In today’s maritime landscape, Strategies for Effective LNG Bunkering Operations and Their ExecutionLNG Bunkering Training serves as the backbone of a safe, efficient, and regulatory – compliant supply chain for liquefied natural gas as marine fuel. As the industry pivots toward decarbonization, LNG bunkering operations involve multiple stakeholders – vessels, ports, fuel suppliers, regulators – and each must operate with harmonized competence to prevent operational risk. Proper training is not just a regulatory checkbox; it is the key to reducing incidents, ensuring continuity, and building trust across the entire LNG logistics chain.
This evolving environment demands curricula that reach beyond traditional seafarer instruction – addressing interface challenges, harmonizing cross-sector requirements, and filling gaps arising from overlapping regulatory regimes.
LNG Bunkering – Training for the Interface
The STCW contains requirements in Section A/V3 tables A-V/3-1 and A-V/3-2 for a minimum standard of competence in basic and advanced training, respectively, for ships subject to the IGF Code. These tables can be considered highly relevant in setting the wider structure of competencies that should also be considered for the LNG bunkering interface below highlights the relevance of addressing the necessary harmonization of competencies in the context of LNG Bunkering Guidelines: Comprehensive Insights and Best Practices for OperatorsLNG bunkering.
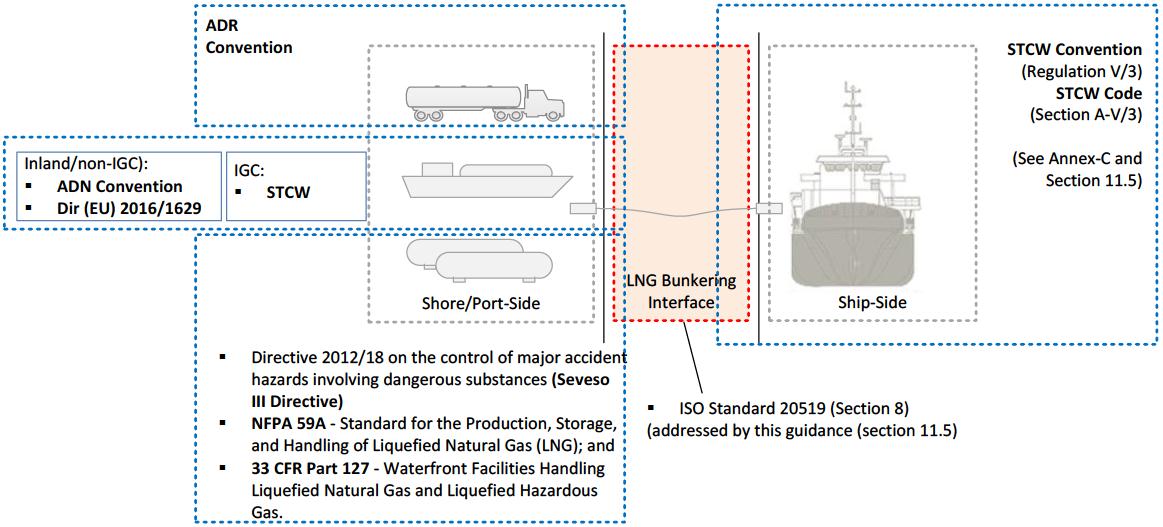
EN ISO 20519 highlights, in Section 8, that all crew members should be trained in the particular aspects of the Standard, as far as LNG bunkering procedures are concerned.
LNG Bunkering Training Matrix
As a main reference for Qualification & Training, a Matrix has been built in the context of the European Sustainable Shipping Forum to better assist all parties willing to develop Qualification and Training schemes, based on relevant legal minimum requirements, for LNG bunkering.
The Training Matrix maps different regulatory regimes, addressing the complex interface of LNG Bunkering where different requirements co-exist, from the ship-side, port-side, fuel supplier side, etc.
Finding conflicting points, and possible overlaps, is still the aim of the work together with the full mapping of the instruments governing the different parts of LNG bunkering operations when training and competencies development and recognition is concerned.
The Training Matrix defines the appropriate references for the training to be set up in different domains and activities of LNG as fuel, both on maritime and inland waterways, and road transport.
The matrix provides an overview of the requirements to all those in the logistic chain in order to identify the gaps and possible overlaps within the existing instruments, with the two main objectives to:
- Maintain the high level of safety for the use of LNG.
- Contribute to the definition of an EU framework.
| MATRIX on LNG Training | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | Activity | Category | Regulatory Instrument on Training & Competences – State of play | Observations |
| Maritime | LNG Vessels (LNG transport) | Crew | IGC Code | To check Directive 2008/106/EC on minimum level of Bunkering training of seafarers |
| STCW convention | ||||
| IMO Model Course – Advanced Training for Liquefied Gas Tanker Cargo Operations | ||||
| Directive 2008/106/EC on the minimum level of training seafarers | ||||
| Bunkering vessels | Crew | Res MSC.392(95): IGF Code, Part C-1, Part D | To identified the modification of Directive 2008/106/EC to apply the rules defined by IMO | |
| Res MSC.395(95): amendments to SOLAS Convention | ||||
| Res MSC.396(95): amendments to STCW Convention – Res MSC.397(95): amendments to STCW Code | ||||
| STCW.7/Circ.23 on interim guidance on training for seafarers on board ships using gases or other low-flashpoint fuels | ||||
| Draft STCW Circular on amendments to Part B of STCW Code | ||||
| Offer to develop an IMO model course on the special training requirements for seafarers on ships using gases or other low flashpoint fuels-Submitted by Norway | ||||
| Inland waterways | LNG fuelled vessels | Crew | Directive 91/672 on the reciprocal recognition of national boat masters’ certificates | |
| Directive 96/50 on the harmonization of the conditions for obtaining national boat masters’ certificates | ||||
| CCNR: Regulation for Rhine navigation personnel (amendment coming into force on 1.07.2016) : special knowledge of crews (chapter 4a) and content of training courses (annex E2) | ||||
| Rhine Police Regulation (amendment in force 1.12.2015): requirement of training certificates for crew | ||||
| Transport of LNG | Crew | ADN 2015 agreement: additional training for boat master required – Directive 2008/68 on the inland transport of dangerous goods | Check the impact of ADN agreement as modified on EU legislation | |
| Ports | LNG Bunkering operations | People involved in bunkering operation | ISO TS 18683 (2015-01-15) Guidelines for systems and installations for supply of LNG as fuel to ships – Chapter 10 Training | |
| Draft ISO/DIS 20519 LNG Bunkering Standard (on consultation 05/02-05/05) – Chapter 8 Personnel training | ||||
| CEN/TC 282 on LNG equipment and installation: ad hoc Group on Training | ||||
| IACS Recommendation 142 on LNG Bunkering | ||||
| Port regulations on bunkering and on dangerous goods | ||||
| IAPH guidelines (version 3.6 Jan 2015): i. Truck to Shipping ii. Ship to Shipping iii. Bunker Station to Ship | ||||
| Directive 2012/18 on the control of major accident hazards involving dangerous substances (Seveso III Directive) | ||||
| CCNR: Standard for a LNG bunker checklist Truck to Ship Edition 1.0 | ||||
| SGMF LNG Bunkering Competence Guidelines 2017 (available for purchase) | ||||
| People on spot | Port regulations and Safety Management System (SMS) | |||
| Health & safety regulations for workers | ||||
| Transport of LNG | Driver | ADR agreement | ||
| Directive 2008/68 on the inland transport of dangerous goods | ||||
| ISO/DIS 16924.2 LNG stations for fuelling (19.5 training). CEN/TC 326 refuelling stations | ||||
| Railway | Transport of LNG | Railways infrastructure manager and carriers | RID agreement | to be investigated |
| Directive 2008/68 on the inland transport of dangerous goods | ||||
| LNG Terminal | Unloading, loading & storage of LNG | LNG infrastructure operator | Directive 2012/18 on the control of major accident hazards involving dangerous substances (Seveso III Directive) | to be investigated with the ongoing works of CEN on standards |
| National regulation concerning classified facilities regarding safety and environmental protection | ||||
| ISO & EN standards (to be investigated) | ||||
| Port regulation | ||||
| SIGTTO/OCIMF recommendations | ||||
| Loading of Bunkering vessels, barges | LNG infrastructure operator | Directive 2012/18 on the control of major accident hazards involving dangerous substances | to be investigated | |
| National regulation concerning classified facilities regarding safety and environmental protection | ||||
| Port regulations | ||||
| Bunker vessel crew | IGC Code | To check Directive 2008/106/EC | ||
| STCW convention | ||||
| IMO Model Course – Advanced Training for Liquefied Gas Tanker Cargo Operations (on revision) | ||||
| Directive 2008/106/EC on the minimum level of training seafarers | ||||
| Port regulation | ||||
| Barge crew relevant to inland waterways regulation | ADN 2015 agreement | |||
| Directive 2008/68 on the inland transport of dangerous goods. Directive 91/672 on the reciprocal recognition of national boat masters’ certificates | ||||
| Directive 96/50 on the harmonization of the conditions for obtaining national boat masters’ certificates | ||||
| CCNR: Regulation for Rhine navigation | ||||
| personnel and Rhine Police Regulations | ||||
| Port regulation | ||||
| Loading of trucks | LNG infrastructure operator | Directive 2012/18 on the control of major accident hazards involving dangerous substances (Seveso III directive) | to be investigated with the ongoing work of CEN on standards | |
| National regulation concerning classified facilities regarding safety and | ||||
| environmental protection | ||||
| ISO and EN standards (to be investigated) | ||||
| Port regulation | ||||
| Driver | ADR agreement | Check the impact of ADR agreement as modified on EU legislation | ||
| Directive 2008/68 on the inland transport of dangerous goods | ||||
| ISO-EN standards (to be investigated with the Commission decision on standards) | ||||
| Port regulation | ||||
| LNG fuel stations | Refuelling of trucks | LNG fuel stations operator | Directive 2012/18 on the control of major accident hazards involving dangerous substances | to be investigated with the ongoing work of CEN on standards |
| National regulation concerning classified facilities regarding safety and environmental protection – ISO/DIS 16924.2 LNG stations for fuelling (19.5 training) | ||||
| CEN/TC 326 refuelling stations | ||||
| Customers deliveries | Unloading of trucks | Driver | ADR agreement | Check the impact of ADR agreement as modified on EU legislation |
| Directive 2008/68 on the inland transport of dangerous goods | ||||
| ISO-EN standards (to be investigated with the Commission decision on standards) | ||||

