As statistic shows, demand in LPG ships significantly grows every year. This article explains basic information for site team about training requirements, aims of training, health and safety risks, rules etc.
What happening?
According to estimates from BIMCO/ISF, there will be a shortfall of 27 000 officers by the year 2015. Within this deficit, the shortage of seafaring officers will be most acute for very specialized ships like liquefied gas carriers and chemical tankers.
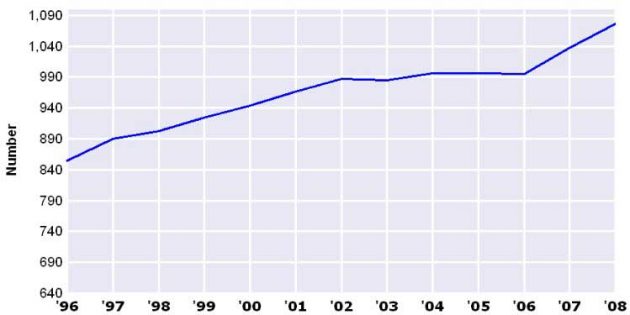
Source: Clarkson Research Services Limited
Training requirements
- Ships
STCW Code Part A/A-V/1
LIQUEFIED GAS TANKER TRAINING PROGRAMME. The specialized training program referred to in paragraph 2.2 of regulation V/1 appropriate to the duties on liquefied gas tankers shall provide theoretical and practical knowledge of the subjects specified in paragraphs 23 to 34 below. - Management
ISM Code Part 2 Ch. 6
6.5. The Company should establish and maintain procedures for identifying any training which may be required in support of the SMS and ensure that such training is provided for all personnel concerned. - Industry
SIGTTO – Crew Safety Standards & Training
LNG Published 2003. LPG currently under development. - LPG vessel in service
- There are clear requirements, guidelines and expected minimum level of knowledge of those personnel involved in the operation and management.
Manning at sea is an issue however there are well established requirements and training courses available for LPG Shipping.
What else?
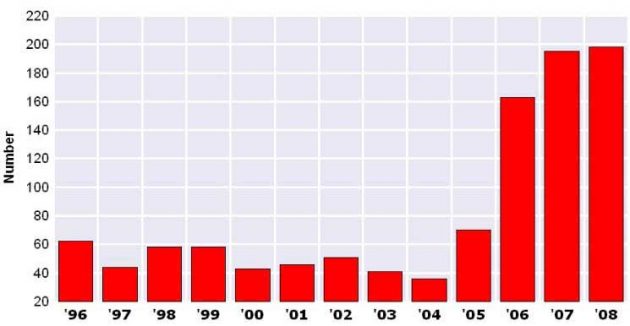
- Increase in Shipbuilding.
- 2003-04 was 81 % greater than 2000-01.
- 2006-Oct 2007 increased 41 %.
- Unprecedented change in rules and legislation.
- Common structural rules;
- Performance standards for protective coatings;
- Construction standards;
- Shipbuilding inspection standards;
- Future IMO goal based standards.
Newbuilding
Building is a partnership involving:
- Shipyard.
- Owner.
- Classification society.
Each party has a distinct role:
- Shipyard – quality of the product.
- Class – that it meets the required rules & regulations.
- Owner – that it is built to contract specification.
Newbuilding resources
Shipyard:
- Building is core business, recruitment and training essential work of the shipyard.
Classification society:
- Survey under construction is core business, training is an essential part.
- Many legal requirements to train and update, through Administrations, IACS etc.
Ship owner site team:
- Core business is operating ships not building.
- Investment in training for Site Team Supervision and Training on the Liquefied Petroleum Gas Vessel Newbuildingnewbuilding – variable.
- Unline in Service – no minimum standards or experience.
- Lack of training scheme aimed at newbuilding inspectors.
- Owners inspectors needed as part of the team. Many inspectors come from seagoing background but unaware of LPG newbuilding process and Issues.
- The newbuilding site team experience is valuable but an understanding of the process and issues around LPG vessel construction is necessary.
- The LPG vessel seagoing experience is valuable but further knowledge is necessary.
- Train before arrival to enable the site manager to concentrate on his role looking after the working of his part of the newbuilding team.
Aims of training
- Provide inspectors with a clear understanding of their individual and joint, roles and responsibilities.
- Provide inspectors with clear understanding of the roles and responsibility of other organisations.
- Provide inspectors with clear understanding of the applicable rules and regulations.
- Provide inspectors with clear understanding of the process and issues with construction of LPG vessels.

Key content
Basic Training Module. (3 days):
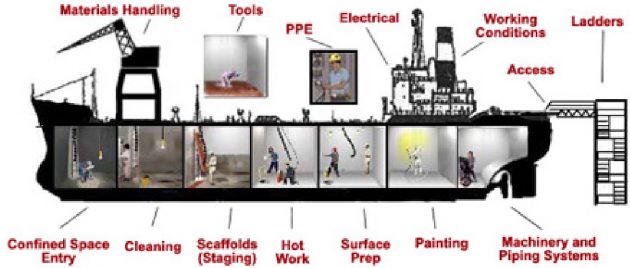
Health and Safety Advice Reminder
In order to maintain the high standards of Health and Safety that the company seeks to maintain in this shipyard, you are asked to study the following and comply with its requirements during your stay in the shipyard.
- In the event of shipyard/vessel emergency arising during your visit the following signal(s) will be given [give details]. In such an event you should take the following action [give details].
- Protect yourself by wearing the following protective clothing whilst visiting the shipyard.
- Boiler Suit, Safety Helmet, Safety Shoes, Safety Glasses, Dust Mask (as applicable).
- Watch where you walk, in particular:
- In the shipyard workshops walkways are clearly marked. Keep to them.
- Stay clear of locations where lifting or working is going on overhead.
- Watch out for vehicles and mobile plant of all types. They may be driven with excessive speed, restricted driver visibility, and outside of the marked roadways, possibly without visible or audible warnings operational.
- Stay well clear or work involving open grinding, disking and gas/arc welding.
- Particularly on board ship look out for tripping hazards and unguarded openings both alongside you and on deck. Trips and falls are a major source of shipyard injuries.
- If you are using ladders and staging ensure they are adequately secured, that there are no missing planks, and that guard-rails are in place. If faults are noticed, keep off.
- Electrical equipment should be treated with caution. Take note of the following:
- Shipyard working supply cables are sometimes not properly insulated.
- Shipyard electrical cubicles are sometimes left open exposing live bus bars and terminals.
- Shipyard electrical cubicles may have internal ground faults but lack a good external earth connection. Such cubicles may be “live” and will give a shock if touched.
- During commissioning the ships electric’s may be unsafe.
- “Keeping clear and avoiding contact are the best precautions”.
- Do not go unescorted into tanks and void spaces, your whereabouts will not be known by the Site Team and the access ways or atmospheres may be unsafe. Advise Site Staff in advance of your intended visit locations in the shipyard and on board ship. Stay out of restricted areas.
- When on board the vessel carries a flashlight, some areas may be poorly lit and lighting is liable to be extinguished without notice.
- Medical aid is available in the shipyard at [location]. A first aid kit is available in the Site office.
- Shipyard safety personnel are identified by [give details]. Follow their instructions at all times.
- If you see an accident, dangerous act or hazard, ensure it is notified to site staff.
- If you are going to use a site team car to drive in/out or around the shipyard, take note of the following driving and road safety precautions [give details].
- Smoking is strictly controlled and is only permitted in designated locations i. e. [give details].
The above list is not exhaustive. Remember that you are in a dangerous environment.
Key documents

TYPE 43.A 60 class steel bulk. VTT-0809-MED-0167 Sept. 20.2005-ROCKWOOL R. I. N. A. – CCEI030I/4 March 8, 2006 – M. I. T. F.
TYPE 44.A 60 class deck VTT-0809-MED-0166 Sept. 28.2005-ROCKWOOL R. I. N. A. – CCEI030I/2 March 8, 2006 – M. I. T. F.
where:
- Rockwool according to recognized type.
- M. I. T. F. according to recognized type applied only on steel without Rockwool R. I. N. A – CCEI030I/4 Sept. 21.2004.
- Aluminium sheet.
- Iron stud bent according to recognized type.
- Calv. steel plague.

Key rules and requirements
| Overview of the different disciplines | ||
|---|---|---|
 | Safety | Material certificates |
| Structural Fire Protection, SFP | ||
| Safety monitoring and control systems | ||
| Firefighting systems | ||
| Stability | ||
| Life Saving Appliances LSA | ||
 | Cryogenic | Containment Systems |
| NDT | ||
| Insulation | ||
| Purging | ||
| Drying | ||
| Machinery | ||
 | Structure/steel | Basic knowledge in Metallurgy |
| Deck Fairing | ||
| Welding methods, techniques and processes | ||
| None Destructive Testing, (NDT) | ||
 | Coating | Coating preparation |
| Coating types | ||
| Tank passport | ||
| Common Faults/Issues | ||
 | Piping & Machinery | Introduction to pipe work |
| Class of piping systems | ||
| Material choice | ||
| Pipe joints and welding | ||
| Hydro testing & Flushing | ||
 | Electrical | Medium voltage |
| Low voltage | ||
| Control systems | ||
| Insulation Resistance (IR) testing | ||
| Earth Bonding | ||
Summary content
- Overview of the different disciplines.
- Shipyard health and safety.
- Key documents.
- Key rules and requirements.
- Inspection & Test procedures.
- Commissioning & Sea Trials.
- Give Inspectors the knowledge to work as a team.
- Understanding of each other’s roles and problems.
- Enable efficient patrol and inspection regimes.
- Improve communication.
- Improve health and safety.
- Improve the quality and satisfaction with the end product.
- Identify any need for specialised training.








