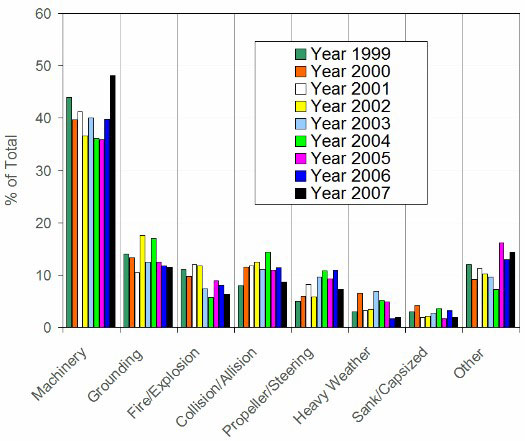
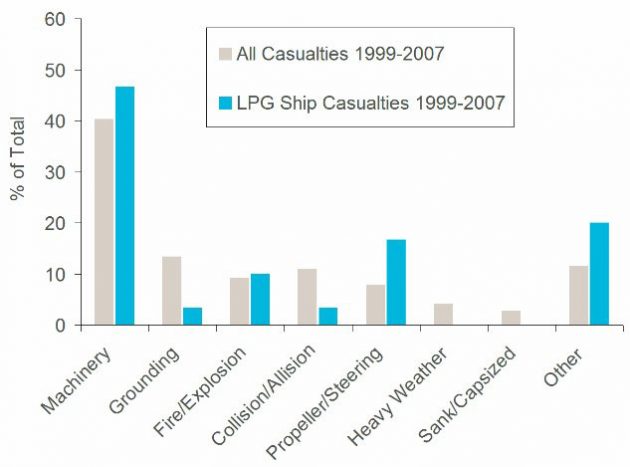
Demand of the Liquefied Petroleum Gas in XXI century increases. This article contains basic information about LPG vessels, risk assessment and their identification, and the measures to loss prevention.
СодержаниеСвернуть
- Properties of LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
- Natural Gas Processing and Liquefaction
- LPG Vessels
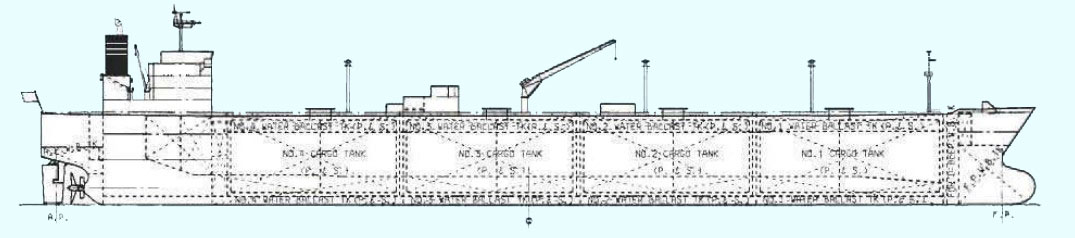
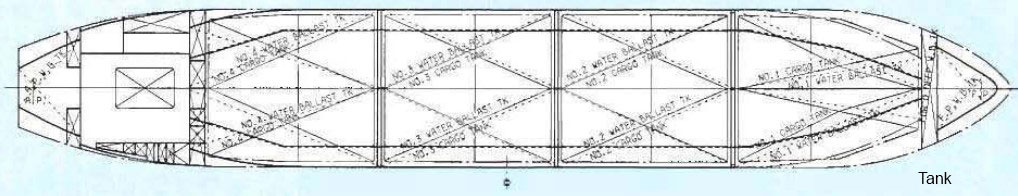
- General Arrangement of “GAS XXX”
- Risks to LPG Vessels
- Risks Particular to LPG vessels
- General Risks to LPG Ships
- Case Reports
- Sample of Risks Identification of LPG Ships
- Measures Taken to Reduce Risk (Loss Prevention) on LPG Ships
- Risk Due To Shortage Of Experienced Gas Tanker Crew
- Shipbuilding Risks
- Conclusions
- LPG Properties (Physical and chemical properties).
- LPG Ships.
- Risks of LPG Ships.
- Risk Assessment and Loss Preventions of LPG Ships.
- Example of Risks.
Properties of LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
Physical and chemical properties:
- Weight of LPG: Half the weight of Water.
- Weight of GPG (Gaseous LPG): 1,5 to 2 times the weight of Air.
- Boiling Temperature of Propane: -43 °C.
- Boiling Temperature of Butane: -0,5 °C.
Consists mainly of:
- Propane (C3H8).
- Butane (C4H10).
- Non-corrosive, non-toxic, odorless, colorless.
- Transformed from gas to liquid for transportation.
- Odorant added to LP gas which gives a distinctive odour.

USES:
- Used for refrigeration/air-conditioning/heating, cooking, auto fuel, etc.
- A “Clear uncontaminated fuel” – An environmental friendly fuel. (Less particles and SOx emissions).
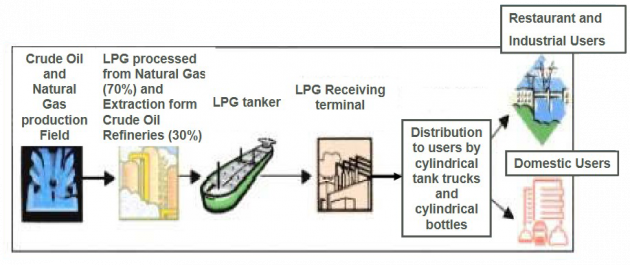
Natural Gas Processing and Liquefaction
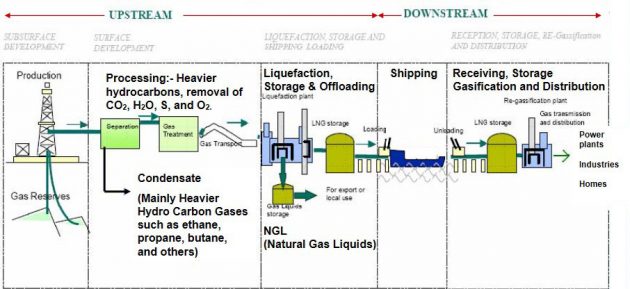
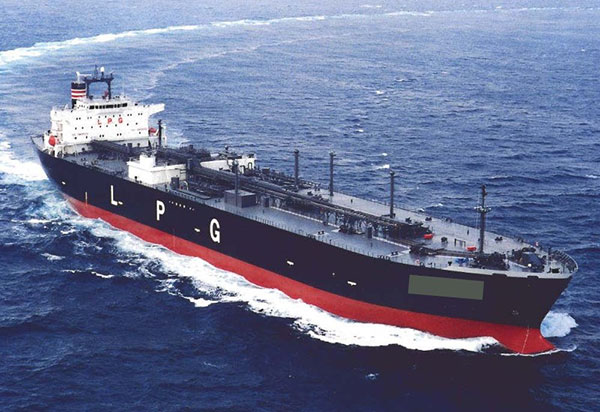
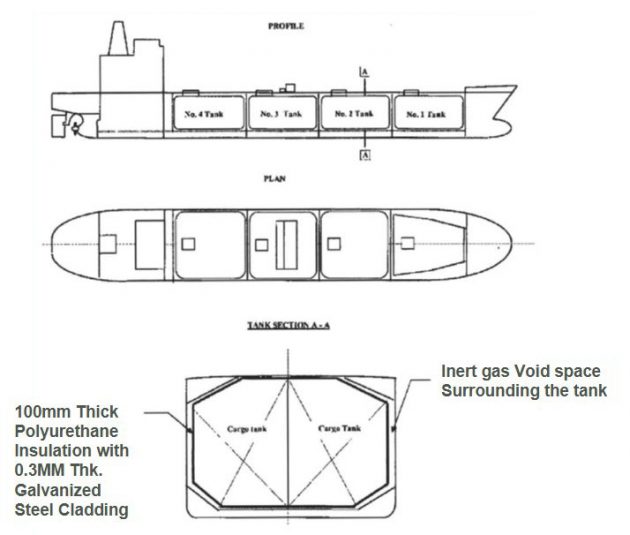
LPG Vessels
- Fully pressurised ships.
- Semi-pressurised.
- Fully refrigerated.
LPG Tankers
General Arrangement of “GAS XXX”
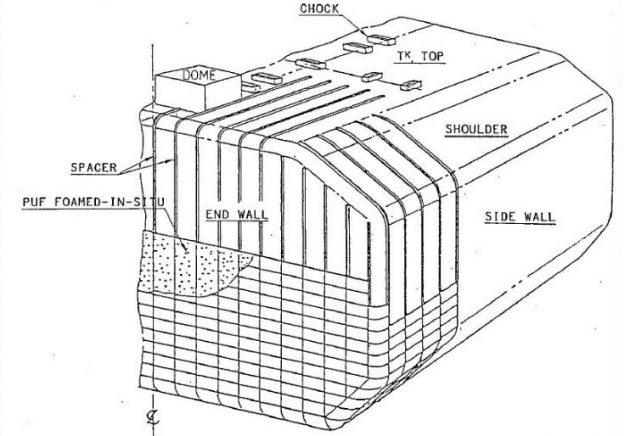
Risks to LPG Vessels
- Because of usual role we normally look at those risks that will affect insurers, such as damage to vessel or cargo.
- Risks that are particular to the vessel type.
- Risks that are general to any vessel type.
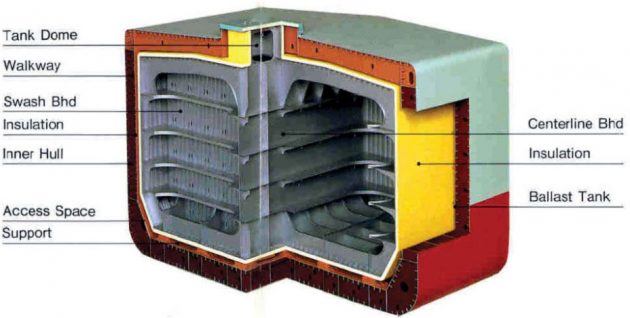
Risks Particular to LPG vessels
- Generally most risks are similar to tankers.
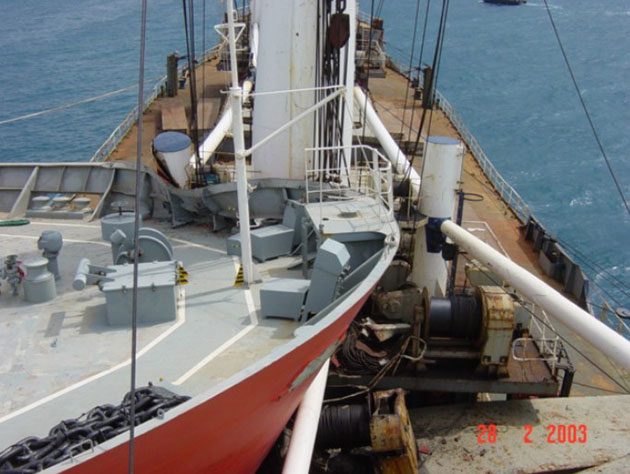
- Collision or grounding may penetrate insulation and/or cargo tanks.
- Leakage from cargo tanks into void spaces.
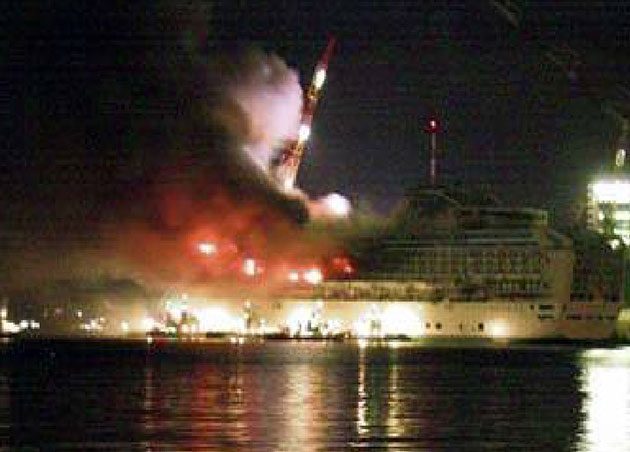
- Fires/explosions due to cargo leakage.
- Any damage which involves the tanks and insulation tend to be very costly.
General Risks to LPG Ships
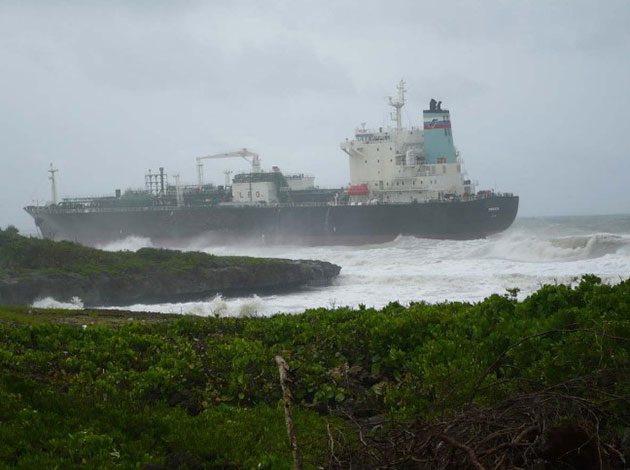
Accidents during sea voyage or during towage:
- Grounding – Navigation error.
- Striking a fixed object or a wreck – Navigation error.
- Collision (with vessel or object) – Navigation error.
- Unloading/Loading.
- Sudden pull-away and damage of loading/discharging arms and human injury.
- Terrorism – Missile attack, boat based explosive and hijacking.
- Cargo machinery and cargo containment failures.
- Natural risks – Lightning, typhoon, hurricanes, and tsunami.
- Other hull/machinery accidents, such as fire in engine room, on bridge and in accommodation, diesel engine damages, and hull structural failures.
Note: Apart from the above LPG risk we must be aware of the high costs and long repair
period arising from damage to cargo containment system on LPG Ships.
Case Reports
Sample of Risks Identification of LPG Ships
Measures Taken to Reduce Risk (Loss Prevention) on LPG Ships
- Design e. g. Steel cargo tanks: reduce spill, surge, vacuum, or accidental leak.
- Gas detection safety and firefighting equipments: Manual and automatic gas detections, foam, powder, water curtain, and sea water fire fighting systems.
- Safety and Operation Internal Inspection/Audit by crew/shipmanagers: Monthly.
- Safety and Operation Internal Inspection/Audit yearly by shipmanagers.
- Safety and Operational and Management Inspection/Audit and Security Screening every 2 or 2 ½ years by External Surveyors.
- Pre-employment crew training, licensing.
- Continuous Crew and ship management training.
- Proper exclusion and buffer zones between public areas, ships, and LPG terminals.
- Terrorist risk prevention based on ISPS (International Ship and Port Security).
- Entry and Routine Condition Survey for insurers by BMT Surveys.
- JH115A general condition survey by BMT M&O Surveys.
- JH722 Structural survey by BMT M&O Surveys.
- JH2006/010 A, B, C, Engine room and office management and condition survey by BMT M&O Surveys.
- JH143 Shipyard Risk Assessment Survey for construction/conversion of LPG Ships by BMT M&O Surveys.
Risk Due To Shortage Of Experienced Gas Tanker Crew
- 5 experienced senior officers are required for each LPG Ship: Master, Chief Mate, Chief Enginner, 1st Enginner, Cargo Engineer.
- Experienced Gas Tanker crew receive better pay on LNG Ships than LPG Ships.
- In addition, due to increase in the construction of LPG & LNG Ships more experienced seafarers are employed as owner’s superintendants during building and operation.
- There is a great shortage of experienced LPG senior officers in the marine industries.
- Pre-employment training, licensing, security screening are essential and need to be continuous.
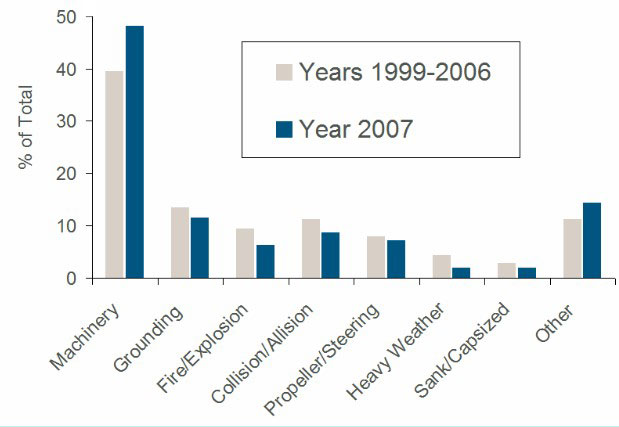
Prevailing risks in the Maritime industry
- Collision.
- Grounding.
- Machinery breakdown.
- Natural disasters.
- Fire.
- Explosions.
- War risks.
- Water ingress.
- Piracy.
- Terrorism
Common Reported Losses
- Extensive ship wreckage.
- Hull damage.
- Machinery damage.
- Damage to cargo.
- Loss of human life.
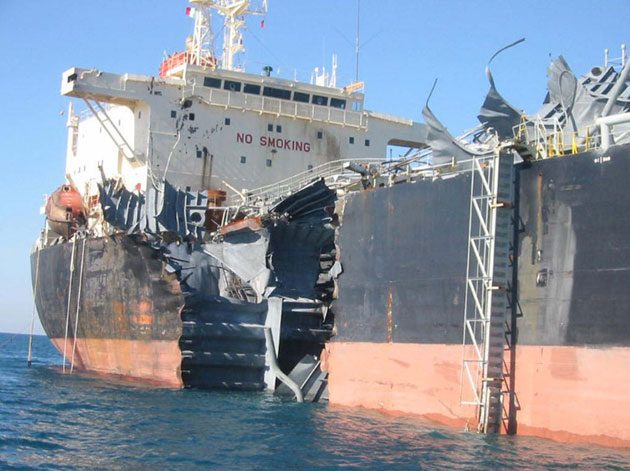
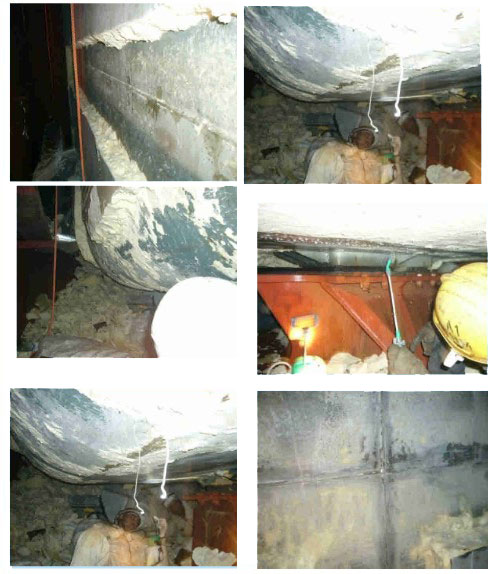
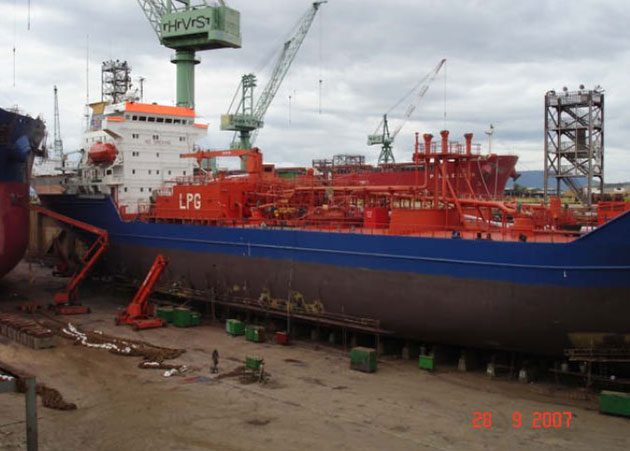









Shipbuilding Risks
- Worldwide order book.
- New inexperienced shipyards – quality control.
- Shortage of trained workers – high demand.
- Fire safety.
- Insulation.
- Typhoon risks in Far East.
- Subcontractors.
- General training.
Conclusions
- Generally risks are similar as for a tanker.
- Specific risks relate to temperature and volatility of cargo, containment etc.
- Discharge & transhipment risks.
- Crew expertise and experience – training.
- High repair costs for containment damage e. g. grounding, contact & collision.
- Shipbuilding risks increased due to high order book.
Footnotes
🤝 Support Our Work
To continue the project, we need your help!
👥 We are supported:
Vitaliy, Gennadiy, Reggae Denz, Elvin Cmi, Paul Jack, Pana
and 26 others
There are also transfers to the card • Thanks to everyone!