy equipment around within the engine room.
Overhead cranes.
Jib arm cranes.
Tripod lifts.
____ are often located close to the side of a vessel to lift either equipment or provisions to and from the shore.
Jib arm cranes.
Overhead cranes.
Tripod lifts.
____ are used mainly to move heavy equipment in locations that are not accessible by fixed lifting equipment.
Tripod lifts.
Overhead cranes.
Jib arm cranes.
Select the answers that apply. It is important to ____ general experience with lifting operations, ____ familiarisation with the specific equipment. The supervisor should have a ____.
… consider both … and … clear view.
… not consider … and … clear view.
… consider … account only for … clear view.
What should be done if the weight of a load is not known and cannot be weighed or the information cannot be sufficiently trusted?
The weight should be estimated based on the volume and density.
Loading should be refused and the load returned.
____ is the most simple but effective setup where the weight will be distributed evenly on both slings.
The use of two vertical slings.
The choker hitch.
The basket hitch.
The bridle hitch.
____ leads the sling around the load with one end through the other eye, thus tightening itself.
The choker hitch.
The use of two vertical slings.
The basket hitch.
The bridle hitch.
____ can be used for objects such as pallets as the sling is lead through the pallet or around the bottom of the cargo and back into the hook.
The basket hitch.
The use of two vertical slings.
The choker hitch.
The bridle hitch.
____ is used for uneven loads with lifting points.
The bridle hitch.
The use of two vertical slings.
The choker hitch.
The basket hitch.
The Safe Working Load (SWL) is independent of the potential equipment configuration and remains constant for each piece of equipment.
False.
True.
How should rigging equipment be stored?
Controlled to prevent unauthorised use.
Accessible to be easily checked prior to use.
Securely to reduce the risk of accidental damage and to slow down deterioration.
Onshore only.
In an open area to be quickly accessible.
Which of the following are characteristics of chain slings?
They are resistant to cutting and abrasion.
They are very durable.
They are light weight.
They are cheaper than other slings.
When selecting the rigging equipment to be used, which of the following should you take into consideration?
The purpose for which it will be used.
The place it will be used.
The safe working load (SWL).
The conditions under which it will be used.
Shift patterns.
Crane maintenance schedules.
The amount of personnel on board at the time of the lift.
Safe Welding Operations
Which of these are control measures used to mitigate electrical risks and hazards?
Always use the correct current and voltage for the equipment.
Keep the area and clothing dry.
Connect welding equipment properly to complete the circuit.
Always use new cables and leads to avoid wear.
Which of the following are hazards associated with welding operations?
Burns.
Cuts and abrasions.
Electric shock.
Asbestosis.
Welding refers to a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often achieved by melting the work-pieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material (known as the weld pool) that cools to form a strong joints.
True.
False.
Select the items of PPE that should be worn for welding operations:
Insulated gloves.
Rubber soled safety shoes.
Eye and face protection.
Chemical suit.
Which of the following are methods of welding?
Gas metal arc welding.
Shielded metal arc welding.
Gas tungsten arc welding.
Oil powered arc welding.
How can common weld faults be avoided?
Follow safety procedures.
Consider all aspects of the welding operation.
Only conduct welding operations when in dry dock.
Which of the following are common causes of weld failures?
Overload.
Joint design.
Metallurgical failure.
Excess heat.
Fire is a major risk associated with most types of welding.
True.
False.
Which of these are long-term risks associated with welding?
Cancer and neurological problems.
Hand-arm vibration syndrome (HAVS).
Arthritis and other joint problems.
Repetitive stress injuries (RSIs).
Which of the following are the most common shipboard methods of welding?
Arc welding.
Gas welding.
Gas cutting.
Forge welding.
What are some actions required before starting a welding job?
Remove flammable materials and objects.
Have welding equipment and tools checked by a competent person.
Secure a hot work permit and any other required permits.
Secure a hot work permit only.
Remove portable or temporary lighting.
Which of the following are control measures to mitigate fire hazards and risks during welding?
Never weld near tanks associated with flammable substances while at sea.
Keep an appropriate fire extinguisher to hand.
Check the site frequently after work finishes in case of delaying fires.
Set a fire watch for the duration of the work.
If the welding operation must be carried out in a space without adequate ventilation, what options should be considered?
Using a double-layered cloth mask.
Using external fume extraction.
Using a respirator.
Completing the job as quickly as possible.
Who is responsible for determining whether a welding job is necessary, justified and possible to do safely?
The Chief Engineer.
The designated safety officer.
Any competent deck officer.
The Master.
Which of these are control measures used to mitigate risks and hazards when welding in an enclosed space?
Use specialised PPE, such as a harness or respirator.
Check the ventilation periodically during the welding operation.
Set up adequate ventilation where possible.
Test the atmosphere for oxygen and gas levels before entry.
Arrange for an attendant to check on the welder a few times.
What are some of the risks and hazards associated with welding in enclosed spaces?
Limited openings for entry and exit.
Limited personnel are qualified to perform the task.
Restricted movement due to tight spaces.
Poor ventilation, resulting in dangerous atmospheres.
Which of these are options for eye protection when welding?
Spark screen or blanket.
Welding helmet or mask with a filter.
Handheld welding shield with a filter.
Tinted goggles.
Safety Officer
Which of the following are responsibilities of the SSO?
Inspecting and maintaining safety equipment.
Updating relevant legislation.
Acting as the safety advisor aboard ships and ensuring that all health and safety requirements are met.
Assisting the ship’s safety committee in enhancing the safety of the ship.
Showing strong knowledge of the shipping Company’s safety policies and the ship’s operational procedures.
What should new crew members be trained on when they join a new ship?
Cooking equipment.
The location of lifesaving equipment.
Equipment and operations aboard the ship.
Machinery and systems.
The location of shipboard emergency alarms.
It is the Master who appoints the Ship Safety Officer, as they are responsible for the safety of the crew and the ship, but cannot take the responsibility on as their own due to their duties.
False.
True.
Which regulations provide details on crew safety?
As Low As Reasonably Practicable (ALARP).
The International Safety Management Code (ISM).
Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW).
Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS).
Which of the following areas onboard a vessel may present extra hazard?
In enclosed spaces.
In the engine and pump room.
Top deck.
Around the deck hatch and tank opening.
Sewage and Wastewater Treatment
Among other things, which of the following may be checked during a Port State Control inspection?
That all crew members know the international and local regulations.
The chlorine content in the effluent.
The sewage treatment plant is being operated correctly by the ship’s crew.
The validity of the International Sewage Pollution Prevention Certificate.
The humidity of the tank.
The value of the treatment plant.
The details of the sewage discharge regulations can be found in MARPOL Annex IV.
True.
False.
What is the final step in the treatment process?
The disinfection of effluent using chemicals or ultraviolet light in the contact tank.
The separation of solids from liquid waste using a screen or grinder in the primary tank.
The breaking down of organic matter by microorganisms in the treatment tank.
To reduce the risk of fire, cigarette buds should be flushed down the toilet.
False.
True.
Which of the following is an indicator that the tank is turning anaerobic?
A foul smell, similar to rotten eggs.
The formation of rust.
A distinctive colour change.
Slips, Trips and Falls
!!! Which of the following are the responsibilities of shipowners and employers in relation to preventing, or reducing the risk of, slips, trips and falls in the workplace?
!! Deciding who might be harmed and how.
!! Looking for slip and trip hazards around the workplace.
!! Cleaning up spills immediately.
Providing hearing protection.
Reviewing risk assessments on a regular basis.
____, trips and falls are the most common cause of major ____ in the workplace. ____ of major slips result in broken bones and they can also be the initial cause of a range of other types of accident, such as ____.
Slips … injury … 95 % … falls from height.
Slips … collisions … 15 % … dropped objects.
Which of the following measures can be put in place to control contamination and prevent it from spreading into other areas?
Fitting stairs with suitable handrails.
Improving lighting.
Using mats at internal/external interfaces.
Fitting drip trays under machines and racking.
Choose the correct answer to complete the Trip Potential Triangle.
1. Walkways; 2. Design and maintenance; 3. Housekeeping.
1. Housekeeping; 2. Design and maintenance; 3. Walkways.
1. Design and maintenance; 2. Housekeeping; 3. Walkways.
Negative and complacent attitudes towards health and safety, where workers do not take responsibility increase the risk of accidents occurring.
False.
True.
Which of the following actions can personnel take to reduce the risk of slips, trips and falls?
Reduce the level of lighting to save energy.
Remove all warning signs.
Clean up spills immediately.
Dispose of waste materials appropriately.
Store goods safely.
Wear sensible footwear.
If a person cannot see where they are going, there is always a risk of a slip or trip.
False.
True.
Which of the following factors can cause slips, trips and falls?
Protruding objects, service lines and hoses running across the deck.
Missing or removed grates, plates or manholes.
Tidy worksites.
Improperly marked or closed access holes.
Wearing appropriate PPE.
Trip Potential Triangle. Walkways – Design and Maintenance – ____.
Equipment manufacturers.
Scaffolding.
Housekeeping.
Which of the following environmental conditions can make travelling around the ship difficult and increase the risks of slips and falls?
Anti slip surfaces on the deck.
Vessel movements.
Changes in weather conditions.
Changes in surf conditions.
Tank Cleaning and Wall Wash
Even a small amount of cargo residue left behind can cause issues. Therefore, tanks must be thoroughly cleaned to prevent the likelihood of cross-contamination.
True.
False.
What gases should be tested for immediately before entering a confined space?
Toxic atmospheres.
Flammable atmospheres.
Oxygen deficient or enriched atmospheres.
Helium.
What should a permit to work include?
A record of all the potential risks.
The time the work should end.
Outline safe methods of work.
The sequence of the precautions to be taken.
The location of the shadows within the tank.
Which of the following must be complied with when a tank contains residue of noxious liquid substances?
The International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) Convention.
The International Bulk Chemical Code (BC).
The International Tank Cleaning Code (TCC).
What is the purpose of “stripping”?
To prevent a build up of wash water.
To ensure the tank is safe before the competent person enters.
What is a wall wash sample tested for?
Non-volatile matter.
Impurities.
Hydrocarbons.
Nitrogen.
As a minimum, which of the following pieces of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) should be worn?
Gloves.
The gas detector.
Steel toe cap boots or shoes.
Respiratory protection.
Hard-wearing overalls.
When conducting a risk assessment for confined space entry, what should be taken into account?
Assessing all of the risks.
Determining the appropriate safety measures.
Identifying all of the hazards present.
When each crew member on board is on break.
Which role is described below? This person should be in continual attendance outside the confined space. This person must have the necessary communications capability to raise an alarm and summon help.
The Standby Person.
The Master.
The Competent Person.
Which of the following are common dangers associated with confined space entry?
Radiation.
Source of ignition.
Heat.
Fire and explosions.
Drowning.
Working in a confined space is not suited to everyone. Which person may want to avoid this type of work?
Those who suffer from claustrophobia.
Those with heart or breathing problems.
Those with physical disabilities.
Those who are in good physical health.
Some areas within the tanks are not directly in the trajectory of the washing machines and can be harder to clean. What are these areas called?
Shadows.
Drop lines.
Impurities.
What are acceptable oxygen test results for confined space entry?
20,6 to 22,0 %.
10 %.
25,5 to 30,0 %.
What is the purpose of tank cleaning?
To remove sediment from the tank top plating.
To remove the build-up of seawater.
To prepare the tankers for internal inspection.
To ensure that all vessel containment systems are cleaned for the next load of cargo.
To ensure the ballast is clean.
What are the characteristics of a confined space?
The space is not used in daily activities or for continuous work.
The space has limited opening for entry and exit.
The space has inadequate ventilation.
The space has no entry or exit.
Tanker Operations – Bunkering
Why do crew members have a pre-bunkering meeting?
To discuss plans.
To identify risks.
To agree upon a fixed set of operating procedures.
To undertake the relevant training before beginning operations.
Why are stringent measures taken to keep fuel restricted to the designated tanks and pipelines?
Because heavier grade oil is more difficult to clean up after a spill.
Because marine fuels are pollutants toxic to marine life.
Because mixing the fuel could cause an explosion.
What is a “Bunker Supervisor”?
A “Bunker Supervisor” is a qualified person appointed by the bunker supplier to supervise the bunkering operations on behalf of the bunker supplier.
A “Bunker Supervisor” is the qualified person appointed by the Ship’s Master to oversee the bunkering operations.
A “Bunker Supervisor” is the party supplying bunker to a ship, receiving bunker from a ship or shore facility or receiving ship-generated waste from a ship.
Making mistakes in bunkering can result in which of the following?
Pollution.
Imprisonment.
High penalties.
Illness.
Which of the following measures are precautionary for fire safety?
Wear suitable working protective clothing.
Keep all doors to the accommodation areas closed during bunkering and shut off or recirculate the air conditioning system.
Never enter enclosed spaces not approved for entry.
Only smoke towards the back of the deck away from naked flames.
Which of the following actions will be found on the ship’s Master and supplier checklist that is completed prior to the bunker delivery?
Decide procedures for setting up the pipelines, valves and receiving tanks.
Decide which order the tanks will be consumed in.
Ensure that the supplier knows the type and required amount of fuel to be loaded.
Execute a “disconnection” plan on completion of the bunkering operation.
Decide a safe access point between ship to shore or ship to ship.
Before the bunkering process ____, the Chief Officer must ensure that all persons on board are adequately ____ and have been allocated to their designated ____ and work area.
… begins … prepared … job.
… begins … rested … ends.
… rested … begins … job.
What is the most common means of communication during bunker operations?
VHF radio.
Hand signals.
Verbal.
What should the Master do following an oil spill?
Call up for a meeting to discuss the accident to avoid such accidents in the future.
Record the scenario in the ship incident report form.
Refresh training to all crew.
Which of the following are charter types?
Demise charter.
Time charter.
Voyage charter.
Cruise charter.
Which members of the crew play the main roles in the bunkering operation?
Chief Officer.
Master.
Chief Engineer.
Bunkering Supervisor.
What are the two principle types of bunker fuel oil?
Distillate fuel.
Residual fuel.
Fossil fuel.
Oil spill accidents can happen without any warning, leaving very little time to act.
True.
False.
The loading of bunker on board a ship is a vital and critical operation. Everyone involved in the process must take due care to ensure safety and mitigate the risk of an oil spill.
True.
False.
Tanker Operations – Ship to Ship (STS)
When selecting fenders, consideration must be given to which of the following fundamental criteria?
Under the worst operating conditions, the reaction force inflicted by the fender onto the structure of the vessel must be greater than the hull’s pressure limits.
The reaction force inflicted by the fender onto the structure of the vessel must be less that the hull’s pressure limit.
Under the worst operating conditions, the energy capacity of the fender must be greater that the berthing energy of the manoeuvring ship.
The energy capacity of the fender must be less than the berthing energy of the manoeuvring ship.
The Master remains responsible, at all time, for the safety of which of the following?
Luggage.
Ship.
Cargo.
Equipment.
Crew.
Which of the following actions can help to reduce the risk of incidents during STS transfers?
Selecting a high traffic area for the transfer to take place.
Constantly monitoring weather conditions.
Only carrying out operations during periods of inclement weather.
Following the requirements of the STS Operations Plan.
Selecting a suitable location for the transfer to take place.
A copy of the STS Operations Plan must be available in which of the following locations onboard?
Engine room.
Bridge.
Cargo transfer control station.
Galley.
Chain locker.
This is correct order? 1. Pre-arrival Planning; 2. Arrival; 3. Mooring; 4. Transfer of Cargo; 5. Departure.
Yes.
No.
The Master remains responsible, at all time, for the safety of which of the following?
Cargo.
Crew.
Ship.
Equipment.
Luggage.
When selecting an area for a transfer to take place, which of the following should be considered?
The availability of safe anchorage.
Traffic density.
Sea room.
Water depth.
Salinity.
Wi-fi access.
Which of the following are responsibilities of the Person in Overall Advisory Control (POAC)?
Carrying out regular safety checks before, during and after operations are complete.
Ensuring the STS Operations Plan (of both vessels) are followed.
Manually carrying out the transfer.
Ensuring that both crews have been briefed and understand their responsibilities during each phase of the operation.
Ensuring that an appropriate communication strategy is in place.
Training the crew on safe hose operation.
Which of the following details should be included within a ship’s STS Operations plan?
Procedures for reporting spills.
The names of all crew onboard.
An approved contingency plan.
A description of the berthing and unberthing procedures and arrangements.
A step-by-step instruction of the entire STS Operation.
Which of the following statements is true?
Vessels intending to carry out STS operations are not required to notify authorities before operations begin.
Vessels intending to carry out STS operations must notify authorities no less than 72 hours before operations begin (or as soon as reasonably practicable following an incident).
Vessels intending to carry out STS operations must notify authorities no less than 48 hours before operations begin (or as soon as reasonably practicable following an incident).
Which sequence is correct?
Pre-arrival Planning – Arrival – Mooring – Transfer of Cargo – Departure.
Pre-arrival Planning – Arrival – Transfer of Cargo – Mooring – Departure.
Departure – Pre-arrival Planning – Arrival – Transfer of Cargo – Mooring.
STS notices must include which of the following?
Whether the transfer will take place at anchor or underway.
The departure port of both vessels.
The name, flag, call sign, IMO Number and estimated time of arrival of all vessels involved.
Identification and contact details of the Chief Steward.
Planned duration of the operation.
The cargo type and quantity.
Ship to ship transfer is regulated by which of the following pieces of legislation?
The International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL).
The International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW).
The The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC).
To carry out safe STS transfer operations, personnel involved in the transfer must be fully trained and competent in all areas of the operation.
True.
False.
Ship to Ship (STS) transfer (or lightering) is the transfer of cargo between two vessels.
True.
False.
Use and Storage of Pressurised Cylinders
What is pressurised oxygen used for?
Medical emergencies.
Purge gas.
Leak testing.
Oxy-fuel cutting.
Why should oxygen cylinders be stored separately from propane cylinders?
To ensure the creation of an oxygen and flammable gas mixture.
To avoid the creation of an oxygen and flammable gas mixture and reduce the risk of explosion.
To ensure the creation of an oxygen deficient atmosphere.
The seamless cylinder allows ____ of gases and liquids at high pressure and provides a convenient way of ____ gases to the end user.
… storage … transporting.
… mixture … transporting.
Which of the following mitigation measures can be used to control the risks created by the use of pressurised cylinders?
Storing cylinders in direct sunlight.
Storing cylinders on their side.
Using the correct method of connection.
Using the correct pressure regulator.
What are the key hazards associated with the use of pressurised cylinders?
The cylinder rolling away.
The release of flammable gas.
The sudden release of stored energy.
The cylinder becoming hot when in use.
High pressure oxygen coming into contact with lubricants or grease.
Vapour Emission Control
Vapour emission control allows vapour from oil or chemical tankers to be returned to shore in a closed system.
True.
False.
All personnel with responsibility for carrying out VOC management should receive training in which of the following?
Why VOC emission control is required.
Why engine analysis is important.
The specific systems in place onboard for the control of emissions.
The principles of VOC emission control.
Atmospheric emissions from the international maritime industry contribute to global pollution which causes which of the following?
Damage to people’s health in coastal areas.
Improved maritime habitats.
Harm to the marine environment.
Damage to vegetation along the coast.
Which of the following is the most common arrangement for vapour emission control?
A shore-based vapour collection system and onboard vapour treatment facility.
An onboard vapour collection system and a shore-based vapour treatment facility.
An onboard vapour collection and treatment facility.
Atmospheric emissions are regulated by which of the following?
MARPOL Annex VI.
MARPOL Annex IV.
MARPOL Annex V.
Working at Height
!! Which of the following are examples of collective protection measures which prevent a fall?
Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs).
Rope access systems.
!!Nets.
!!Scaffolds.
When working with ladders, which of the following rules apply?
Use the 1 in 4 rule for positioning ladders.
Use the 1 in 3 rule for positioning ladders.
Always maintain two points of contact with the ladder.
Fasten the ladder at the top and bottom.
Always maintain three points of contact with the ladder.
Which of the following are specific hazards associated with working at height?
Dropped objects.
Oxygen enrichment.
Sim-Ops.
Oxygen deficiency.
1. Avoid; 2. Prevent; 3. Mitigate. This is the correct order of priority according to the Hierarchy of Control?
Yes.
No.
Which of the following conditions must be met before scaffolding can be used?
Scaffolding must be inspected by a competent person prior to use and must only be used by competent and trained personnel.
Scaffolding does not need to be inspected if being used by trained personnel.
Scaffolding decks to be appropriate to the nature of the work to be performed and suitable for the loads to be carried.
Scaffolding decks to be of sufficient dimensions to permit the safe passage of personnel and the safe use of any plant or materials required.
Hazard warning signs to be displayed, and restrictions in place, when scaffolding is not in use, to prevent unauthorised access to the danger zone.
Work at height should be properly planned and organised appropriately supervised and carried out by trained and competent personnel.
True.
False.
Which of the following factors should be considered when selecting equipment for work at height?
Location of muster stations.
Duration and frequency of the task.
Evacuation and rescue measures.
COSHH Assessment.
Work at height not only encompasses work that takes place on a ladder, scaffold or platform, it may also include which of the following?
Working in, entering or exiting a deep tank.
Working in the ship’s galley.
Working alongside an open hatch or other opening in a ship’s structure.
Working in close proximity to, or supported from, a ship’s side.
How often should working at height equipment be inspected?
Monthly.
Following modifications.
Weekly.
After use.
Before use.
Working at height involves carrying out a task from any place above 2 metres in height from which a person could be injured falling from it.
True.
False.
Working with High Voltage
What are the three phases of risk evaluation?
Preliminary phase, planning phase and execution phase.
Precautionary phase, executive phase and evacuation phase.
Can the “Dead working” method be applied if there is a danger of coming into contact with live parts?
Yes, but only if the live parts can be de-energised and protected against accidental re-energising or shrouded.
No, in such cases we must always choose an alternative working method.
Live working presents little risk if undertaken by a person with the correct competence.
False.
True.
The Regulations require that everyone working on, or in the vicinity of, electrical installations, undertakes safety training.
True.
False.
Who is responsible for removing safety measures on high voltage installations?
The crew member who carried out the work.
The Chief Engineer.
The The Master.
What is the purpose of a single-line diagram?
To provide necessary information about the installation’s lay-out.
To provide an overview of the installation’s fuse layout.
To provide description of the work that is to be performed.
What must you do if there is anything that you are unsure about before starting the work?
Obtain clarification.
Choose a different working method.
Proceed anyway, but exercise extra caution.
A barrier can reduce the probability of an undesirable event occurring or its consequences.
True.
False.
Which of the following items is considered personal protective equipment?
Insulated gloves.
Insulated tools.
Insulated floor-mats.
When working on electrical installations, it is important that hearing protection has a metal head-band.
False.
True.
Which of the following is the correct definition of the term “high voltage”?
Voltage which normally exceeds 1 000 V alternating current (AC) or 1 500 V direct current (DC).
Voltage which normally exceeds 500 V alternating current (AC) or 1 000 V direct current (DC).
Voltage which normally exceeds 100 V alternating current (AC) or 150 V direct current (DC).
What is the purpose of the Regulations?
To maintain a high level of safety during operation and work on, or in the vicinity of, electrical installations by requiring that all activities are adequately planned and the necessary safety precautions are put in place.
To prescribe the work activities that may be carried out on or in the vicinity of electrical installations.
To ensure that ship owners are held accountable for any accidents or incidents that occur onboard their vessels.
The definition below describes which of the following terms? “Equipment that gives protection against direct contact from any usual approach or access point”.
Shrouding.
Safety switching.
Earthing.
Is work on “partly de-energised” installations within the framework of the Regulations?
Yes.
No.
Which of the following statements about portable earthing devices is true?
The earth connection must be established before it is connected to the installation.
You must connect the device to the installation that is to be earthed before establishing the connection to earth.
Which of the following safety barriers are required for “live working”?
l) Installation protection; ll) Protection against accidental re-energising.
l) Distances; ll) Personal protective equipment.
l) Personal protective equipment; ll) Installation protection.
Why is it so dangerous for an electronic current to pass from hand to hand or hand to foot?
Because much of the current will pass through the heart.
Because much of the current will pass through the brain.
Because much of the current will pass through the liver.
What is the first thing you should do if you find a person trapped in a live installation?
Call 113.
Turn off the main switch and separate the person from the live circuit using an object that does not conduct electricity.
Check their breathing and look for burns.
What do the different categories of insulated gloves determine?
The voltages they may be used with.
Which external influences (such as acid or low temperature for example) they may be used.
How durable the gloves are.
In which of the following circumstances does the two-person requirement apply?
When working on or in the vicinity of high voltage installations.
When working on or in the vicinity of low voltage installations with a high degree of risk.
When working on or in the vicinity of low voltage installations with a low degree of risk.
Live working is more dangerous than dead working.
True.
False.
Voltage testing must be performed in such a manner that it never entails danger to the life or health of the person performing the check.
True.
False.
What is temporary earthing for work?
Earthing and short-circuiting of installation parts with a less than fully dimensioned earthing device on or in close proximity to the work location.
Fully dimensioned earthing and short-circuiting of all isolation points from which an installation may be energised.
Fully dimensioned earthing and short-circuiting of installation parts where work is being conducted.
Which of the following working methods requires control measurements be taken to ensure that the installation is de-energised?
Dead working.
Live working.
Working in the vicinity of live parts.
Do crew members require training in the use of live working equipment to perform live work on low voltage installations?
Yes.
No.
Which of the following safety barriers are required when working in the vicinity of live parts on a high-voltage installation?
l) Distances; ll) Personal protective equipment.
l) Safe distances; ll) Installation protection.
l) Personal protective equipment; ll) Installation protection.
What is the first thing you must do when removing safety measures?
Notify the work team that the job has been completed and no further work is allowed.
Leave the work location.
Remove obstacles to re-energising.
Who is responsible for reporting accidents involving personal injury caused by electricity?
The Master or the Shipowner.
The injured person.
The Safety Supervisor.
Are risk evaluations and the choice of working method integral parts of planning a job?
Yes.
No.
Which of the following statements about earthing sticks is true?
An earthing stick is an insulated rod that can be used to attach phase clamps to the part of the installation that is to be earthed and short-circuited.
An earthing stick can be used within the live working zone and can come into direct contact with live parts.
An earthing stick can be used as a hot stick.
Which of the following statements about insulated tools is true?
Hand-insulated tools only have protection on the handle/grip while the ‘business-end’ is not insulated.
Operationally insulated tools only have protection on the handle/grip while the “business-end” is insulated.
During maintenance, is deviation from the two-barrier requirement ever allowed?
No, never.
Yes, but only if the requirement cannot be fulfilled in practice and there is a procedure that helps ensure personal safety.
Yes, as long as four crew members are working on the job.
Installations which are not protected from direct contact must be locked and the keys only made available to which of the following?
Access-permit holders.
The vessel owner.
All crew.
Before using an electrically insulated helmet, you should always examine it for damage.
True.
False.
Who usually performs the risk evaluation before work in a high voltage installation?
The Chief Engineer.
The Master.
The Officer of the Watch.
Which of the following safety barriers are required when using the “dead working” method?
I) De-energising and voltage testing; ll) Protection against accidental re-energising.
I) De-energising and voltage testing; ll) Personal protective equipment.
I) Protection against de-energising; ll) Installation protection.
What does the class of an electrically insulated helmet determine?
The test voltage that the helmet tolerates and the nominal voltage at which it can be used.
It’s size.
I) When it must be replaced.
The degree to which tools must be insulated and the necessary extent of the use of protective shielding must be evaluated in combination with the personal protective equipment used for each job.
True.
False.
When disconnecting an electrical installation using isolation switches – why must the switches have visible isolation points or a reliable indicator.
So that it is simple to carry out a reliable check of the disconnection.
So that the switches can be easily turned back.
What is the purpose of security cards for high voltage installations?
To document who has access to high voltage installations.
To document who has performed work high voltage installations.
To document who has visited the vessel.
Cyber Security
What has been done by many countries and international organizations to combat cyber-crime?
They have implemented individual data rights and created laws that enable data protection standards. In addition they have created and sponsored best practice standards.
They have denied access to certain web-pages.
Is the following statement true or false? Turn off Bluetooth when you don’t intend to use it. It is a potential gateway for cyber-criminals to get access to your smartphone.
True.
False.
Which of the following statements indicates a way of lowering the risk of catching an e-mail virus?
Knowing who sent you an e-mail and why can help you reduce the risk of catching a virus.
You must first download an attachment from your e-mail to be infected by malware.
My antivirus software catches all e-mail viruses.
Which of the following is a common way for cyber-criminals to make a personal approach?
Spear Phishing.
By sending spam e-mails.
Via a Secure WiFi.
What is generally safer to use?
Your smartphone as a mobile hotspot.
Public WiFi.
Which of the following is an easy way to enhance your cyber-security?
By changing your attitude from “It won’t happen to me” to “I’m a potential target”.
By only updating the software programs you use most commonly.
By using the same password on all your accounts.
When I post personal information on social media, it does not compromise my cyber-security.
False.
True.
Your company depends on you to be the first line of defence and your online habits are important.
True.
False.
Don’t open an attachment unless you know who it is from and you are expecting the file.
True.
False.
Is the following statement true or false? Always use a strong password and never share it.
True.
False.
Is the following statement true or false? I have never had a problem downloading free music and movies. So it is basically safe.
False.
True.
Is the following statement true or false? Your smartphone can get viruses just like a computer.
True.
False.
Will a reputable business ask for your personal information or credit card details via e-mail?
No.
Yes.
Only if it’s an urgent matter.
COLREGS General
You are underway in an area of reduced visibility and hear a sound signal. It is likely coming from the starboard bow; however you cannot locate the other vessel either visually or with the radar. Which of the following actions should you take?
As the sound signal appeared to come from forward of your vessel’s beam, you should reduce speed to the minimum and navigate with extreme caution.
As the sound signal appeared to come from starboard side, you should alter your course to starboard and carefully pass astern of the other vessel.
As the sound signal appeared to come from forward of your vessel’s beam, you should alter your course to port side and observe the situation.
You should immediately clarify the situation with a radio call, since you cannot detect the other vessel.
You have visually detected a vessel displaying the lights below. What is the status of this vessel?

Not under command.
Not making way through the water.
Making way through the water.
Constrained by their draught.
Restricted in their ability to manoeuvre.
Take a look at the scenario being shown on screen now. Which of the vessels should take action to avoid a collision and what should that action be?

The vessel(s) should alter their course to starboard side until a safe passing distance is predicted.
Both vessels should take action.
The vessel(s) should alter their course to port side until a safe passing distance is predicted.
The vessel(s) should reduce their speed until a safe passing distance is predicted.
Only vessel A should take action.
Only vessel B should take action.
You have visually detected a vessel displaying the day shapes below. What is this status of this vessel?

Vessel towing another vessel, length of the tow is over 200 m.
Vessel towing another vessel, length of the tow is less than 200 m.
You have visually detected a vessel displaying the lights below. What is the size and status of this vessel?

Vessel under 50 m in length towing, total length of the tow is under 200 m.
Vessel over 50 m in length towing, total length of the tow is under 200 m.
Vessel over 50 m in length towing, total length of the tow is over 200 m.
Vessel under 50 m in length towing, total length of the tow is over 200 m.
The International Maritime Organization implemented traffic separation schemes (TSS) to ensure safe navigation in such areas. Which of the following statements are true when navigating near a TSS?
When entering or leaving a lane, vessels should keep a small angle to the direction of traffic.
If a TSS lane is inconvenient vessels can navigate in opposite directions next to it.
Crossing TSS is not permitted, vessels should navigate around them.
Vessels are only permitted to join a TSS at the beginning or end of the lane and not in between.
When entering or leaving a lane, vessels should indicate this with a large angle to the direction of traffic.
Whenever possible, ships should join or leave the TSS at the beginning or end of the lane with particular caution.
Any vessel that is not using or crossing the scheme should keep a wide distance to it.
Please complete the following sentences: “Generally, the COLREGS apply to ____ upon the high seas and in ____. In territorial waters, ____ national regulations may apply.”
… all vessels … all connected waters … additional.
… commercial vessels … all connected waters … additional.
… all vessels … international waters only … additional.
The COLREGS require actions taken to avoid collision to be clearly visible to other vessels. What does this mean for collision avoidance manoeuvres?
One large manoeuvre should be carried out so that the affect is clearly visible to the other vessel.
Several small manoeuvres should be carried out, to ensure that the other vessel is watching during the manoeuvres.
No manoeuvres are necessary if the other vessel is detected with radar only.
Which of the following statements regarding the “stand-on” vessel is true?
If early actions have failed and the vessels are close to each other, the stand-on vessel is urged to carry out whatever manoeuvre is necessary to avoid a collision.
It may be necessary for the stand-on vessel to alter their course or speed if it becomes clear that the give-way vessel is not taking appropriate action to avoid a collision.
IF a stand-on vessel needs to act during a crossing situation, it should avoid course alterations to the port side so as not to counter any action that the give-way vessel might still take.
If a stand-on vessel needs to act during a crossing situation, it should avoid course alterations to the starboard side so as not to counter any action that the give-way vessel might still take.
Rule 17 requires stand-on vessels to maintain their course and speed under any circumstance.
While navigating in restricted visibility, you hear one long blast, given as a sound signal from another vessel. What does this indicate?
The vessel is power-driven and making way through the water.
The vessel is unsure about the intentions of another approaching vessel.
The vessel will alter its course to port.
The vessel is approaching a bend or obscured area.
The vessel will alter its course to starboard.
While navigating in good visibility, you hear one long blast given as a sound signal from another vessel. What does this indicate?
The vessel is approaching a bend or obscured area.
The vessel will alter its course to starboard.
The vessel is operating with astern propulsion.
The vessel will alter its course to port.
The vessel is unsure about the intentions of another approaching vessel.
You have visually detected a vessel displaying the lights shown below. What type of vessel is it?

Non-trawling fishing vessel.
Vessel restricted in their ability to manoeuvre.
Air-cushion vessel.
Pilot vessel.
Trawling fishing vessel.
Sailing vessel.
You have visually detected a vessel displaying the lights shown below. What is the vessel’s type and status?

A vessel engaged in mine clearance operations making way through the water.
A fishing vessel not making way through the water.
A vessel engaged in underwater operations that is restricted in its ability to manoeuvre.
A vessel under tow.
You have visually detected a vessel displaying the day shapes below. What is this status of this vessel?

Aground.
Not under command.
Constrained by their draught.
At anchor.
Restricted in their ability to manoeuvre.
You are underway in an area of reduced visibility and hear a sound signal. It is likely coming from the starboard bow; however you cannot locate the other vessel either visually or with the radar. Which of the following actions should you take?
As the sound signal appeared to come from forward of your vessel’s beam, you should alter your course to port side and observe the situation.
You should immediately clarify the situation with a radio call, since you cannot detect the other vessel.
As the sound signal appeared to come from starboard side, you should alter your course to starboard and carefully pass astern of the other vessel.
As the sound signal appeared to come from forward of your vessel’s beam, you should reduce speed to the minimum and navigate with extreme caution.
Take a look at the scenario being shown on screen now. Which of the vessels should take action to avoid a collision and what should that action be?
Only vessel A should take action.
Both vessels should take action.
It is good practice for the vessel(s) to alter their course to starboard side.
It is good practice for the vessel(s) to alter their course to port side.
Only vessel B should take action.
It is good practice for the vessel(s) to alter their course to starboard side.
Specific rules apply to vessels inside narrow channels. All vessels travelling along a narrow channel should:
Stay as much to their starboard side as safely possible.
Sound one prolonged blast to alert others of their presence.
Also sound one prolonged blast as an answer.
Avoid anchoring.
Specific rules apply to vessels inside narrow channels. Ships that approach bends of the channel, or visually obstructed areas, should:
Stay as much to their starboard side as safely possible.
Sound one prolonged blast to alert others of their presence.
Also sound one prolonged blast as an answer.
Avoid anchoring.
Specific rules apply to vessels inside narrow channels. Any approaching vessel that hears this signal should:
Stay as much to their starboard side as safely possible.
Sound one prolonged blast to alert others of their presence.
Also sound one prolonged blast as an answer.
Avoid anchoring.
Specific rules apply to vessels inside narrow channels. Any vessel inside a narrow channel should:
Stay as much to their starboard side as safely possible.
Sound one prolonged blast to alert others of their presence.
Also sound one prolonged blast as an answer.
Avoid anchoring.
You have visually detected a vessel displaying the lights shown below. What type of vessel is it?

Air-cushion vessel.
Vessel restricted in their ability to manoeuvre.
Pilot vessel.
Sailing vessel.
Non-trawling fishing vessel.
Besides actions to avoid collisions, the COLREGS may also require vessels to take action so as not to impede the safe passage of other ships, for example, when the other vessel is restricted by their draught. In these circumstances, which of the following statements are true?
Actions to not impede the safe passage of other ships do not relieve the other vessel from their obligation to take action to avoid a collision.
Actions to not impede the safe passage of other ships should be taken early to allow sufficient sea-room for the other ship.
Actions to not impede the safe passage of other ships mean that the other vessel does not need to take action to avoid a collision.
Actions to not impede the safe passage of other ships are only required for non-commercial ships, such as sailing boats.
You have visually detected a vessel displaying the lights shown below. What is the vessel’s type and status?

An obstruction exists on the vessel’s port side (if seen from ahead).
The vessel is engaged in underwater operations and restricted in its ability to manoeuvre.
The vessel is not making way through the water.
The vessel is towing.
The vessel is engaged in mine clearance operations.
Which of the following statements are true in relation to the visibility of navigational lights?
The visibility of mast headlights is greater than that of other lights.
Longer vessels are generally required to have a higher range of visibility for their navigational lights.
The visibility of sternlights is greater than that of other lights.
All lights have the same visibility range.
Piracy and Armed Robbery
Which of the following are contributing causes of piracy and armed robbery?
Political and social instability.
Long-distance migration.
Economic disparity.
Passive (non-lethal) defensive preparation can include razor wire.
True.
False.
What ship’s document has the complete guidance for piracy and armed robbery?
Ship Security Plan.
International Safety Manual.
Charterer Instructions.
Ships passage planning guidance.
Those that are held hostage need to concentrate on survival. Which of the following principles should be followed?
Encourage the crew to work together.
Stay neutral.
Resist the captors to show them that you are in charge.
Where are the four areas considered piracy and armed robbery “hotspots”?
Gulf of Aden.
Gulf of Guinea.
Straits of Malacca.
Anchorages in Venezuela.
Baltic Sea.
Which of the following principles serve as guidelines to seafarers to survive a kidnapping?
Retain dignity.
Be patient.
Take photographs.
Be confrontational.
When attackers are threatening the ship, what should the Ship Master do?
Activate the ship security alert system (SSAS).
Slow down speed.
Initiate the ship’s pre-prepared piracy attack procedures.
Stop all radio activity.
Water cannons may be useful for passive (non-lethal) defence.
True.
False.
If attackers take control of the ship, violence or the threat of violence is often used to subdue the crew. Is the chance of injury or harm reduced if the crew are compliant and cooperative?
Yes.
No.
If you are held hostage, a good principle is to hide your hands from the attackers.
True.
False.
Drug and Alcohol Awareness and Policy
What is the medical definition of a drug?
A substance intended for use in the treatment, cure, mitigation or prevention of disease.
A controlled substance that have long term health benefits.
An illegal substance that have long term psychological effects.
A Drug and Alcohol Policy is determined by:
The company.
The local coast guard.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO).
Addiction is considered an illness.
True.
False.
Who can perform a drug test?
Drug testing agency engaged by the company.
Law enforcement.
Anyone as long as they follow the drug testing instructions.
Drug and Alcohol testing trained company safety delegate.
Safety delegate.
The laws and regulations you have to adhere to can depend on:
The country you working in.
Only your home county’s regulations.
The country you are transitioning through.
Only your company’s regulations.
Prescription drugs can alter your mental abilities.
True.
False.
You do not need to keep the doctor issued drug prescription with you at work and during travel if you are taking long term medication prescribed by a doctor.
True.
False.
A comprehensive company safety management plan includes:
A drug testing kit in all living quarters.
A written drug and alcohol policy.
A drug and alcohol employee statement.
What should you do if you suspect someone is under the influence of drugs or alcohol?
Confront them.
Nothing, it shouldn’t concern you.
Report it.
When can a company perform a drug test?
Pre-employment drug tests.
After an accident.
Random unannounced tests, but always on a group of people.
When you are at home on leave.
Can “over the counter” non-prescription drugs have similar psychological effects as doctor prescribed drugs?
Yes, because they can have the same or similar ingredients and effects.
No, because drugs are only prescribed by doctors.
No, because “over the counter” medicine are not drugs.
Which of these do you think should be included in a drug and alcohol policy?
Training programmes for key personnel.
Problem identification and intervention.
Employee health and well-being education.
Work environment improvements.
Profiling employees on nationality or appearance.
What is addiction?
Addiction is the continuation of an activity that leads it to become a compulsive behaviour that interferes with ordinary responsibilities such as work, relationships and personal health and hygiene.
Addiction is always a criminal act and should be punished.
Addiction is constantly craving something illegal.
A company’s Drug and Alcohol policy is to help employees by:
Clarifying the company’s policy for drugs and alcohol.
Placing blame for drug abuse.
Avoiding legal responsibility for employee drug abuse.
Can the company perform a drug test upon suspicion?
Yes, a company can perform a random drug test, but a group of employees have to be tested, not singling out one person.
Yes, a company can perform a random drug test on one person.
No, a company cannot perform a random drug test based on suspicion alone.
Safe use of Maritime Cranes Training
What should be discussed during the Pre-Lift Safety Meeting?
The roles and responsibilities of the Lift Team.
The results of the risk assessment.
Where barriers and signs should be placed to ensure that the lift area remains free from unauthorised entry.
The isolation confirmation certificate.
Break times.
What happens if the load to be lifted is heavier than the Safe Working Load of the crane?
A warning light and alarm will sound in the Crane Operator’s cab.
The Crane Operator shall consult the Banksman before carrying on with the lift.
The Crane Operator must override any alarms and carry on with the lift.
Crane hooks should be inspected for which of the following?
Nicks and gouges.
Deformation.
Wear and corrosion.
The date of manufacture.
The maker’s mark.
What types of cargo do bulk carriers normally ship?
Steel Coils.
Cement.
Crude oil.
Ore.
Coal.
Grains.
The hand signal internationally recognised for an emergency stop is both arms raised with palms facing forward.
True.
False.
Remedial ____ are then put in place to reduce the risk of a hazard occurring to as ____ as reasonably practicable (ALARP).
… actions … low.
… actions … large.
… equipment … high.
All lifting equipment, including cranes, must be certified and clearly show the Safe Working Load (SWL).
True.
False.
Which of the following must be carried out before every lift?
A risk assessment.
A COSHH assessment.
Atmospheric testing.
How often should a visual inspection of the crane be carried out?
Every day and before use.
Annually and after every third use.
Once every three months and after every use.
Once hazards have been identified, what is the next step in the risk assessment process?
Assessing the likelihood of the hazards occurring.
Gas testing.
Implementing controls that increase the risks to an unacceptable level.
If a derrick crane winch is powered by electricity, what happens if the power supply is lost?
The winch will automatically apply a brake to stop the lift and maintain the load in a safe position.
The Crane Operator shall lower the load to the deck.
The Crane Operator shall slew the crane 90 degrees.
Before the lifting operations begin, the Captain should visit the worksite to identify if there are any additional hazards that were not identified during the risk assessment.
True.
False.
What is the ideal included angle between chains when lifting a load using twin chains attached to a master link?
90 degrees.
45 degrees.
180 degrees.
A typical ____ crane is of the overhead ____ type. Engine room gantry run on ____ allowing the crane to run from the ____ to the aft of the engine room.
… gantry … bridge … rails … fore.
… bridge … gantry … rails … fore.
… engine room … girders … rails … fore.
Life Rafts
What spurred on the initial development of international rules governing the safety of life at sea?
The 1912 Titanic disaster.
The 1988 Sydney to Hobart race tragedy.
Which of the following are the benefits of the Marine Evacuation System (MES)?
An MES can save up to 700 people in 30 minutes.
An MES requires little time and effort to assemble.
An MES can be deployed in 90 seconds by only two members of the crew.
An MES takes up very little deck space – positioned on the front of the embarkation deck and on the sides of the ship.
An MES can provide shelter at sea for a long period of time before help arrives.
Which of the following actions are advised to seafarers to better prepare them for an emergency?
Find out what type of life raft is on board the ship and be familiarised with the launching instructions.
Take full advantage of the training.
Perform your own emergency drill with the life rafts on board.
If the Stenhouse slip hook was attached to the deck, the raft would never be able to deploy on its own.
True.
False.
Which of the following statements are true?
The EPIRB signal is detected by satellites operated by an international rescue service.
The SART is used to locate distressed life rafts or vessels by creating a series of dots on a rescuing ship’s radar display.
The EPIRB is used to locate distressed life rafts or vessels by creating a series of dots on a rescuing ship’s radar display.
The SART signal is detected by satellites operated by an international rescue service.
Why does a coastal life raft have reduced capability compared to offshore life rafts?
Because the coastal life raft concept is based on the assumption that occupants will spend a short period of time here as help is minutes away.
Because the coastal life raft concept is based on the assumption that occupants will spend a long time within the raft until help arrives.
Which of the following is an offshore life raft equipped with?
Advanced survival gear in the equipment pack.
A large self-erecting canopy.
A single large buoyancy tube or two stacked tubes.
An insulated floor to keep the occupants warm.
A solar phone charger.
Where on a ship should life rafts be stowed?
Life rafts should be located at the forward of the ship and at embarkation stations on both port and starboard sides.
Life rafts should be located below deck.
If there is no lifeboat available, the best chance for survival is to swim to shore.
False.
True.
During visual checks of davits what should be considered?
Moving parts should move freely and be well lubricated.
Wire, falls, blocks and securing arrangements should be well-greased at all times.
Equipment should be free from corrosion.
Moving parts should move slowly and be free of grease.
Life Rafts
A concerning situation is when person is reported missing and has not been seen for many hours or longer. It is imperative to establish when the person was last seen and to confirm if they have fallen overboard so that emergency action and recovery can be attempted.
True.
False.
What are the three types of turns that can be performed?
Sharnow Turn.
Anderson or Single Turn.
Williamson Turn.
Coordinated Vessel-aircraft Search Pattern.
What does the code flag OSCAR mean?
Man overboard.
Shark.
Release lifeboats.
In which of the following situations might it be harder to spot someone in the water?
Inclement weather.
Reduced visibility.
On a clear day.
As per the International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW), no matter what rank or position, all crew members must complete which of the following basic training?
First aid.
Proficiency in Survival Craft and Rescue Boats (PSCRB).
Personal Survival Techniques (PST).
Firefighting.
Proficiency in Fast Rescue Boats (PFRB).
Which of the following are dangers for those who have fallen into the water?
Marine wildlife such as sharks or jellyfish.
Soaked clothes becoming heavy and making it harder to stay afloat.
Effects of cold water such as hypothermia.
Debris or rocks which can cause harm to the body.
Electrocution.
Which of the following are reasons a person can fall overboard?
Vulnerable persons or people who suffer from mental health disorders may involuntarily or voluntarily become too close to the edge.
During a recreational activity, such as boating, sailing and water sports.
During an operational activity, such as fishing, working over the side or pilot transfers.
If PPE has been misused or not used at all.
When resting in the cabin.
The training for competence in Personal Survival Techniques (PST) is mandatory for all personnel prior to employment on a ship as per the STCW.
True.
False.
How should the rescue boat approach a casualty for recovery?
Take extra care in heavy weather.
Ensure that the boat is not swept onto the casualty by the wind or waves.
Approach at a safe speed.
Approach the casualty quickly.
Once on board, it is imperative that the ____ is given the necessary medical attention available and that they are transported to the nearest ____ or rendezvous point. There is always a risk in moving a casualty, especially on a ship at sea with inclement weather, therefore, it should only be done if a threat is imminent. The decision will be made by the onboard ____ as necessary.
… casualty … port … medical officer or doctor.
… casualty … port … captain.
… casualty … ship … captain.
… crew … casualty … medical officer or doctor.
Respiratory Protection
A key component of any RPE is the filter. Which of the following are types of filters?
Gas and / or vapour filter.
Particle filter.
Solid filter.
Steam filter.
Which of the following statements apply to breathing apparatus?
They supply air from an independent source such as a compressed air cylinder.
They can be used against a range of airborne hazards and in different atmospheres.
They rely on the user’s breathing to draw air through a filter.
They can only be used with loose-fitting face-pieces.
Respiratory Protective Equipment (RPE) is a particular type of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) designed to protect the wearer from breathing in harmful substances or from oxygen-deficient atmospheres when other controls are either not possible or are insufficient on their own.
True.
False.
Which of the following indicates that Respiratory Protective Equipment meets the minimum legal requirements for its design?
CE marking.
PPE marking.
FTP marking.
RP marking.
Which of the following types of respirator relies on the user’s breathing to draw air through the filter?
Non-powered respirator.
Fresh air hose breathing apparatus.
Constant flow airline breathing apparatus.
Powered respirator.
Rescue and Fast Rescue Boat – Launch and Operations
What is the maximum length of a rescue boat?
8,5 metres.
3,8 metres.
5,5 metres.
During an emergency, the need to recover or assist a casualty efficiently is important, however, the ____ of the ship’s crew is equally vital, especially during launch and ____. Therefore, regular drills are performed to increase the ____ of the rescue boat crew.
… safety … recovery … competency.
… recovery … safety … competency.
… competency … safety … recovery.
What are secondary means of communication during a rescue?
Buoyant smoke.
Flares.
Verbal.
Why might a rescue boat be launched?
To pick up survivors from an abandonment and transfer them to a suitable survival craft.
To aid the search, rescue and recovery of a casualty falling overboard from a ship or an aircraft.
To transfer a sick person from ship to ship for use of better medical facilities.
To move crew from ship to ship.
As per SOLAS, how often should a rescue boat be launched and manoeuvred in the water?
Every three months.
Every day.
Every week.
Every month.
During inclement weather, why might there be a higher risk when reconnecting a rescue boat to the ship?
Because the fall blocks are swinging around at the head height of the crew.
Because the movement of the ship and boat can affect the ability of the crew to recover the rescue boat.
Because the release mechanism may not release.
Who is in overall command of a rescue operation?
The Master.
The Chief Engineer.
The Deck Officer.
The helmsman.
What type of training must to be completed to work on a fast rescue boat?
STCW Proficiency in Fast Rescue Boats.
STCW Proficiency in Survival Craft and Rescue Boats.
Maritime and Coastguard Agency Training.
A rescue boat can never be a boat that is already on board the ship.
False.
True.
Which of the following pieces of Life-Saving Appliances should be checked annually?
Davits.
Release mechanisms.
Clutches.
Strops.
Which type of Life-Saving Appliances are kept on board the rescue boats?
Thermal protective aids for any casualties.
Portable fire-extinguishing equipment.
First aid kits.
Buoyant lines.
A stretcher for moving casualties.
CO2 Firefighting Systems
How often should the CO2 firefighting system be inspected?
Monthly.
Weekly.
Daily.
Which of the following spaces are typically covered by a fixed carbon dioxide system?
Cargo holds.
Engine rooms.
Pump rooms.
The bridge.
Accommodation spaces.
Carbon dioxide levels higher than 17 % can result in which of the following?
Loss of bodily control, unconsciousness, convulsions, coma and death.
Nausea, nosebleeds and tingling in extremities.
Increased heart rate, headache, perspiration and rapid, shallow breathing.
Which of the following will occur when the system’s control cabinet is opened?
The fire flaps will close.
The space’s ventilation will be deactivated.
The carbon dioxide alarm will activate.
Ventilation within the space will be activated.
The fire flaps will open.
Before re-entry, how long must a carbon dioxide filled space be left for (as a minimum)?
24 hours.
30 minutes.
1 hour.
12 hours.
Anchoring – Operational Safety
At what length of chain is each joining shackle located?
27,5 metre.
20,5 metre.
30,5 metre.
Why is running both anchors in operations avoided?
In case one tangles with a nearby vessel.
To avoid the chains getting twisted together.
To ensure one is available for backup.
What should the watchkeeper ensure as a minimum?
That environmental conditions are observed.
That measures are in place to protect the environment from pollution by the ship.
There is an accurate perception of the ship’s position.
Where all personnel are located.
What steps should be taken when anchoring in inclement weather?
The correct PPE and clothing should be worn to protect all personnel from the elements as best possible.
Ensure, at the Toolbox Talk stage, that everyone is aware of the weather and the unexpected movements that the ship can take.
Keep a lookout for ships and hazards and report immediately if a sound signal is heard.
Ensure that the anchor is not lowered whilst it’s raining.
Who has overall command and will guide the bridge and engine room team?
The Master.
The Bosun.
Certified Deck Officer.
Why are there two anchors on the standard seagoing ship?
To help moor the ship in a more secure position.
To provide a backup to the main anchor.
To even out the weight.
Which of the following are safety critical items?
Emergency generators and steering gear.
Life saving appliances.
Bunkering davit.
Firefighting equipment.
Which of the following Personal Protective Equipment should be worn at all times as a minimum?
Eye protection or safety spectacles.
Steel toecap boots or shoes.
Safety goggles.
A hard hat a chinstrap.
A boilersuit.
The Master often acts as the watchkeeper.
True.
False.
Which of the following are typical items that would be listed in a Toolbox Talk?
What is on the menu for dinner.
Which communications channel will be used.
Who has overall command of the operation.
The required PPE to be worn by personnel.
The reason for going to anchor and the expected duration.
The International Safety Management Code is mandatory for all commercial ships over 500 gross tonnes.
True.
False.
New personnel should only operate the equipment under strict supervision from a competent person.
True.
False.
For what reason might an anchor be used?
A long-term layup due to a downturn in the industry.
Waiting for the berth to become clear.
Anchoring in a sheltered area to fix a problem onboard.
Anchoring off port limits.
To see how deep the water is.
Best Navigational Practices
Which of the following statements regarding the Cross Track Distance (XTD) Corridor are true?
The XTD should be as large as safely possible to have as much safe water for manoeuvering as possible.
The XTD corridor should be free of any dangers.
The XTD should be the same for the whole route.
The XTD should be set up individually for each leg.
Which of the following statements regarding global navigational satellite systems (GNSS), such as GPS, is true?
GNSS should be cross checked with other positioning methods often enough to avoid an incident.
GNSS are reliable and precise enough to fully replace other positioning methods.
GNSS are so unreliable that they should not be used on board at all.
Match the alert icon with correct description.

Alarm are high priority alerts that require immediate attention and action.
Warnings advise about conditions that can present a danger if left unchecked and require immediate attention, but not necessarily immediate action.
Cautions are the lowest priority alert to inform about a situation without distracting from other duties.
Match the alert icon with correct description.

Alarm are high priority alerts that require immediate attention and action.
Warnings advise about conditions that can present a danger if left unchecked and require immediate attention, but not necessarily immediate action.
Cautions are the lowest priority alert to inform about a situation without distracting from other duties.
Match the alert icon with correct description.

Alarm are high priority alerts that require immediate attention and action.
Warnings advise about conditions that can present a danger if left unchecked and require immediate attention, but not necessarily immediate action.
Cautions are the lowest priority alert to inform about a situation without distracting from other duties.
Which of the following statements regarding contingency planning are true?
Emergency ports or sheltered emergency anchorages should be identified.
Contingency planning is optional and can be done on the spot, when the exact circumstances are known.
It is best practice to include a thorough contingency plan during voyage planning.
Only emergency ports should be listed in contingency planning.
Before executing any collision avoidance manoeuvres, which of the following should be considered?
The available safe water.
If grounding is a viable alternative.
How quickly the vessel can exit the route corridor.
Which of the following statements regarding teamwork on the bridge are true?
Routine situations can help build experience and coordination to improve teamwork.
All team members should be willing to work openly and co-operatively with each other.
The clear command structure makes teamwork unnecessary.
Teamwork can be easily achieved without practice.
Alarm fatigue occurs as a result of an overabundance of alerts, especially audible alarms, on the bridge.
True.
False.
After the route is planned, it needs to be carefully checked for which of the following?
Any prohibited or special areas.
Any objects or obstructions.
Any other vessels.
Using ECDIS to check the chart area in from of the vessel for safe water provides which of the following advantages?
The graphical display of the ship’s position is in real time.
It is able to detect dangers in a defined area ahead of the vessel based on the defined safety contour.
The automatic application of safety values based on the vessel’s draught.
The inclusion of echo sounder.
The IMO resolution “Guidelines for Voyage Planning” divides voyage planning into which of the following phases?
Monitoring.
Appraisal.
Planning.
Routing.
Execution.
The Under Keel Clearance Policy:
Is a value declaring how much water is needed underneath the vessel’s keel at any given time.
Is caused by the speed of the vessel and results in a lower water depth under the ship, compared to a stationary object of the same draught.
Describes how thorough the hydrographic measurements were and how precise the values in the charts are.
Chart accuracy:
Is a value declaring how much water is needed underneath the vessel’s keel at any given time.
Is caused by the speed of the vessel and results in a lower water depth under the ship, compared to a stationary object of the same draught.
Describes how thorough the hydrographic measurements were and how precise the values in the charts are.
The hydrodynamic squat effect:
Is a value declaring how much water is needed underneath the vessel’s keel at any given time.
Is caused by the speed of the vessel and results in a lower water depth under the ship, compared to a stationary object of the same draught.
Describes how thorough the hydrographic measurements were and how precise the values in the charts are.
Which of the following factors can influence safety calculations?
Draught increase by rolling or pitching.
Static draught.
Chart accuracy.
Squat effect.
Load lines.
Which of the following systems ensures that should the Officer of the Watch become incapacitated, the vessel does not remain without command?
The Officer of the Watch Alert System (OOWAS).
The Bridge Navigational Watch Alarm System (BNWAS).
The Bridge Resource Management System (BRMS).
Before any voyage begins, it is essential that the vessel is adequately ____. Extraordinary circumstances may leave a vessel with insufficient, inexperienced or ____ personnel. In such circumstances, it is the responsible of the ____ to find an adequate solution, together with the owner or charterer.
… manned … exhausted … Master.
… manned … respective … crew.
… painted … respective … Master.
Besides the requirements for visible actions made in good time, the COLREGS also requires the observance of good seamanship. Which of the following are examples of good seamanship?
Granting safe passage where required, for example when a vessel is restricted by its draught.
Making small manoeuvres and passing starboard of another vessel when changing course.
Passing aft of another vessel when changing course or speed in a crossing situation.
Which of the following members of the Bridge Team has the overall responsibility for collision avoidance?
The Helmsman.
The Pilot.
The Officer of the Watch.
Watch handover can present additional risk, even if both bridge teams are highly skilled. As a minimum, watch handover procedures should include which of the following?
The status of the vessel in regard to draught, heel, trim and other influences on the under keel clearance.
Any standing orders or special instructions.
Current traffic, weather, visibility and tidal situation.
The position of the vessel and characteristics of the area, especially water depth and obstructions.
Any news regarding the duration of the next port stay.
All vessels are required to travel at a safe speed. Which of the following should be considered when determining an appropriate speed?
Current visibility and light conditions, such as background light at night.
Available water depth in comparison to current draught.
Traffic density, including smaller crafts and fishing boats.
Weather conditions like wind, sea and current.
Manoeuvring characteristics of the vessel itself, especially stopping distance and turning ability.
Request of the charterer to arrive at the next port as soon as possible.
You have visually detected a vessel in front of you, displaying the light shown below. The radar shows that the vessel is moving away from your ship.

Stern light.
Anchorage light.
Masthead light.
Side light.
In line with technical advancements, the issue of over-reliance on electronic tools on the bridge has increased in recent years. Which of the following statements regarding over-reliance are true?
All available means, such as electronic tools and visual look-out, need to be balanced against each other.
Routine use of equipment, for example for route planning, gives the operator important insight in to how the settings for the voyage influence chart systems.
A sound knowledge of the capabilities and limitations of the equipment onboard is important to avoid over-reliance.
Only electronic tools should be used for lookout and navigation.
Electronic tools are not reliable for lookout or navigation.
Effective and clear communication of the shared goal is essential for efficient bridge resource management.
True.
False.
A good voyage plan does not need to comply with regulatory requirements but should be a useful reference tool for the Bridge Team.
True.
False.
Command and Control of an Incident
Emergency response team members must know which of the following?
Where emergency equipment is located.
What personal protective equipment is required.
How to carry out a safety intervention.
Where to muster and the quickest route there.
The specific alarms and sounds onboard.
How often should fire drills be carried out?
Monthly.
Quarterly.
Weekly.
During an emergency, access to equipment in good working order isn’t sufficient to successfully resolve an incident. The safety of the ship and its crew is also dependent on which of the following?
Strong leadership.
Organisation.
Appropriate training.
Good procedures.
Poor decisions.
Inadequate processes.
Emergency Team:
Carrying out rescues, firefighting, boundary control and evacuations.
Ensuring that additional equipment (e. g. hoses or air cylinders for breathing apparatus) is readily available and readying the lifeboats if required.
Maintaining power supplies and ensuring that the main engine is available for manoeuvring.
Engine Room Team:
Carrying out rescues, firefighting, boundary control and evacuations.
Ensuring that additional equipment (e. g. hoses or air cylinders for breathing apparatus) is readily available and readying the lifeboats if required.
Maintaining power supplies and ensuring that the main engine is available for manoeuvring.
Support Team:
Carrying out rescues, firefighting, boundary control and evacuations.
Ensuring that additional equipment (e. g. hoses or air cylinders for breathing apparatus) is readily available and readying the lifeboats if required.
Maintaining power supplies and ensuring that the main engine is available for manoeuvring.
Which of the following should crew members do when communicating via radio?
Identify their location.
Keep information precise and to the point.
Shout.
Speak in a normal tone.
Always sign off to end the call.
ECDIS – Practises and Port State Control Inspections
To what types of equipment is an Integrated Bridge System generally connected?
Radar.
NAVTEX.
Echo Sounder.
Gyro.
Position fixing systems.
Power distribution system.
ECDIS.
Autopilot.
What are the benefits of ECDIS?
It provides an advanced ability to manage the chart display, safety settings, and audible and visual warnings and alarms.
Electronic Navigational Charts (ENCs) include up-to-date chart corrections.
Radar, AIS, depth contours and weather information are all available as display overlays.
Readily available real-time navigation information makes voyage planning simpler.
The company’s Safety Management System (SMS) manual is complex.
Successful completion of the generic ECDIS training is required for a new or renewed Certificate of Competency (CoC) under STCW, but further certificate documentation is required.
True.
False.
What type of deficiencies might a typical PSC inspection identify?
Failure to demonstrate adequate knowledge of how to use the primary and backup systems.
Failure to provide evidence that ECDIS type-specific training has been completed.
Failure to use the latest correct ENC.
Failure to have equipment in an acceptable condition.
Failure to maintain and update ECDIS to meet carriage requirements.
Inadequate crew morale.
The acronym ECDIS stands for “Electronic Chart Display and Information System”.
True.
False.
What methods are used to update ECDIS?
DVDs.
USB sticks.
CDs.
Online through an ENC chart update software service.
Email Attachments.
ECDIS updates automatically.
What are some potential difficulties in using ECDIS?
Users may not be familiar with a specific manufacturer’s equipment type, system controls and settings.
Configuration sub-menus may be overly complex, resulting in users failing to correctly set warnings and alarms.
A complex display system that can show too much information at once may cause confusion.
Radar, AIS, depth contours and weather information display overlays are all available.
Only an approved ECDIS system can be used for navigation. What requirements must it follow?
It must be type approved by the Flag Administration or by another recognised and approved organisation to meet performance standards.
It must be checked by a member of the IMO every year.
It must use the International Hydrographic Organisation (IHO) approved standards for chart data.
It must have an approved (navigation) backup system.
What are adequate backup arrangements for ECDIS?
A set of paper charts.
A second independent ECDIS.
Chart printouts.
A raster chart display system.
What are the potential sources of cyber risks to ECDIS?
Personal computers, tablets and smart phones.
Crewmembers inadvertently or maliciously introducing malware into the ship’s network and then to the ECDIS.
Remote software updates and service maintenance from third party service providers via satellite broadband.
From within the ship network and its connection to other electronic systems onboard.
Unauthorised or inadvertent use of compromised portable memory sources such a USB sticks.
Use of ECDIS in accordance with cybersecurity procedures.
Energy Efficiency
The shipping industry is responsible for about 3 % of Green House Gas emissions.
True.
False.
Which of the following acronyms are correct?
EEXI – Energy Efficiency Operational Index.
SEEMP – Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan.
EEOI – Energy Efficiency Operational Indicator.
SEEMP – Ship Energy Electricity Management Plan.
What should be checked under ISO 5001 compliance when visiting vessels?
Are the crew aware of the various factors that affect the energy efficiency and optimisation of the vessel?
Do the crew have an idea of energy efficiency measures as part of the SEEMP and how they can help reduce it?
Are the crew aware of fuel optimisation on a daily basis?
The relationship between the crew and the officers.
Which of the following statements are true?
All vessels with rating B for 2021 must achieve rating D in 2022.
All vessels with rating E for 2021 must achieve rating D in 2022.
All vessels with rating E for 2021 must achieve rating D in 2025.
ISO 50001 can offer significant reputational benefits by demonstrating to an organisation’s stakeholders that it is fully committed to managing its energy consumption and seeking ways to increase its energy efficiency.
True.
False.
Which of the following are energy saving options?
Using alternative fuels.
Weather routing.
Slow steaming.
Long steaming.
Hull cleaning and propeller polishing.
Which of the following factors does ISO 50001:2018 set out as an energy management framework?
Specific energy tasks to meet an organisation’s energy objectives.
Procedures.
Budgets.
Establishing policies.
Processes.
How can staff awareness and incentives be increased?
Ice breaker activities.
Training on Ship Energy Efficiency.
Poster campaigns.
Regular onboard meetings.
What are the benefits of the implementation of ISO 50001?
Carbon reduction.
Cost reduction.
Team building.
Organisational engagement.
Any energy reductions identified through an EnMS will, in turn, offer demonstrable savings on energy bills, which will reduce the overhead of a business and in some cases substantially.
True.
False.
The formula shown on screen is used to work out which of the following?

The Energy Efficiency Operational Index.
The Energy Efficiency Design Index.
The Energy Efficiency Operational Indicator.
Which of the following are key requirements of the energy management system?
Identifying the main factors that have an influence on energy consumption.
The Using company newsletters or other publicity documents, or seminars for raising awareness.
Conducting an initial diagnosis of energy consumption for all activities.
Establishing, implementing and maintaining an energy policy with a commitment for achieving energy performance.
What is an Energy Performance Indicator (EnPI) used for?
To compare energy performance after the implementation of action plans.
The A tool to access fuel consumption and CO2 emissions.
Managing a Safety Committee
Aside from the committee’s regular safety meetings, in which of the following situations should a meeting also be held?
Before a hazardous situation.
When at least two members request a meeting to resolve an issue.
After a serious incident.
When at least five members request a meeting to resolve an issue.
After every toolbox talk.
The safety committee should be consulted when emergency operations are required. Which of the following should take place if there is an urgent need for an informal safety meeting at short notice?
Toolbox talk.
360 review.
Safety intervention.
The safety committee is an essential part of the ship’s safety management system (SMS).
True.
False.
Which of the following are key roles of the safety committee?
Chief engineer.
Treasurer.
Chairperson.
Safety officer.
Which of the following are functions of the safety committee?
Inspecting the ship to verify that onboard safety procedures are fulfilled.
Ignoring suggestions for improvement from the crew.
Passing on findings to the crew, managers and the shipowner.
Participating in planning, managing and coordinating work which is required for safe and healthy working conditions on board.
Finding ways to reduce costs by cutting corners.
Medicals and Medication
Any illness or accident will have an immediate effect on the efficient running of the vessel.
True.
False.
The International Labour Organisation (ILO) and Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) stipulate that all ships should have which of the following on board?
A medicine chest, medical equipment and a medical guide.
A medicine chest, all seafarers prescriptions, and a medical guide.
A medical professional, medicine chest, and a full medical centre.
Which of the following statements are true?
Seafarers may be asked to declare medication to the Master every time they join the ship.
Accident investigation reports have highlighted the side effects of medication as a contributing factor.
It is okay to take a half course of antibiotics.
It is the Master’s responsibility to bring along seafarers prescribed medication, such as pills and inhalers on board.
This is the correct order of actions that seafarers should perform in an emergency? 1. Assess the scene and any dangers; 2. Assess the casualty; 3. Raise the alarm; 4. Stabilise the casualty; 5. Clear up and log the incident afterwards.
Yes.
No.
Launches and Personnel Transfers
Which of the following should be considered before any basket transfer operation?
The amount of clear space between the embarkation and the point of landing.
Weather conditions.
The cost involved with the transfer.
The height of the transfer basket, and minimise where possible.
Which of the following personnel is responsible for instructing the Crane Operator during lifting operations?
Master.
Pumpman.
Banksman.
____ communication should be established on an agreed ____ and maintained during the ____ operation.
radio … frequency … transfer.
frequency … radio … transfer.
transfer … frequency … radio.
What questions should you ask yourself before using a gangway to board a vessel?
Are the handrails intact and free from damage?
Is there a watchman at the top of the gangway?
Is the gangway wet and slippery?
Is the angle too steep due to the tide?
Is there a safety net strung under the gangway?
Is the paintwork in good condition?
Mooring System Maintenance
Ensuring that lines are stored correctly is an important part of ____. Storage of lines should be done in ____ area. ____ should be removed from lines before storing.
… preventive maintenance … a protected … twist and turns.
… inspections … an open … protective.
What should be considered during inspections of mooring systems?
Specific processes onboard.
Ease of handling a mooring line.
Practical experience with specific lines.
Preferences of shore-side mooring personnel.
The same type and size of mooring line should be used for the same service.
True.
False.
Winch break tests should be performed to ensure the break does not render before the MBL of the line is reached.
True.
False.
The safe working load (SWL):
Is the maximum safe load that a fixed piece of equipment can handle without risk of breaking.
Is the maximum safe load for a mooring line.
Is the minimum load at which a new and dry mooring line could break.
The working load limit (WLL):
Is the maximum safe load that a fixed piece of equipment can handle without risk of breaking.
Is the maximum safe load for a mooring line.
Is the minimum load at which a new and dry mooring line could break.
The Ship Design Minimum Breaking Load (MBL):
Is the maximum safe load that a fixed piece of equipment can handle without risk of breaking.
Is the maximum safe load for a mooring line.
Is the minimum load at which a new and dry mooring line could break.
Which of the following actions can ensure that mooring lines maintain a long and safe service life?
Storing lines in a protected area.
Removing twist and turns before storage.
Using covers, mats or protective sleeves.
Increasing the winch heaving load.
Drying lines before storage.
Pilot Transfer Arrangements
Pilots are ____ and highly trained to safely assist a ship on its passage. Their knowledge of local areas is beneficial when ____ may be considered hazardous or if a shipmaster is unfamiliar with the relevant port and/or area. Pilots are equipped with an understanding of local languages and ____, which can assist in communication.
… certified … navigation … dialects.
… enthusiastic … anchoring … customs.
Pilot ladders over which age should have a certificate of strength testing as per ISO 799?
30 months.
90 months.
3 months.
Which of the following safety arrangements should be in place for the pilot moving on and off the ladder?
The heaving line should be available to assist the pilot if they have a bag or equipment.
The heaving line should be available to assist a second pilot onboard.
A lifebuoy with self-igniting light will be placed near the ladder.
A responsible officer must be in constant communication with the bridge to relay pilot movements to confirm they are safely onboard or offboard and communicate instructions from the pilot or Master.
Pilotage refers to activities related to the navigation of vessels in which the pilot acts as an advisor to the master of the vessel and as an expert on the local waters and their navigation.
True.
False.
After a long sea passage, the pilot ladder and associated equipment should be inspected to allow time to repair or make further checks if required. What should crew members inspecting equipment look out for?
Damage, wear and twists to any of the ropes, including the manropes.
Broken or damaged chocks.
Broken or damaged steps or spreaders.
The condition of the gangway.
Port State Control
Who carries out a Port State Control inspection?
A Port State Control Officer.
A Port State Control Inspector.
The Chief Officer.
Every year, more than 50 000 inspections are carried out on board foreign ships in the ports under the Paris MOU.
True.
False.
What does STCW stand for?
The International Convention on Seafarers’ Training, Certification and Working.
The International Convention on Seafarers’ Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers.
This notice of national appeal can be found on the reverse side of the detention notice form and are of a similar format in all Paris MOU member states.
True.
False.
Which of the following should the crew do during an inspection?
Follow the inspection with their full attention.
Present any issues, with necessary corrective measures, at the beginning of the inspection to avoid the PSCO bringing the issue up.
Address the PSCO with respect at all times.
Stay in their accommodation.
High Risk Ships (HRS):
Between 5-6 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Between 10-12 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Between 24-36 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Standard Risk Ships (SRS):
Between 5-6 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Between 10-12 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Between 24-36 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Low Risk Ships (LRS):
Between 5-6 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Between 10-12 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Between 24-36 months after the last inspection in the Paris MOU region.
Which of the following ships are exempt from PSC inspections?
Fishing vessels.
Naval auxiliaries.
Pleasure yachts that are not trading.
Foreign ships.
What should a Port State Control Officer (PSCO) do when conducting inspections?
Seek advice if unsure of findings.
Ensure that the findings from the inspection and any corrective actions required are explained clearly to the Master and that the inspection report is clearly understood.
Advise the Master of the complaints procedure if a disagreement is not able to be resolved within a reasonable period.
Consider accepting any attempts of bribery.
Which of the following are principles from the Paris MOU code of conduct?
Integrity is the state of moral soundness, honesty and freedom from corrupting influences or motives.
Professionalism is applying accepted professional standards of conduct and technical knowledge.
Transparency implies openness and accountability.
Transparency implies openness and accountability unless you need to protect your crew.
Which of the following findings might lead to a more detailed inspection being carried out?
Evidence that the Master or crew are familiar with essential shipboard operations.
Indications that key personnel may not be able to communicate with each other or with others on board.
The absence of principal equipment that is required on board.
Sending false distress alerts that have not followed the correct cancellation procedures.
Evidence that the Master or crew are not familiar with essential shipboard operations.
Recovery Person From the Water
What does the code flag OSCAR mean?
Man overboard.
Shark.
Release lifeboats.
In which of the following situations might it be harder to spot someone in the water?
Reduced visibility.
Inclement weather.
On a clear day.
Which of the following are reasons a person can fall overboard?
During a recreational activity, such as boating, sailing and water sport.
If PPE has been misused or not used at all.
Vulnerable persons or people who suffer from mental health disorder involuntarily or voluntarily become too close to the edge.
During an operational activity, such as fishing, working over the side transfers.
When resting in the cabin.
How should the rescue boat approach a casualty for recovery?
Take extra care in heavy weather.
Approach at a safe speed.
Ensure that the boat is not swept onto the casualty by the wind or wave.
Approach the casualty quickly.
Which of the following are dangers for those who have fallen into the water?
Debris or rocks which can cause harm to the body.
Soaked clothes becoming heavy and making it harder to stay afloat.
Effects of cold water such as hypothermia.
Marine wildlife such as sharks and jellyfish.
Electrocution.
The training for competence in Personal Survival Techniques (PST) is mandatory for all personnel prior to employment on a ship as per the STCW.
True.
False.
A concerning situation is when a person is reported missing and has not been seen for many hours or longer. It is imperative to establish when the person was last seen and to confirm if they may have fallen overboard so that emergency action and recovery can be attempted.
True.
False.
Once on board, it is imperative that the ____ receives the necessary medical attention available and that they are transported to the nearest ____ or rendezvous point. There is always a risk in moving a casualty, especially in inclement weather; therefore, it should only be done if necessary. The decision will be made by the onboard ____.
… casualty … port … medical officer or doctor.
… crew … ship … captain.
Resource Management
A resource management training programme must have a lasting result to be effective, ensuring that the individual’s communication skills, ____ and ways of coping with pressure and ____ are well developed. This creates a crew with a focus on preventing minor errors that can lead to serious incidents or even ____ events.
… assertiveness … stress … catastrophic.
… attractiveness … injury … mundane.
There is a strong correlation between the behaviours and attitudes of seafarers on board a ship and the cultures that seafarers belong to, for example, professional, national and organisational cultures.
True.
False.
How can effective decision-making be supported?
By having seafarers complete surveys based on their work experience.
By carrying out regular meetings to let officers and crew members interact and share opinions.
Which factor contributes to a large majority of shipping related accidents?
Human factors.
Equipment failure factor.
How is resource management training carried out?
At workshops.
Using computer based training.
On a teacher-led 2 month course.
Ship Safety Officer
Which of the following are responsibilities of the SSO?
Inspecting and maintaining safety equipment.
Showing strong knowledge of the shipping Company’s safety policies and the ship’s operational procedures.
Acting as the safety advisor aboard ships and ensuring that all health and safety requirements are met.
Assisting the ship’s safety committee in enhancing the safety of the ship.
Updating relevant legislation.
What should new crew members be trained on when they join a new ship?
Equipment and operations aboard the ship.
The location of lifesaving equipment.
The location of shipboard emergency alarms.
Cooking equipment.
Machinery and systems.
It is the Master who appoints the Ship Safety Officer, as they are responsible for the safety of the crew and the ship, but cannot take the responsibility on as their own due to their duties.
True.
False.
Which regulations provide details on crew safety?
Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW).
The International Safety Management Code (ISM).
The Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS).
The As Low as Reasonably Practiced (ALARP).
Which of the following areas onboard a vessel may present extra hazards?
Around the deck hatch and tank opening.
In the engine and pump room.
In enclosed spaces.
Top deck.
Enclosed Places Are Dangerous Places
In the opening scene of the programme, we see an officer accompanied by how many seafarers?
2.
3.
4.
Before entering the enclosed space, which safety checks did the officer carry out?
He tested the entry door.
He tested his radio.
None.
What safety equipment did the seafarer who followed the officer into the enclosed space have with him?
His helmet.
A life line.
A safety harness.
Why are enclosed spaces dangerous?
The atmosphere inside enclosed spaces lacks adequate oxygen.
They are seldom ventilated.
They have limited entry and exit openings.
What are the consequences of someone entering an enclosed space without checking the oxygen level inside?
Loss of balance.
Loss of consciousness.
Death.
All of the above.
What is the normal level of oxygen in the atmosphere?
8 %.
20,9 %.
50 %.
What are the reasons for oxygen depletion in enclosed spaces on board ships?
Rusting of steel walls.
Deterioration of some organic cargos.
Cargo vapours filling the atmosphere in enclosed cargo holds.
All of the above.
Are there any other places where we encounter dangerously low levels of oxygen?
No. The atmosphere surrounding the Earth contains 20,9 % safe level.
Yes, in tropical forests.
Yes, flying at a height of 10 000 metres, pilots encounter oxygen levels at around 5 %.
What is the survival time when the oxygen level in the atmosphere is at 10 %?
Between 20 and 30 minutes.
Less than 45 minutes.
Around 1 hour.
What is the survival time when the oxygen level in the atmosphere is at 5 %?
Between 30 and 60 seconds.
1,5 minutes.
2 minutes.
How does our body obtain the required level of oxygen?
Body cells separate the oxygen from the air breathed in.
Body cells need a constant supply of oxygen which they get from the oxygen dissolved in the blood.
Oxygen enters the body and is distributed via body cells.
How important is the saturation level of oxygen in the body?
Very important. If it falls below 80 %, brain and organ failure begins.
Ideally it should be 100 % at all times.
Very important. In hospitals, the saturation level of oxygen in patients is measured by a clip on the finger.
All of the above.
What happens when someone enters an unchecked, low oxygen enclosed space?
They will lose consciousness and die.
Exhaustion will set in.
They will quickly start feeling dizzy.
How does one feel in an atmosphere low in oxygen?
Mounting chest pressure.
The same as being drowned or being strangled.
Tired.
Can we guess or estimate what the oxygen level is in an enclosed space?
Yes, we can smell the atmosphere after opening up.
Yes, we can look for signs of rusting or other decay.
No, the only way to ascertain the level is by accurate measuring.
Are only seafarers on board ship in danger of entering a low oxygen space?
Yes, there are no enclosed spaces on shore.
No, people on shore wear oxygen cylinders when entering enclosed spaces.
No, miners, mountaineers and high flying military pilots may also do so.
Why is oxygen so vital for us?
Our 30 trillion body cells use oxygen to maintain life.
Our cells obtain the oxygen they need from oxygen rich blood.
The amount of oxygen held in the blood is illustrated by its saturation level.
All of the above.
What is the first thing to be done before a rescue attempt is made?
The alarm must be raised.
The oxygen level in the enclosed space must be tested.
Emergency equipment that provides oxygen must be donned.
What are the dangers in attempting an unplanned rescue in enclosed spaces?
The ship’s crew may not be aware of the emergency.
The rescuer will die.
There is a minimal chance of a successful rescue.
What are the key rules applicable to entering an enclosed space?
Do a risk assessment prior to entry.
Monitor the oxygen levels regularly during entry.
Maintain regular radio communication with the outside.
All of the above.
SIRE 2.0 – What to Expect
What does the acronym SIRE stand for?
Ships Inspection Reporting.
Ships Investigation Report Exercise.
Service Inspection Reporting.
Service Investigation Report Exercise.
What does the acronym OCIMF stand for?
Oil Companies’ International Marine Fortress.
Oil Companies’ International Maritime Forum.
Oil Conglomerates International Maritime Forum.
Oil Conglomerates International Marine Fortress.
When was the SIRE program first launched?
1992.
1993.
1994.
1995.
Which of these is not an enhancement of the SIRE program expected by the 2.0 system?
Enchanced inspection criteria on equipment, procedures and human factors, to further improve control over vessel safety systems and processes.
Significant enchancements to training and continuing development of inspectors to ensure the highest standard of delivery is maintained and improved.
The use of web-enabled tablet devices to allow inspections and feedback to be reported and documented in real-time.
Making the inspection take longer by enforcing the use of new systems that will take longer to apply.
What does the acronym TMSA stand for?
Tanker Management Self-Aggrandisement.
Tank Maintenance Self-Aggrandisement.
Tanker Management Self-Assessment.
Tank Maintenance Self-Assessment.
What is recognised as the main focus for SIRE 2.0 for 2022?
Human factor awareness.
Correct use of maintenance procedures.
Cargo handling practices.
Galley fire responses.
The SIRE 2.0 inspection process will not allow for the ship to respond to the findings. Is this statement true or false?
True.
False.
The initial survey for SIRE 2.0 may take longer than usual due to the need to upload photos and documents to the system. Is this statement true or false?
True.
False.
How long will it take to complete an average inspection under SIRE 2.0?
4 hours.
8 hours.
16 hours.
24 hours.
The tablet must remain connected to the internet throughout the SIRE 2.0 inspection. Is this statement true or false?
True.
False.
SOLAS Safety Radio
On most vessels, the emergency power or generator will need to be manually turned on if there is a loss of main power, in order for safety critical systems on board to be maintained.
True.
False.
What is the purpose of the GMDSS sea areas?
To define what radio equipment GMDSS ships must carry.
To describe areas where GMDSS services are available.
To describe areas where GMDSS is banned.
Which of the following actions would cost a crew member a large penalty?
Sending SOS by Morse code, by light flashes or by sounds.
Sending SOS by Morse code, by light flashes or by sounds when there is no emergency.
Firing a gun or other explosive signal every minute.
As per SOLAS, every GMDSS should provide ships, whilst at sea, with the capability of which of the following actions?
Transmitting and receiving search and rescue co-ordinating communications.
Transmitting and receiving on-scene communications when another vessel is in distress.
Crew must be able to call home from the accommodation.
Receiving shore-to-ship distress alerts.
How can the range of the VHF radio be increased?
By increasing the height of the antenna.
By turning the squelch control on the device.
By decreasing the height of the antenna.
What is the most COMMON high-frequency communication?
Sky wave.
Ground wave.
Radio wave.
Using the Greek alphabet, allows each letter to be heard with a totally unique sound and is easier to decipher.
True.
False.
Match the following letter up to the correct message. Navigational Warnings:
A.
B.
C.
D.
Match the following letter up to the correct message. Weather warnings:
A.
B.
C.
D.
Match the following letter up to the correct message. Search and rescue of piracy and armed robbery:
A.
B.
C.
D.
The GMDSS uses Morse code to communicate.
True.
False.
Which of the following outcomes are covered in the General Operator’s Certificate (GOC) training?
Lifeboat rescue and retrieval training.
Knowledge of the search and rescue procedures including procedures in International Aeronautical and Maritime Search and Rescue (IAMSAR).
Transmit and receive information using GMDSS and equipment and fulfil the functional requirements of GMDSS.
The ability to carry out radio services in emergencies such as – abandon ship, fire on board, breakdown of radio installations.
Which of the following equipment should be carried in Sea Area A1?
Three approved portable survival craft VHF radios for vessels over fifty gross tonnes.
Two SARTs, or one if the vessel is under 500 gross tonnes.
One NAVTEX receiver.
Three NAVTEX receivers.
What is a call sign?
A unique identification code that is given to vessels with radio licences to make communication easier.
The name of a vessel.
A unique identification code that marks a vessel as a pirate ship.
As per ____, all vessels are permitted to carry portable ____ transceivers that operate on VHF channel ____ and at least one other channel (VHF channel 6 is recommended). The radios are kept on charge at the navigational bridge.
… SOLAS … survival craft VHF radio … 16.
… IMO … Inmarsat C (Sat C) … 10.
… COSPAS-SARSAT … Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB) … 20.
Which of the following are key components of the GMDSS?
Short Range Radio (VHF).
Long Range Radio (MF/HF).
Emergency Position-Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB).
Search and Rescue Transponder (SART).
COSPAS-SARSAT.
____ is an emergency word used internationally as a distress signal on radio voice communications. It is the ____ important call that can be made. It signals that there is ____, and that immediate assistance is required.
… Mayday … most … an imminent threat to life or to the vessel.
… Securite … least … a threat from piracy.
… Pan-pan … most … a threat of the ship sinking.
Which of the following statements are true?
… Over longer distances lower frequency radio waves, below three MHz, travel efficiently as ground waves.
Radio waves above the thirty MHz frequency travel as direct waves or line of sight, between the transmitter and receiver.
Radio waves are transmitted easily through the air but are very dangerous to the human body.
Ground waves are not affected by changes in atmospheric conditions, which is a disadvantage.
Match up the test functions to the correct device. This device can be tested using the test button on the device without sending a distress signal:
EPIRB.
SART.
NAVTEX.
SAT C.
Match up the test functions to the correct device. This device is tested on board by using the self-test mechanism briefly and looking at the X-band or three cm radar display to see if concentric circles are displayed:
EPIRB.
SART.
NAVTEX.
SAT C.
Match up the test functions to the correct device. This unit an internal test function that can test the battery and general functions. The result of the test can be printed:
EPIRB.
SART.
NAVTEX.
SAT C.
Match up the test functions to the correct device. This device has an internal diagnistic test to ensure functionality. It is possible to do a performance verification (PV) test, from a local earth station:
EPIRB.
SART.
NAVTEX.
SAT C.
What are the three common words used to indicate distress via radio communication?
Pan-pan.
Securite.
Mayday.
Help.
What is channel 16 used for?
Channel 16 is used to signal distress.
Channel 16 is used to signal navigational warnings.
Channel 16 is used for ship-to-ship, or ship-to-aircraft coordinating search and rescue operations.
The function of all the VHF and MF/HF DSC facilities should be tested daily.
True.
False.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) as Fuel Bunkering Operations
After an understanding has been reached, new personnel can participate at any time with the bunkering operation.
True.
False.
If at any time there is a communication failure, bunkering operations should be stopped in a safe condition and should not be resumed until communications are re-established.
True.
False.
What type of extinguishers can be used on LNG fires?
Dry powder.
High expansion foam.
Carbon dioxide.
Wet chemical.
Water.
Which of the following negative effects can sulphur oxide (SOx) cause?
Acid rain.
Acidification of the oceans.
Inflammation of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems in humans.
Gas clouds.
What area of guidance does The International Safety Guide for Oil Tankers and Terminals (ISGOTT) provide for bunkering LNG as fuel operations?
Risk assessments.
Vapour and pressure control.
Process and procedures.
Control zones.
Personnel training requirements.
What is the flashpoint of LNG when it is returned to vapour?
Minus 188 degrees Celsius.
537 degrees Celsius.
Minus 160 degrees Celsius.
Which of the following information is correct considering the use of checklists?
Checklists are only required when performing a ship to ship transfer.
Checklistis should not be mixed.
Both checklists from ISO and IAPH can be used together.
The term bunkering comes from the word “bunker” as in the early days of shipping, the coal used to fuel the ships was stored in a space called the bunker.
True.
False.
Match the following zones to their correct description. Hazardous Zone:
In this zone risk of a flammable atmosphere is present at all times, this is an area directly around the bunkering area.
This zone extends beyond the hazardous zone and has further precautions due to the nature of LNG if spilled.
This zone ensures passing traffic does not affect the safety of the operation. Assistance may be required from the port to enforce.
This zone is where other shipboard activities and SIMOPS are monitored to ensure there is no encroachment of the safety zone.
This zone is a large area that is intended to protect public access as per local regulations.
Match the following zones to their correct description. Safety Zone:
In this zone risk of a flammable atmosphere is present at all times, this is an area directly around the bunkering area.
This zone extends beyond the hazardous zone and has further precautions due to the nature of LNG if spilled.
This zone ensures passing traffic does not affect the safety of the operation. Assistance may be required from the port to enforce.
This zone is where other shipboard activities and SIMOPS are monitored to ensure there is no encroachment of the safety zone.
This zone is a large area that is intended to protect public access as per local regulations.
Match the following zones to their correct description. Marine Exclusion Zone:
In this zone risk of a flammable atmosphere is present at all times, this is an area directly around the bunkering area.
This zone extends beyond the hazardous zone and has further precautions due to the nature of LNG if spilled.
This zone ensures passing traffic does not affect the safety of the operation. Assistance may be required from the port to enforce.
This zone is where other shipboard activities and SIMOPS are monitored to ensure there is no encroachment of the safety zone.
This zone is a large area that is intended to protect public access as per local regulations.
Match the following zones to their correct description. External Zone:
In this zone risk of a flammable atmosphere is present at all times, this is an area directly around the bunkering area.
This zone extends beyond the hazardous zone and has further precautions due to the nature of LNG if spilled.
This zone ensures passing traffic does not affect the safety of the operation. Assistance may be required from the port to enforce.
This zone is where other shipboard activities and SIMOPS are monitored to ensure there is no encroachment of the safety zone.
This zone is a large area that is intended to protect public access as per local regulations.
Match the following zones to their correct description. Monitoring and Security Area:
In this zone risk of a flammable atmosphere is present at all times, this is an area directly around the bunkering area.
This zone extends beyond the hazardous zone and has further precautions due to the nature of LNG if spilled.
This zone ensures passing traffic does not affect the safety of the operation. Assistance may be required from the port to enforce.
This zone is where other shipboard activities and SIMOPS are monitored to ensure there is no encroachment of the safety zone.
This zone is a large area that is intended to protect public access as per local regulations.
The IMO 2020 limit reduced the amount of sulphur in fuel used on board (outside emission control areas) to which of the following percentages?
0,5 %.
3,5 %.
5 %.
10 %.
Which of the following describes LNG?
Colourless.
Odourless.
Black in colour.
Non-corrosive.
Toxic.
A closed system can only be practised if which of the following components are in place?
LNG articulated rigid piping and certified hoses, valves and couplings.
Suitability constructed tanks that allow pressure build-up within a safe range.
An ESD system which is connected to both the supplier and receiver of LNG.
Drip or insulated trays.
How can the “dry disconnect” process be achieved?
By draining or inerting the system, so that no LNG vapour is present before disconnection.
By top spraying and filling in the receiving tanks to provide cooling and avoid the occurrence of BOG.
Using dry connect and disconnect couplings, which close in any LNG vapour before disconnection.
What are the disadvantages of a ship to ship transfer?
The bunker barge is vulnerable to vessels in the vicinity.
The rate of transfer is much faster than other methods.
There are no checklists for this type of transfer.
Which of the following describes LNG?
Non-corrosive.
Colourless.
Odourless.
Toxic.
Black in colour.
??? Which of the following are parts that may be included in a checklist?
The Planning Stage.
Personnel training Information.
Terminal Information.
Post-transfer Checks.
LNG Transfer Data.
Pre-transfer Checks.
Social Media Awareness (Maritime) MGM-061
As a minimuym, a typical Social Media Policy will include specific details on which of the following?
The information that you are permitted to share.
How long you are permitted to spend on social media.
The sites that you are permitted to access while at work.
The username you should chose.
How many hours are lost (globally) as a result of personnel spending time on social media sites when they should be working?
233 million.
23 million.
2,3 million.
Social media can help both business and individuals to do which of the following?
Meet new people.
Stay in touch with family, friends and customers.
Stay informed about world news.
Share customer’s personal information without their permission.
Share important events.
Target competitors with negative comments.
Social media is a generic term that is used to describe any internet-based platform that enables online interaction and communication between users.
True.
False.
Which of the following should never be discussed online?
Networking events.
Company values.
Confidential or commercially sensitive information.
Introduction to Safe Cargo Operations MGM-113
Is the following statement true or false? «The CSM provides detailed instructions and guidelines, based on a cargo’s weight, size, and shape».
False.
True.
What is the final stage of a cargo operation?
Monitoring.
Briefing.
Debrief.
What document will determine the scope of the emergency response planning required prior to a cargo operation taking place?
ISGOTT.
Cargo securing manual.
Risk assessment.
What is an SMS?
Ship Management System.
Safety Maintenance System.
Safety Management System.
What is Class 2 of the IMDG Code?
Gases.
Solids.
Liquids.
What code of practice covers the safe handling of hazardous cargo?
BLU Code.
ISMBC Code.
IMDG Code.
What types of vessels are covered by the IGC Code?
Chemical Tankers.
Car Carriers.
Gas Carriers.
Is the following statement true or false? «MARPOL regulations need not be taken into account for cargo operations».
True.
False.
Which code covers the regulations for solid bulk cargoes?
IBC Code.
ISMBC.
ISGOTT.
What does the CSS Code provide regulations for?
Cargo Securing and Stowage.
Cargo Security and Safety.
Cargo Securing and Security.
International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargo (IMSBC) Code (Maritime) MGM-084
If the cargo is Group ____ then carriage can be ____ by the port of loading and the competent authorities of the unloading port and ____ state will be informed of the authorisation.
… C … authorised … flag.
… C … rejected … flag.
… B … other … removed.
… B … authorised … flag.
What can be produced when Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) reacts with water and air?
Hydrogen and heat.
Oxygen may be depleted in enclosed spaces.
Sulphuric acid.
Citric acid.
What risk mitigation should be considered for Group В cargo?
Precautions against toxic gas.
Precautions against fire and explosion.
Precautions against corrosion.
Precautions against rough seas.
Who decides whether an exemption is accepted or rejected when issued by the loading port authority?
The flag state authority.
The unloading port authority.
The Shipper.
What are the two common links that bulk cargo have?
The product is generally sold by weight or volume.
The product is nearly uniform no matter who the producer is.
The product is not uniform in manufacture.
The product is manufactured by a sole supplier.
What two groups can coal cargo belong to?
Group A and В.
Group B and C.
Group A and C.
What should the Master of the vessel obtain from the shipper prior to loading?
The cargo’s physical properties.
The cargo’s chemical properties.
The cargo’s selling price.
The cargo’s country of origin.
Is the following statement true or false? «Ships carrying solid bulk cargo can involve serious risks, which must be managed carefully to safeguard the crew and the ship».
False.
True.
Where would the ship’s Master find the individual schedules for cargo?
In the safety management procedure.
In Appendix I of the IMSBC Code.
On the manufacturer’s website.
During loading, cargo must be properly distributed throughout the ship’s hold. Where can this information be found?
The ship’s safety management system.
By use of loading calculators.
It can be found in the ship’s stability information.
The ship’s station bill.
Which checks should be performed before loading cargo?
That the bilge lines, sounding pipes and other service lines are in good order.
That the bilge wells and strainer plates are prepared to facilitate drainage and prevent cargo entering the bilge system.
That the radar is in good working order.
That the PA system is working.
Is the following statement true or false? «Ventilation systems should be switched off before loading of cargo starts».
True.
False.
Which Group classification do cargo come under that may liquefy?
Group A.
Group C.
Group В.
Mentoring
Who, amongst the members of the experienced crew, can become a mentor?
Anyone from the Master to the AB.
Only those with academic qualifications.
Only those who are given the task by the Master.
What did he mentee say the main effect of mentoring was for him?
My mentor showed me how to practically apply the knowledge I had learnt at school.
The mentor helped me to develop my self-confidence.
The mentor helped me to overcome my fear of the unknown.
What did the mentor say the main effect of mentoring should be?
Making sure that the mentees know clearly how to do the task correctly.
Developing a mutually convenient mentoring schedule.
Making sure that the mentees are happy about the work they do.
When dealing with mentees who have not been on board ship before, what should be the first task of a mentor?
Mentors should conduct an introductory visit to all parts of the ship.
Mentors should point out the potentially dangerous areas on board.
Mentors should explain how the mentee’s tasks fit in with the functioning of the ship.
What methods of mentoring would be the most rewarding for the mentees?
Task based mentoring would be the most rewarding for both parties.
Mentees hould be given a suitable office environment for their studies.
Mentees should be offered some books to read concerning their function on board.
For mentoring to be successful, what is the most effective relationship to be developed between mentor and mentee?
Mutual trust.
Mutual respect.
Friendliness.
While the mentee is busy with the task, how could the mentor be most effective in assisting?
All of the above.
The mentee should be encouraged to ask questions and be given clear indications as to how the situation may progress.
Any criticism should be constructive and accompaneed by the suggestion of alternatives that might work better.
The mentees should be praised when they do well or show signs of improvement.
When a mentee faces a new task, what would be the most effective way for a mentor to be helpful?
The mentor should brief the mentee beforehand about the expected outcome and of any dangers that could arise.
The mentor should boos the self-confidence of the mentee.
The mentor should assure the mentee that the task is being supervised.
What effective steps should a mentor take to achieve optimum results?
The mentor needs to identify the gaps in the mentee’s knowledge and skills.
The mentor must ensure that any discussion with the mentee happens in a quiet place.
The mentor must ensure that the mentee has clearly understood what was discussed.
What impact does effective mentoring have on senior crew members?
Senior Officers develop greater confidence in the reliability of their juniors.
Senior crew members can concentrate more on their own functions.
Senior crew members feel more relaxed when delegating tasks to their junior crew.
What attitude of experienced seafarers could be detrimental to mentoring?
Some may feel that passing on their knowledge may undermine their own status and position within the hierarchy of the crew.
Some may feel they do not have the necessary time.
Some may feel they are insufficient qualified to be mentors.
What is the fundamental basis on which mentoring works?
There has to be a full commitment by both parties for it to work.
It has to be a continuous process.
Mentoring must not overwhelm the mentee.
How does an effective mentoring system on board benefit the ship?
It improves the experience and competences of junior crew members and reduces the likelihood of errors.
It reduces the need for extra overtime work.
It helps to develop good working practices.
How does effective mentoring work on board?
Mentoring develops a practical relationship between mentor and mentee, enabling the mentor’s own experience to grow the mentee’s confidence and knowledge.
A sensitive approach by the mentor helps the mentee to progress faster.
It gives mentees the effective supervision they require.
How does Mentoring help new crew members at the start of their on-board life?
Mentoring by and experienced crew member provides a vital component for all seafarers in their progress to becoming an effective member of the ship’s crew.
An experienced Mentor develops a programme of easy tutoring.
An experienced Mentor develops a welcoming relationship with his mentees.
What challenges do new crew members face on board ship?
All of the above.
Learning to work with people from different backgrounds and cultures.
Staying safe in potentially hazardous environment.
Long periods of absence from friends and family.
What is the main benefit of taking part in initial training at a Nautical College?
It provides a theoretical understanding to new seafarers of all aspects of ship operation.
It enables new seafarers to ask questions about matters they don’t fully understand.
It enables new seafaresr to meed other new seafarers.
What challenges do new seafarers face when arriving on board ship at the start of their careers?
The need to develop new skills and acquire practical experience to function effectively on board.
They need to get used to the varying hours of shift work.
They have to get used to living in close proximity with others.
What is the main function of Mentoring on board ship?
To assist seafarers who boarded the ship for the first time to familiarise themselves with the new environment.
To assis a new crew member in dealing with the different languages spoken on board.
To assist a new crew member in getting to know the ship’s layout.
What is the meaning of Mentoring?
Assisting people to understand the new situation which they have entered.
Helping people to achieve a better lifestyle.
Teaching young people to get along with each other.
Waste Management
Which of the following actions can companies take to manage and control waste?
Report waste quantities and disposal routes to the Regulator through EEMS.
Ensure that all wastes are segregated and stored in secure and clearly labelled skips.
Undertake regular waste audits.
Avoid including the waste aspects of operations in pre-job risk assessment.
Report waste quantities and disposal routes to the Maritime and Coastguard Agency (MCA).
Select the answers that apply:
General/non-hazardous waste: Wood, Scrap metal, Plastics; Special/hazardous waste: Oily rags, Batteries, Contaminated drill cuttings.
General/non-hazardous waste: Wood, Scrap metal, Contaminated drill cuttings; Special/hazardous waste: Oily rags, Batteries, Plastics.
Please complete the following question. Everyone has a part to play in ____, recycling and disposing of waste properly. Taken together, the ____ of all individuals on a daily basis CAN make a difference and can help to ____ environmental impacts.
… re-using … actions … maximise.
… re-using … actions … minimise.
… mixing … actions … maximise.
Which of the following actions can individuals take on a daily basis to help minimise environmental impacts?
Re-use resources where possible.
Place waste in the correct storage bins provided.
Place waste in one large storage bin and ship to onshore for separation.
Follow company waste policies and procedures.
Which of the following environmental impacts are associated with waste disposal to landfill?
Liquid drainage which can contaminate water supplies and water courses.
Odour, vermin and increased traffic levels of nearby residents.
Acid rain.
Marine pollution.
Which of the following must all offshore platforms and mobile offshore drilling units have in place in order to control and manage all waste streams?
Garbage Record Book.
Garbage bags.
Garbage Management Plan.
Competence matrices.
Which of the following pieces of legislation are concerned with the management of waste?
Landfill Directive.
Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations.
Merchant Shipping (Prevention of Pollution by Sewage and Garbage from Ships) Regulations.
Environmental Protection (Duty of Care) Regulations.
Control of Vibration at Work Regulations.
Under legislation, companies have a ____ to ensure that waste is ____ properly and recovered or disposed of carefully. However, waste is ____ responsibility and everyone has a part to play in managing waste properly.
… “Duty of Care” … managed … everyone’s.
… “Duty of Responsibility” … managed … everyone’s.
… “Duty of Care” … mixed … the manage’s.
Select the correct waste hierarhy, starting with the most preferred measure:
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover, Treat, Dispose.
Reuse, Reduce, Recycle, Treat, Recover, Dispose.
Treat, Reduce, Recycle, Reuse, Recover, Dispose.
The incineration of wastes can cause which of the following problems?
Production of toxic substances.
Production of ash which may contain heavy metals and other toxins.
Marine pollution.
Production of gases which may cause air pollution.
Increased traffic levels.
Mooring Deck Safety (DNV Certified)
Which of the following members of personnel are involved in a mooring team?
Winch Operator.
Deckhand.
Person in Charge of the Mooring Station.
3rd Engineer.
Which of the following factors should be considered before any mooring?
Weather.
Deck Hazards.
Port Security Level.
Lighting.
Which of the following is an outstretched arm with a flat open hand being waved downward?
Slack off.
Let go.
Stop.
Which of the following is a circular movement of the hand above the head?
Heave away.
Make fast.
What does the mooring station crew do once the tugboat has secured the mooring line?
Confirm to the bridge that the tugboat has secured the line.
Remove the heaving or messenger line.
Signal the tugboat to pull.
Call the tugboat on VHF.
Which of the following are examples of preparing the mooring area with safety in mind?
Restricting access to the mooring line.
Labelling and painting safe working areas and hazards.
Treating decks with non-slip treatment.
Lighting the mooring area adequately.
Moving observers onto the mooring area before starting the operations.
Which of the following is considered one of the biggest hazards associated with mooring operations?
Wire rope strains.
Rope burns.
Lines parting with little or no indication.
Flashlights.
Which of the following personal protective equipment should be used in addition to standard PPE when handling wire ropes?
Rigging knives.
Flashlights.
Gloves.
Swimwear.
Deckhands are responsible for handling the lines that are used to moor the vessel. Deckhands work under supervision and are responsible for making sure that the lines are secured correctly:
True.
False.
The Maritime Safety Committee revised the SOLAS regulation II-1/3-8 to prevent unsafe working conditions during mooring operations.
True.
False.
Why is adequate lighting required on the mooring station?
Good lighting helps the crew to see the winch controls.
Adequate lighting enables tug or line boat operators to see the mooring station.
Sufficient deck lighting ensures the crew can avoid any trip fall or any other deck hazards.
Bad lighting may cause sleepiness.
Which of the following are important steps in arranging mooring ropes properly?
Laying each rope out along the deck, making sure that they are not tangled or knotted.
Tying the messenger line around the rope, pulling it through the fairlead and leaving it on the bulwark, in preparation for throwing.
Connecting rat guards to all mooring lines.
Ensuring all ropes are fully rolled up on the winches or windlasses.
As mooring is a routine job operation, personnel engaged in mooring operations do not need to wear PPE.
True.
False.
Which of the following rules is a professional mooring plan based upon?
Headlines primarily prevent the bow from moving astern.
Mooring lines should not overload the quick release hook ashore.
Spring lines should be placed as parallel to the vessel as possible.
Breast lines should be placed perpendicular to the vessel.
Breast lines should be placed as parallel to the vessel.
Spring lines should be placed as as square to the vessel as possible.
Which of the following personal protective equipment should be worn when carrying out mooring operations?
Swimwear.
Hardhat with chin strap.
Safety goggles.
High visibility coveralls.
Which of the following statements regarding mooring safety and planning are true?
A sufficient number of crew involved should be competent and trained and be aware of agreed safety measures.
All crew involved should be competent and trained and be aware of agreed safety measures.
Every crew member on each deck mooring location needs to be experienced.
A sufficient number of available crew for each deck mooring location should be experienced.
How can equipment failure be mitigated?
Mooring teams should monitor weather conditions and adjust their operations accordingly.
Mooring equipment should be inspected regularly and any defects or damage should be repaired or replaced promptly.
Aramid fibres are suspectible to axial compression. What is axial compression?
When a line undergoes deformation or compression when subjected to loads that act along their length.
Where workers are more likely to get their fingers, hands or other body parts caught in the lines as they tighten or loosen them.
Specific areas on a ship’s line where sudden and dangerous release of tension can occur during mooring operations.
During the mooring operation, the Master and Pilot may make last minute adjustments to the plan based on which of the following?
Changing weather conditions.
Loading conditions.
Port regulations.
While certain areas are more dangerous, snapping lines can affect the whole mooring area. Therefore, the whole mooring area should be seen as a potential snap-back zone.
True.
False.
Which of the following statements regarding the Person in Charge of the Mooring Station are true?
It is their duty to oversee the mooring team.
They need to maintain control and oversight.
It is their direct task to control the winches.
They are responsible for handling the lines that are used to moor the vessel.
What does an outstretched arm pointing down and making a circle motion signal during mooring operations?
Slack off.
Let go.
Stop.
Once the vessel is in position, it must be secured to the berth. Typically, which of the following ropes will be used?
Breast line.
Stern line.
Bowline.
Spring lines.
Basic maritime communication phrases include mooring terminology and are included as a The International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW) requirement, using the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Standard Marine Communication Phrases as a standard.
True.
False.
Which of the following should be included in a management plan for inspection and maintenance of mooring equipment?
Criteria for replacement of mooring equipment based on the manufacturer’s information.
Procedures for identification, operation, inspection, maintenance of all mooring equipment.
Record of the original design concept and of inspection and maintenance.
Predictions on when to replace each line based on the average.
Lists of which lines where used at which port with detailed guidance on the length of berthing.
The International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW) requires the use of the International Maritime Organization (IMO‘s’) Standard Marine Communication Phrases as a standard.
True.
False.
What are some factors that influence berthing?
Ship and berth size.
Estimate cargo operations.
Traffic.
It is the responsibility of the captain to direct the operation and lead the crew by being physically present on the mooring station.
True.
False.
While mooring lines should work together, lines in the same service do not need to always have the same diameter.
True.
False.
The mooring safety process includes the crew ensuring that the ship’s equipment is in good working order and confirming that the manoeuvring equipment is ready for use.
True.
False.
- Introduction to Abrasive Wheels
- Accident and Incident Investigation
- Accommodation Safety
- Behaviour Based Safety
- Chemical Tankers – Basic
- Cultural Awareness
- Dangerous Edges
- Diesel Engine Analysis
- Electrical Safety Rules
- Enclosed Space Entry
- Engine Room Safety
- Engine Room Watchkeeping
- Examining Lifting Appliances and Loose Gear
- Fatigue Management
- Fluid Hammer Effect
- Garbage Record Book
- Good Business Writer
- Hand-Arm Vibration Safety
- Handling and Storage of Hazardous Substances
- Harassment and Bullying
- Hazard Identification
- Helicopter Operations at Sea
- Hydrogen Sulphide Awareness
- Personal Hygiene
- Interventions
- Introduction to Inert Gas Systems
- Introduction to Oily Water Separators
- Introduction to ISO 14001 and Environmental Management
- ISO 45001 Occupational Health and Safety
- Ladder Safety
- Liquefied Gaz Fire Hazard Management
- Lubrication Systems
- Marine Fuel Management and Switching Operations
- Maritime Health and Lifestyle
- Maritime Leadership
- Mental Health
- Oil Record Book
- On-board Assessor
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Prevention of Marine Spills (SOPEP)
- Prevention of Vessel Air Pollution
- Risk Assessment
- Safe Cargo Handling
- Safe Use of Rigging Equipment
- Safe Welding Operations
- Safety Officer
- Sewage and Wastewater Treatment
- Slips, Trips and Falls
- Tank Cleaning and Wall Wash
- Tanker Operations – Bunkering
- Tanker Operations – Ship to Ship (STS)
- Use and Storage of Pressurised Cylinders
- Vapour Emission Control
- Working at Height
- Working with High Voltage
- Cyber Security
- COLREGS General
- Piracy and Armed Robbery
- Drug and Alcohol Awareness and Policy
- Safe use of Maritime Cranes Training
- Life Rafts
- Respiratory Protection
- Rescue and Fast Rescue Boat – Launch and Operations
- CO2 Firefighting Systems
- Anchoring – Operational Safety
- Best Navigational Practices
- Command and Control of an Incident
- ECDIS – Practises and Port State Control Inspections
- Energy Efficiency
- Managing a Safety Committee
- Medicals and Medication
- Launches and Personnel Transfers
- Mooring System Maintenance
- Pilot Transfer Arrangements
- Port State Control
- Recovery Person From the Water
- Resource Management
- Ship Safety Officer
- Enclosed Places Are Dangerous Places
- SIRE 2.0 – What to Expect
- SOLAS Safety Radio
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) as Fuel Bunkering Operations
- Social Media Awareness (Maritime) MGM-061
- Introduction to Safe Cargo Operations MGM-113
- International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargo (IMSBC) Code (Maritime) MGM-084
- Mentoring
- Waste Management
- Mooring Deck Safety (DNV Sertified)
Modules
CES tests for seafarers
Start taking Mintra tests with us to prepare for your exams. We wish you success!

In test ON-BOARD ASSESSOR question: DURING STEP 5 OF THE ASSESSMENT (CONDUCT AN ASSESSMENT DEBRIEF), THE ASSESSOR SHOULD START WITH THE AREAS WHERE THE CANDIDATE'S PERFORMANCE DID NOT FULFIL EXPACTATIONS. The correct answer is FALSE
Thank you so much
Good
Maybe you have also test with answers:
Designated Security Duties?