LNG Bunkering Port Emergency Preparedness Procedures
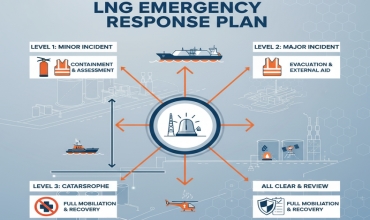
Effective emergency response within LNG bunkering operations necessitates the implementation of a structured procedural framework predicated upon risk-based scenarios and hazard identification methodologies. The framework delineates sequential response protocols commencing with event detection and culminating in post-incident analysis, thereby ensuring continuity of operations and mitigation of secondary risks. Integration of these procedures within the broader port emergency management system enhances interoperability among stakeholders and facilitates rapid activation of contingency measures.
Coordination Among Port Stakeholders
The efficacy of emergency response procedures is largely contingent upon the establishment of clear lines of communication and predefined roles among port authorities, LNG operators, emergency services and ancillary service providers. Inter-agency memoranda of understanding (MoUs), joint training exercises and shared digital platforms for real-time data exchange constitute critical enablers of coordinated action. By formalising these collaborative arrangements, ports can minimise latency in decision-making and optimise resource allocation during high-pressure incidents involving LNG release, fire or explosion hazards.
Technical and Operational Contingency Measures
Contingency planning must account for both immediate containment strategies and longer-term recovery objectives. Technical measures include the deployment of spill containment booms, deluge systems and remote-operated shut-off valves designed to minimise LNG dispersion and thermal radiation exposure. Operationally, bunkering operations must incorporate fail-safe termination protocols enabling instantaneous cessation of fuel transfer under defined emergency thresholds. Regular validation of these measures through tabletop simulations and full-scale drills is essential to ensure compliance with Directive 2014/94/EU and associated EMSA guidance frameworks.